Abstract
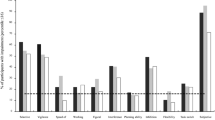
Adults with persistent attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may show cognitive deficits as compared to healthy control subjects. The aim of this study was to compare a sample of adult outpatients with ADHD on medication to healthy controls on a comprehensive neuropsychological assessment battery. Thirty adults with ADHD under stable psychopharmacological treatment and 27 healthy controls matched for age, gender, and IQ were assessed with ten tests measuring performance with regard to attention, memory, executive function, and fine motor control. Lower performance in patients as compared to controls was found in tests of verbal and visual memory, speed of visuo-motor search, set shifting, and divided attention. Indicators of response inhibition and simple response speed were less affected. Adults with ADHD show indicators of lowered cognitive performance under medication. These are related more to memory and attention under high mental load than to response inhibition or simple attention or motor performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aron AR, Dowson JH, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2003) Methylphenidate improves response inhibition in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 54:1465–1468
Barkley RA (1997) Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull 121:65–94
Bäumler G (1985) Farbe-Wort-Interferenztest (FWIT) nach J.R. Stroop. Hogrefe Verlag, Göttingen
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Benton AL, Hamsher KdS (1989) Multilingual aphasia examination. AJA Associates, Iowa City, Iowa
Cohen J (1977) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Academic Press, San Diego
Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E (1999) Conners’ adult ADHD ratings scales (CAARS). Multi-Health Systems, North Tonawanda, NY
Dalsgaard S, Mortensen PB, Frydenberg M, Thomsen PH (2002) Conduct problems, gender and adult psychiatric outcome of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brit J Psychiatry 181:416–421
Davids E, Krause DA, Specka M, Gastpar M (2004) [Analysis of a special consultation for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults]. Gesundheitswesen 66:416–422
Davids E, Zhang K, Tarazi FI, Baldessarini RJ (2003) Animal models of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 42:1–21
Epstein JN, Johnson DE, Varia IM, Conners CK (2001) Neuropsychological assessment of response inhibition in adults with ADHD. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 23:362–371
Fleishmann EA (1972) Structure and measurement of psychomotor abilities. In: Singer RN (ed) The psychomotor domain. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 78–106
Ford T, Goodman R, Meltzer H (2003) The British Child and Adolescent Mental Health Survey 1999: the prevalence of DSM-IV disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:1203–1211
Hamster W (1980) Klinische Normen zur Motorischen Leistungsseries. Dr. G. Schuhfried GmbH, Mölding, Austria
Hautzinger M (1991) Das Beck-Depressionsinventar (BDI) in der Klinik. Der Nervenarzt 62:689–696
Hautzinger M, Bailer M, Worall H, Keller F (1995) Beck-Depressions-Inventar (BDI) Bearbeitung der deutschen Ausgabe. Verlag Hans Huber, Göttingen
Hesslinger B, Tebartz van Elst L, Nyberg E, Dykierek P, Richter H, Berner M, Ebert D (2002) Psychotherapy of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults–a pilot study using a structured skills training program. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 252:177–184
Kahnemann D (1973) Attention and effort. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Laux L, Glanzmann P, Schaffner P, Spielberger CD (1981) Das State-Trait-Angstinventar. Beltz, Weinheim
Lehrl S (1995) Mehrfachwahl-Wortschatz-Intelligenztest MWT-B. PERMED-spitta Medizinische Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Balingen
Mackworth NH (1948) The breakdown of vigilance during prolonged visual search. Q J Exp Psychol 1:6–21
McLean A, Dowson J, Toone B, Young S, Bazanis E, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2004) Characteristic neurocognitive profile associated with adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychol Med 34:681–692
Mick E, Faraone SV, Biederman J (2004) Age-dependent expression of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms. Psychiatr Clin North Am 27:215–224
Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES (1995) Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol 51:768–774
Posner MI, Petersen SE (1990) The attention system of the human brain. Ann Rev Neurosci 13:25–42
Retz W, Retz-Junginger P, Hengesch G, Schneider M, Thome J, Pajonk FG, Salahi-Disfan A, Rees O, Wender PH, Rösler M (2004) Psychometric and psychopathological characterization of young male prison inmates with and without attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 254:201–208
Retz-Junginger P, Retz W, Blocher D, Stieglitz RD, Georg T, Supprian T, Wender PH, Rosler M (2003) [Reliability and validity of the Wender-Utah-Rating-Scale short form. Retrospective assessment of symptoms for attention deficit/huperactivity disorder]. Nervenarzt 74:987–993
Rösler M, Retz W, Retz-Junginger P, Hengesch G, Schneider M, Supprian T, Schwitzgebel P, Pinhard K, Dovi-Akue N, Wender P, Thome J (2004) Prevalence of attention deficit-/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid disorders in young male prison inmates*. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 254:365–371
Rösler M, Retz W, Retz-Junginger P, Thome J, Supprian T, Nissen T, Stieglitz RD, Blocher D, Hengesch G, Trott GE (2004) [Tools for the diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults. Self-rating behaviour questionnaire and diagnostic checklist. Nervenarzt 75:888–895
Rubia K, Taylor E, Smith AB, Oksanen H, Overmeyer S, Newman S (2001) Neuropsychological analyses of impulsiveness in childhood hyperactivity. Brit J Psychiatry 179: 138–143
Sayal K, Taylor E, Beecham J, Byrne P (2002) Pathways to care in children at risk of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brit J Psychiatry 181:43–48
Schall U, Johnston P, Lagopoulos J, Juptner M, Jentzen W, Thienel R, Dittmann-Balcar A, Bender S, Ward PB (2003) Functional brain maps of Tower of London performance: a positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 20:1154–1161
Schoppe KJ (1974) Das MLS-Gerät: ein neuer Testapparat zur Messung feinmotorischer Leistungen. Diagnostica 20:43–47
Shallice T (1982) Specific impairments of planning. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 298:199–209
Spencer T, Biederman J, Wilens T, Faraone SV (1994) Is attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults a valid disorder? Harv Rev Psychiatry 1:326–335
Spielberger CD, Gosruch RL, Lushene RE (1970) STAI, Manual for the State-Trait-Anxiety-Inventory. Consulting Psychologist Press, Palo Alto
Spreen O, Strauss E (1991) A compendium of neuropsychological tests. Oxford University Press, New York
Stroop JR (1935) Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18:643–662
Thapar A, Harrington R, McGuffin P (2001) Examining the comorbidity of ADHD-related behaviours and conduct problems using a twin study design. Brit J Psychiatry 179:224–229
Turner DC, Clark L, Dowson J, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2004) Modafinil improves cognition and response inhibition in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 55:1031–1040
Vossel S, Thiel CM, Fink GR (2006) Cue validity modulates the neural correlates of covert endogenous orienting of attention in parietal and frontal cortex. Neuroimage 32:1257–1264
Ward MF, Wender PH, Reimherr FW (1993) The Wender Utah Rating Scale: an aid in the retrospective diagnosis of childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 150:885–890
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler Memory Scale - Revised. The Psychological Corporation / Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, San Antonio, TX
Wiebel B, Happe A, Piekara FH (1995) Das neuropsychologische Testprogramm TESTBAT (the neuropsychological test battery TESTBAT). PSYMED, Dülmen
Woodward TS, Ruff CC, Ngan ET (2006) Short- and long-term changes in anterior cingulate activation during resolution of task-set competition. Brain Res 1068:161–169
Zimmermann P, Fimm B (2002) A test battery for attentional performance. In: Leclercq M, Zimmermann P (eds) Applied Neuropsychology of Attention. Theory, Diagnosis and Rehabilitation. Psychology Press, London, pp 101–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, B.W., Gimbel, K., Keller-Pließnig, A. et al. Neuropsychological assessment of adult patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257, 112–119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0688-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0688-9