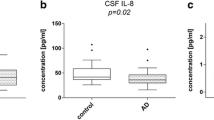
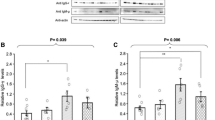
Abstract
Involvement of the interleukin–6 receptor complex (IL–6RC) in neuroregulatory and immunological processes of the brain and particularly in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been hypothesized. The functionally active IL–6RC consists of the cytokine IL–6, which acts through the ligand binding IL–6R and the signal transducing gp130. Using a new immunocytochemical protocol on rapid autopsy cryostat brain sections we studied the expression of the IL–6RC in Braak IV–V staged AD patients compared to normal age–matched controls (HC) across five different cortical regions. Inter–rater reliability of the method was high. The “baseline” expression in normal human brain was determined for IL–6,IL–6R and gp130 in all cortical regions. In normal tissue IL–6 expression was lower in parietal cortex. Higher IL–6R expression was shown in frontal, occipital and parietal cortex, lower expression in temporal cortex and cerebellum. In AD IL–6 expression levels were generally increased in parietal cortex and decreased in occipital cortex compared to controls. IL–6R expression levels were strongly increased in AD frontal and occipital cortex and decreased in temporal cortex and cerebellum. Our findings indicate an altered cortical immunoreactivity pattern of the functional IL–6RC in AD supporting the hypothesis of a disease–related role of IL–6 in AD pathophysiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WST, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue LF, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray A (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Bauer J, Strauss S, Schreiter-Gasser U, Ganter U, Schlegel P, Witt I, Volk B, Berger M (1991) Interleukin-6 and α-2-macroglobulin indicate an acute phase state in Alzheimer’s disease cortices. FEBS Lett 285:111–114
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E, Kemper P, Inglis JD, Oldstone MB, Mucke L (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10061–10065
Cohen J (1960) A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Measur 20:37–46
DeSerio A, Graziani R, Laufer R, Ciliberto G, Paonessa G (1995) In vitro binding of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor to its Receptors: Evidence for the formation of an IL-6 type hexameric Complex. J Mol Biol 254:795–800
Ehlers MRW, Riordan JF (1991) Membrane proteins with soluble counterparts: role of proteolysis in the release of transmembrane proteins. Biochemistry 30:10065–10074
Fabry Z, Fitzsimmons KM, Herlein JA, Moninger TO, Dobbs BM, Hart MN (1993) Production of the cytokines interleukin-1 and -6 by murine brain microvessel endothelium and smooth muscle pericytes. J Neuroimmunol 47:23–34
Fattory E, Lazzaro D,Musiani P,Modesti A, Alonzi T, Cilberto G (1995) IL-6 expression in neurons of transgenic mice causes reactive astrocytosis and increase in ramified microglial cells but no neuronal damage. Eur J Neurosci 7:2441–2449
Frank RA, Galasko D, Hampel H, Hardy J, De Leon M, Mehta DP, Rogers J, Siemers E, Trojanowsky QJ (2003) Proceedings of a working group; NIA initiative on neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s disease; Biological Measures Working group. Neurobiol Aging 24(4):521–536
Frei K, Malipiero UV, Leist TP, Zinkernagel RM, Schwab ME, Fontana A (1989) On the cellular source and function of interleukin-6 produced in the central nervous system in viral diseases. Eur J Immunol 19:689–694
Frei K, Leist TP, Meager A, Gallo P, Leppert D, Zinkernagel RM, Fontana A (1988) Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med 168:449–453
Gadient RA, Otten UH (1997) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) – A molecule with both beneficial and destructive potential. Prog Neurobiol 52:379–390
Gadient RA, Otten U (1995) Interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 receptor mRNA expression in rat central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 762:403–406
Gadient RA, Otten U (1994) Identification of interleukin-6 (IL- 6)-expressing neurons in the cerebellum and hippocampus of normal adult rats. Neurosci Lett 182:243–246
Gallo P, Frei K, Rordorf C, Lazdins J, Tavolato B, Fontana A (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 23:109–116
Grötzinger J, Kurapkat G, Wollmer A, Kalai M, Rose-John S (1997) The family of the IL-6-Type cytokines: specitivity and promiscuity of the receptor complexes. Proteins 27:96–109
Gruol DL,Nelson TE (1997) Physiological and pathological roles of interleukin-6 in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 15:307–339
Hama T, Kushima Y, Miyamoto M, Kubota M, Takei N, Hatanaka H (1991) Interleukin-6 improves the survival of mesencephalic catecholaminergic and septal cholinergic neurons from postnatal, two-week-old rats in cultures. Neuroscience 40:445–452
