Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effectiveness of multiple group family treatment for Schizophrenia.
Method
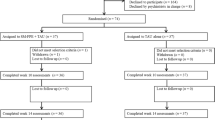
Relatives were randomly provided with an informative programme (n = 50), or allocated to receive an additional support programme (n = 26). Patients did not attend the programme to overcome cultural and organizational implementation barriers. The 12 and 24 months clinical and family outcomes were assessed.
Results
Patients’ compliance with standard care was greater at 12 months in the more intensive behavioural management group over a control group receiving treatment as usual (TAU) (n = 25). A reduction in levels of expressed emotion (EE), significantly more frequent in those receiving the additional support programme than just the informative, occurred after treatment completion. Other clinical and family outcomes did not differ. However, treatment benefits declined at 24 months, when baseline high EE was again predictive of patient’s admission and relatives were more vulnerable to objective burden. Baseline illness severity variables predicted a number of medium and long-term poor clinical outcomes.
Conclusions
Although family psychoeducation has been tested in a wide range of Anglo-Saxon settings, there remains need to assess outcomes more internationally. Effective family interventions for people with schizophrenia probably require continued administration of key-elements or ongoing informal support to deal with the vicissitudes of illnesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Baronet AM (1999) Factors associated with caregiver burden in mental illness: a critical review of the research literature. Clin Psychol Rev 19:819–841
Bebbington P, Kuipers L (1994a) The predictive utility of expressed emotion in schizophrenia: an aggregate analysis. Psychol Med 24:707–718
Bebbington P, Kuipers L (1994b) The clinical utility of expressed emotion in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 382:46–53
Bertrando P, Beltz J, Bressi C, Clerici M, Farma T, Invernizzi G, Cazzullo CL (1992) Expressed emotion and schizophrenia in Italy. A study of an urban population. Br J Psychiatry 161:223–229
Burland J (1998) Family-to-family: a trauma and recovery model of family education. New Dir Ment Health Serv 77:33–44
Bustillo J, Lauriello J, Horan W, Keith S (2001) The psychosocial treatment of schizophrenia: an update. Am J Psychiatry 158:163–175
Butzlaff RL, Hooley JM (1998) Expressed emotion and psychiatric relapse: a meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:547–552
Cazzullo CL, Bertrando P, Clerici M, Bressi C, Da Ponte C, Albertini E (1989) The efficacy of an information group intervention on relatives of schizophrenics. Int J Soc Psychiatry 35:313–323
Cazzullo CL, Clerici M, Bertrando P (1994) Future strategies in family research and intervention. Integr Psychiatry 10:20–23
Chien WT, Chan SW (2004) One-year follow-up of a multiple-family-group intervention for Chinese families of patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Serv 55:1276–1284
De Girolamo G, Cozza M (2000) The Italian Psychiatric Reform. A 20-Year Perspective. Int J Law Psychiatry 23:197–214
Dixon L, Adams C, Lucksted A (2000) Update on family psychoeducation for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 26:5–20
Dixon L, McFarlane WR, Lefley H, Lucksted A, Cohen M, Falloon I, Mueser K, Miklowitz D, Solomon P, Sondheimer D (2001) Evidence-based practices for services to families of people with psychiatric disabilities. Psychiatr Serv 52:903–910
Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiss JL, Cohen J (1976) The Global Assessment Scale: a procedure for measuring the overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:766–771
Grella CE, Grusky O (1989) Families of the seriously mentally ill and their satisfaction with services. Hosp Commun Psychiatry 40:831–835
Hofer A, Rettenbacher MA, Widschwendter ChG, Kemmler G, Hummer M, Fleischhacker WW (2006) Correlates of subjective and functional outcomes in outpatient clinic attendees with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:246–255
Hornung WP, Feldmann R, Klingberg S, Buchkremer G, Reker T (1999) Long-term effects of a psychoeducational psychotherapeutic intervention for schizophrenic outpatients and their key-persons-results of a five-year follow-up. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 249:162–167
Kopelowicz A, Zarate R, Gonzalez V, Lopez SR, Ortega P, Obregon N, Mintz J (2002) Evaluation of expressed emotion in schizophrenia: a comparison of Caucasians and Mexican-Americans. Schizophr Res 55:179–186
Leff J, Berkowitz R, Shavit N, Strachan A, Glass L, Vaughn C (1989) A trial of family therapy v, a relatives group for schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 154:58–66
Leff J, Vaughn C (1985) Expressed emotion in families: its significance for mental illness. Guilford, New York
Lefley H (2001) Impact of mental illness on families and carers. In: Thornicroft G, Szmukler G (eds) Textbook of community psychiatry. Oxford University Press, London, pp 141–154
Liberman DB, Liberman RP (2003) Rehab rounds: Involving families in rehabilitation through behavioral family management. Psychiatr Serv 54:633–635
Linszen D, Dingemans P, Van Der Does J, Nugter A, Scholte P, Lenior R, Goldstein M (1996) Treatment, expressed emotion and relapse in recent onset schizophrenic disorders. Psychol Med 26:333–342
Mari JJ, Streiner DL (1994) An overview of family interventions and relapse in schizophrenia: meta-analysis of research findings. Psychol Med 24:565–578
