Abstract
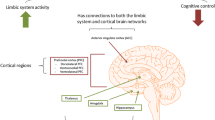
Current perspectives on the molecular underpinnings of major depressive disorder (MDD) posit a mechanistic role of epigenetic DNA modifications in mediating the interaction between environmental risk factors and a genetic predisposition. However, conclusive evidence for differential methylation signatures in the brain’s epigenome of MDD patients as compared to controls is still lacking. To address this issue, we conducted a pilot study including an epigenome-wide methylation analysis in six individuals diagnosed with recurrent MDD and six control subjects matched for age and gender, with a priori focus on the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex as pathophysiologically relevant candidate regions. Our analysis revealed differential methylation profiles of 11 genes in hippocampus and 20 genes in prefrontal cortex, five of which were selected for replication of the methylation status using pyrosequencing. Among these replicated targets, GRIN2A was found to be hypermethylated in both prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. This finding may be of particular functional relevance as GRIN2A encodes the glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit epsilon-1 (NR2A) and is known to be involved in a plethora of synaptic plasticity-related regulatory processes probably disturbed in MDD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2008) The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 455:894–902
Flint J, Kendler KS (2014) The genetics of major depression. Neuron 81:484–503
Henikoff S, Matzke MA (1997) Exploring and explaining epigenetic effects. Trends Genet 13:293–295
Gibney ER, Nolan CM (2010) Epigenetics and gene expression. Heredity 105:4–13
Vialou V, Feng J, Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2013) Epigenetic mechanisms of depression and antidepressant action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:59–87
Dulawa SC (2014) Epigenetic programming of depression during gestation. BioEssays 36:353–358
Jiao J, Opal MD, Dulawa SC (2013) Gestational environment programs adult depression-like behavior through methylation of the calcitonin gene-related peptide gene. Mol Psychiatry 18:1273–1280
Fuchikami M et al (2011) DNA methylation profiles of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene as a potent diagnostic biomarker in major depression. PLoS One 6:e23881
Tadić A (2013) Methylation of the promoter of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IV and antidepressant response in major depression. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2013.58
Moghaddam B (1993) Stress preferentially increases extraneuronal levels of excitatory amino acids in the prefrontal cortex: comparison to hippocampus and basal ganglia. J Neurochem 60:1650–1657
Bartanusz V (1995) Stress-induced changes in messenger RNA levels of N-methyl-d-aspartate and AMPA receptor subunits in selected regions of the rat hippocampus and hypothalamus. Neuroscience 66:247–252
Fitzgerald LW, Ortiz J, Hamedani AG, Nestler EJ (1996) Drugs of abuse and stress increase the expression of GluR1 and NMDAR1 glutamate receptor subunits in the rat ventral tegmental area: common adaptations among cross-sensitizing agents. J Neurosci 16:274–282
Berman RM et al (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354
Zarate CA Jr et al (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Zarate C (2013) New paradigms for treatment-resistant depression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1292:21–31
Kaut O, Schmitt I, Wüllner U (2012) Genome-scale methylation analysis of Parkinson’s disease patients’ brains reveals DNA hypomethylation and increased mRNA expression of cytochrome P450 2E1. Neurogenetics 13:87–91
Touleimat N, Tost J (2012) Complete pipeline for Infinium Human Methylation 450 K BeadChip data processing using subset quantile normalization for accurate DNA methylation estimation. Epigenomics 3:325–341
Hellman A, Chess A (2007) Gene body-specific methylation on the active X chromosome. Science 315:1141–1143
Calabrese F, Guidotti G, Molteni R, Racagni G, Mancini M, Riva MA (2012) Stress-induced changes of hippocampal NMDA receptors: modulation by duloxetine treatment. PLoS One 7(5):e37916
Karolewicz B (2009) Elevated levels of NR2A and PSD-95 in the lateral amygdala in depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:143–153
Karolewicz B, Stockmeier CA, Ordway GA (2005) Elevated levels of the NR2C subunit of the NMDA receptor in the locus coeruleus in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1557–1567
Feyissa AM, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B (2009) Reduced levels of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor and PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:70–75