Hama T, Miyamoto M,Tsukui H, Nishio C, Hatanaka H (1989) Interleukin-6 as a neurotrophic factor for promoting the survival of cultured basal forebrain cholinergic neurons from postnatal rats. Neurosci Lett 104:340–344
Hampel H, Scheloske M, Haslinger A (2001) Physiology and biochemistry of interleukin-6 receptor complex: Implications for CNR disorders and Alzheimer’s disease. In: Rogers J (ed) Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease: basic and clinical research. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 121–143
Hampel H, Teipel SJ, Padberg F, Haslinger A, Riemenschneider M, Schwarz MJ, Kötter HU, Scheloske M, Buch K, Stübner S, Dukoff R, Lasser R, Müller N, Sunderland T, Rapoport S, Möller HJ (1999) Discriminant power of combined cerebrospinal fluid tau protein and of the soluble interleukin-6 receptor complex in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 823:104–112
Hampel H, Sunderland T, Kötter HU, Schneider C, Teipel SJ, Padberg F, Dukoff R, Ley J, Möller HJ (1998) Decreased soluble interleukin- 6 receptor in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res 780:356–359
Hampel H, Schoen D, Schwarz MJ, Kotter HU, Schneider C, Sunderland T, Dukoff R, Levy J, Padberg F, Stübner S, Buch K, Muller N, Möller HJ (1997) Interleukin-6 is not altered in cerebrospinal fluid of first-degree relatives and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 228:143–146
Hans VHJ, Kossmann T, Lenzlinger PM, Probstmeier R, Imhof HG, Trentz O, Morganti-Kossmann MC (1999) Experimental axonal injury triggers interleukin-6 mRNA, protein synthesis and release into cerebrospinal fluid. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:184–194
Haslinger A, Zarow C, Stein L, Bidlingmaier M, Teipel SJ, Scheloske M, Stein M, Padberg F, Freihöfer S, Schweiger R, Möller HJ, Hampel H (1999) Measurement of the soluble and the membrane bound IL-6 receptor complex in human post-mortem brain homogenates of Alzheimer demented patients. J Neurosci 25:1537
Haslinger A, Unger J, Padberg F, Fischer P, Peschl X, Mendel B, Stein L, Müller A, Schön T, Scheloske M, Berova M, Galuschka S, Pongratz D, Möller HJ, Hampel H (1998) Immunohistochemical staining of the Interleukin-6-receptor complex in human brain tissue. J Neurosci 24:1538
Heinrich PC, Horn F, Graeve L, Dittrich E, Kerr I, Muller-Newen G, Grotzinger J,Wollmer A (1998) Interleukin-6 and related cytokines: effect on the acute phase reaction. Eur J Nutr (Suppl 37):43–49
Heinrich PC, Castell J, Andus T (1990) Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J 265:621–636
Hibi M, Nakajima K, Hirano T (1996) IL-6 cytokine family and signal transduction: a model of the cytokine system. J Mol Med 74:1–12
Hibi M, Murakami M, Saito M, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell 63:1149–1157
Hirano T (1999) Molecular basis underlying functional pleiotropy of cytokines and growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 260:303–308
Hirano T, Nakajima K, Hibi M (1997) Signaling mechanisms through gp130: a model of the cytokine system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:241–252
Hirano T, Shizuo A, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1990) Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Trends Immunol 11:443–449
Hofman FM, Hinton DR, Johnson K, Merrill JE (1989) Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med 170:607–612
Horiuchi S, Koyanagi Y, Zhou Y, Miyamoto H, Tanaka Y, Waki M, Matsumoto A, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto N (1994) Soluble interleukin-6 receptors released from T cell or granulocyte/ macrophage cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells are generated through an alternative splicing mechanism. Eur J Immunol 24:1945–1948
Houssiau FA, Bukasa K, Sindic CJ, Van Damme J, Van Snick J (1988) Elevated levels of the 26KD human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin-6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the cerebral nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol 71:320–323
Hulette CM, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Crain B, Szymanski MH, Sinclaire MO, Roses AD (1997) Rapid brain autopsy: the Joseph and Kathleen Bryan Alzheimer’s disease research center experience. Arch Pathol Lab Med 121:615–618
Hüll M, Strauss S, Berger M, Volk B, Bauer J (1996) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 246:124–128
Hüll M, Strauss S, Volk B, Berger M, Bauer J (1995) Interleukin-6 is present in early stage of plaque formation and is restricted to the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 89:544–551
Kishimoto T, Akira S, Taga T (1992) Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science 258:593–597
Klein MA, Möller JC, Jones LL, Buethmann H, Kreutzberg GW, Raivich G (1997) Impaired neuroglial activation in interleukin-6 deficient mice. Glia 19:227–233
Laurenzi MA, Siden A, Persson MA, Norkkrans G, Hagberg L, Chiodi F (1990) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 activity in HIV infection and inflammatory and noninflammatory diseases of the nervous system. Clin Immunol 57:233–241