McCreadie RG, Phillips K (1988) The Nithsdale Schizophrenia Survey. VII. Does relatives’ high expressed emotion predict relapse? Br J Psychiatry 152:477–481
McDonell MG, Short RA, Berry CM, Dyck DG (2003) Burden in schizophrenia caregivers: impact of family psychoeducation and awareness of patient suicidality. Fam Process 42:91–103
McFarlane WR, McNary S, Dixon L, Hornby H, Cimett E (2001) Predictors of dissemination of family psychoeducation in community mental health centers in Maine and Illinois. Psychiatr Serv 52:935–942
McFarlane WR, Hornby H, Dixon L, McNary S (2002) Psychoeducational multifamily groups: research and implementation in the United States. In: McFarlane WR (eds) Multifamily group treatment for severe psychiatric disorders. Guilford, New York, pp 43–60
McFarlane WR, Dixon L, Lukens E, Lucksted A (2003) Family psychoeducation and schizophrenia: a review of the literature. J Marital Fam Ther 29:223–245
Möller-Leimkühler AM (2005) Burden of relatives and predictors of burden. Baseline results from the Munich 5-year-follow-up study on relatives of first hospitalized patients with schizophrenia or depression. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 255:223–231
Montero I, Gomez-Beneyto M, Ruiz I, Puche E, Adam A (1992) The influence of family expressed emotion on the course of schizophrenia in a sample of Spanish patients. A 2-year follow-up study. Br J Psychiatry 161:217–222
Pharoah FM, Rathbone J, Mari JJ, Streiner D (2003) Family intervention for schizophrenia. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 3, Art. No.: CD000088. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000088
Pilling S, Bebbington P, Kuipers E, Garety P, Geddes J, Orbach G, Morgan C (2002) Psychological treatments in schizophrenia: I. Meta-analysis of family intervention and cognitive behaviour therapy. Psychol Med 32:763–782
Pitschel-Walz G, Leucht S, Bauml J, Kissling W, Engel RR (2001) The effect of family interventions on relapse and rehospitalization in schizophrenia-a meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull 27:73–92
Pitschel-Walz G, Bauml J, Bender W, Engel RR, Wagner M, Kissling W (2006) Psychoeducation and compliance in the treatment of schizophrenia: results of the Munich Psychosis Information Project Study. J Clin Psychiatry 67:443–452
Ram Ms, Xiang Mz, Chan Cl, Leff J, Simpson P, Huang Ms, Shan Yh, Li S (2003) Effectiveness of psychoeducational intervention for rural Chinese families experiencing schizophrenia-a randomised controlled trial. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 38:69–75
Ruggeri M, Lasalvia A, Tansella M, Bonetto C, Abate M, Thornicroft G, Allevi L, Ognibene P (2004) Heterogeneity of outcomes in schizophrenia. 3-year follow-up of treated prevalent cases. Br J Psychiatry 184:48–57
Rutter M, Brown GW (1966) The reliability and validity of measures of family life and relationships in families containing a psychiatric patient. Soc Psychiatry 1:38–53
Scazufca M, Kuipers E (1998) Stability of expressed emotion in relatives of those with schizophrenia and its relationship with burden of care and perception of patients’ social functioning. Psychol Med 28:453–61
Stata Corp (2001) Stata Statistical Software, Release 7.0. Stata Corp., College Station, TX
Stengard E (2003) Educational intervention for the relatives of schizophrenia patients in Finland. Nord J Psychiatry 57:271–277
Telles C, Karno M, Mintz J, Paz G, Arias M, Tucker D, Lopez S (1995) Immigrant families coping with schizophrenia. Behavioral family intervention v. case management with a low-income Spanish-speaking population. Br J Psychiatry 167:473–479
Thornicroft G, Tansella M (2004) Components of a modern mental health service: a pragmatic balance of community and hospital care. Overview of systematic evidence. Br J Psychiatry 185:283–290
Tomaras V, Mavreas V, Economou M, Ioannovich E, Karydi V, Stefanis C (2000) The effect of family intervention on chronic schizophrenics under individual psychosocial treatment: a 3-year study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 35:487–493
Üçok A, Polat A, Çakır S, Genç A (2006) One year outcome in first episode schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:37–43
Vaughn C, Leff J (1976) The measurement of expressed emotion in the families of psychiatric patients. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 15:157–165
Vaughn CE, Snyder KS, Jones S, Freeman WB, Falloon IR (1984) Family factors in schizophrenic relapse. Replication in California of British research on expressed emotion. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:1169–1177
Wearden AJ, Tarrier N, Barrowclough C, Zastowny TR, Rahill AA (2000) A review of expressed emotion research in health care. Clin Psychol Rev 20:633–666
World Schizophrenia Fellowship (1998) Families as partners in care: a document developed to launch a strategy for the implementation of programs of family education, training, and support. World Schizophrenia Fellowship, Toronto
Xiong W, Phillips MR, Hu X, Wang R, Dai Q, Kleinman J, Kleinman A (1994) Family-based intervention for schizophrenic patients in China. A randomised controlled trial. Br J Psychiatry 165:239–247
Acknowledgements
We thank Paul Bebbington (Royal Free and University College Medical School, London) for the critical, stimulating and motivating comments on an earlier version of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrà, G., Montomoli, C., Clerici, M. et al. Family interventions for schizophrenia in Italy: randomized controlled trial. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257, 23–30 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0677-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0677-z