Beneyto M, Meador-Woodruff JH (2008) Lamina-specific abnormalities of NMDA receptor-associated postsynaptic protein transcripts in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2175–2186
Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:327–335
Boyce-Rustay JM, Holmes A (2006) Genetic inactivation of the NMDA receptor NR2A subunit has anxiolytic-and antidepressant-like effects in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2405–2414
Diazgranados N et al (2010) A randomized add-on trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67:793–802
Murrough JW et al (2013) Neurocognitive effects of ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression: association with antidepressant response. Psychopharmacology (Berl) Epub ahead of print 2013 Sep 11. PubMed PMID:24022236
Murrough JW et al (2013) Antidepressant efficacy of ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression: a two-site randomized controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry 170:1134–1142
Huang CC et al (2013) Inhibition of glycine transporter-I as a novel mechanism for the treatment of depression. Biol Psychiatry 74:734–741
Akashi K et al (2009) NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. J Neurosci 35:10869–10882
Goswami DB, Jernigan CS, Chandran A, Iyo AH, May WL, Austin MC, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B (2013) Gene expression analysis of novel genes in the prefrontal cortex of major depressive disorder subjects. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 43:126–133
Li N et al (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012) Synaptic dysfunction in depression: potential therapeutic targets. Science 338:68–72
Cherlyn SY et al (2010) Genetic association studies of glutamate, GABA and related genes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a decade of advance. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:958–977
Kiss JP et al (2012) GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors as possible targets for the neuroprotective and antidepressant effects of fluoxetine. Neurochem Int 60:170–176
Spatazza J et al (2013) Choroid-plexus-derived Otx2 homeoprotein constrains adult cortical plasticity. Cell Rep 3:1815–1823
Sabunciyan S et al (2007) Polymorphisms in the homeobox gene OTX2 may be a risk factor for bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B:1083–1086
Morishita H, Miwa JM, Heintz N, Hensch TK (2010) Lynx1, a cholinergic brake, limits plasticity in adult visual cortex. Science 330:1238–1240
Demars MP, Morishita H (2014) Cortical parvalbumin and somatostatin GABA neurons express distinct endogenous modulators of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol Brain 27:75
Millan MJ et al (2012) Cognitive dysfunction in psychiatric disorders: characteristics, causes and the quest for improved therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:141–168
Prömel S, Waller-Evans H, Dixon J, Zahn D, Colledge WH, Doran J, Carlton MB, Grosse J, Schöneberg T, Russ AP, Langenhan T (2012) Characterization and functional study of a cluster of four highly conserved orphan adhesion-GPCR in mouse. Dev Dyn 241:1591–1602
Sherman SK, Maxwell JE, Carr JC, Wang D, O’Dorisio MS, O’Dorisio TM, Howe JR (2014) GIPR expression in gastric and duodenal neuroendocrine tumors. J Surg Res 190:587–593
Rao JS, Keleshian VL, Klein S, Rapoport SI (2012) Epigenetic modifications in frontal cortex from Alzheimer’s disease and bipolar disorder patients. Transl Psychiatry 2:e132
Mill J et al (2008) Epigenomic profiling reveals DNA-methylation changes associated with major psychosis. Am J Hum Genet 82:696–711
Asai T et al (2013) Effect of mood stabilizers on DNA methylation in human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:2285–2294
Acknowledgments
R.H. was supported by a Starting Independent Researcher Grant (“NEMO–Neuromodulation of Emotion”) jointly provided by the Ministry of Innovation, Science, Research & Technology of the German State of North Rhine-Westphalia (MIWFT) and the University of Bonn
Conflict of interest
The authors report no competing biomedical financial interests or personal affiliations in connection with the content of this manuscript.
Ethical standard
This study has been approved by the local ethics committee and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaut, O., Schmitt, I., Hofmann, A. et al. Aberrant NMDA receptor DNA methylation detected by epigenome-wide analysis of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in major depression. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 265, 331–341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0572-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0572-y