Lue L, Rydel R, Brigham EF, Yang LB, Hampel H, Murphy G, Brachova L, Yan SD, Walker D, Shen Y, Rogers J (2001) Inflammatory repertoire of Alzheimer’s disease and non-demented elderly microglia in vitro. Glia 35:72–79
Maimone D, Gregory S, Arnason BG, Reder AT (1991) Cytokine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 32:67–74
März P, Cheng JG, Gadient RA, Patterson PH, Stoyan T, Otten U, Rose-John S (1998) Sympathetic neurons can produce and respond to interleukin-6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3251–3256
März P, Heese K, Hock C, Golombowski S, Müller-Spahn F, Rose-John S, Otten U (1997) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble forms of IL-6 receptors are not altered in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 239:29–32
März P, Gadient RA, Otten U (1996) Expression of interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) and gp130 mRNA in PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons: modulation by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Brain Res 706:71–79
Montero-Julian FA, Brailly H, Sautes C, Joyeux I, Dorval T, Mosseri V, Yasukawa K, Wijdenes J, Adler A, Gorin I, Fridman WH, Tartour E (1997) Characterization of soluble gp130 released by melanoma cell lines: a polyvalent antagonist of cytokines from the interleukin-6 family. Clin Cancer Res 3:1443–1451
Morris CS, Esiri MM (1998) The expression of cytokines and their receptors in normal and mildly reactive human brain. J Neuroimmunol 92:85–97
Müllberg J, Oberthür W, Lottspeich F, Mehl E, Dittrich E, Graeve L, Heinrich PC, Rose-John S (1994) The soluble human IL-6 receptor, Multifunctional characterization of the proteolytic cleavage site. J Immunol 152:4958–4968
Müllberg J, Schoolinkt H, Stoyan T, Heinrich PC, Rose-John S (1992) Protein kinase C activity is rate limiting for shedding of the interleukin-6 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 189:794–800
Müller-Newen G, Küster A, Hemmann U, Keul R, Horsten U, Martens A, Graeve L, Wijdenes J, Heinrich PC (1998) Soluble IL- 6 receptor potentiates the antagonistic activity of soluble gp130 on IL-6 responses. J Immunol 161:6347–6355
Murray RE, McGuigan F, Grant SF, Reid DM, Ralston SH (1997) Polymorphisms of the interleukin-6 gene are associated with bone mineral density. Bone 21:89–92
Narazaki M, Yasukawa K, Saito T, Ohsugi Y, Fukui H, Koishihara Y, Yancopoulos GD, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1993) Soluble forms of the interleukin-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130 in human serum possessing a potential to inhibit signals through membrane-anchored gp130. Blood 82:1120–1126
Navikas V, Link H (1996) Review: cytokines and the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci Res 45:322–333
Padberg F, Haase CG, Feneberg W, Schwarz MJ, Hampel H (2001) No association between anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies and serum/cerebrospinal fluid levels of the soluble interleukin-6 receptor complex in multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Lett 305:13–16
Padberg F, Feneberg W, Schmidt S, Schwarz MJ, Körschenhausen D, Greenberg BD, Nolde T, Müller N, Trapmann H, König N, Möller HJ, Hampel H (1999) CSF and serum levels of soluble interleukin- 6 receptors (sIL-6R and sgp130), but not of interleukin-6 are altered in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 99:218–223
Paonessa G, Graziani R, DeSerio A, Savino R, Ciapponi L, Lahm A, Salvati AL, Toniatti C, Ciliberto G (1995) Two distinct and independent sites on IL-6 trigger gp130 dimer formation and signalling. EMBO J 14:1942–1951
Papassotiropoulos A, Bagli M, Jessen F, Bayer TA,Maier W, Rao ML, Heun R (1999) A genetic variation of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 delays the initial onset and reduces the risk for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 45:666–668
Raivich G, Bohatschek M, Kloss CUA, Werner A, Jones LL, Kreutzberg GW (1999) Neuroglial activation repertoire in the injured brain: graded response,molecular mechanisms and cues to physiological function. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 30:77–105
Raivich G, Galiano M, Jones IL, Kloss CUA, Werner A, Bluethmann H, Kreutzberg GW (1999) Lymphocyte infiltration into the injured nervous brain: role of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α. Ann Anat 181:43–44
Satoh T, Nakamura S, Taga T, Matsuda T, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Kaziro Y (1988) Induction of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells by B-cell stimulatory factor 2/Interleukin-6. Mol Cell Biol 8:3546–3549
Sawada M, Suzumura A, Marunouchi T (1992) TNFα induces IL- 6 production by astrocytes but not by microglia. Brain Res 583:296–299
Scheloske M, Haslinger A, Unger J, Fischer P, Hulette C, Oshita R, Padberg F, Pongratz D, Möller HJ, Hampel H (1999) Expression of the Interleukin-6 receptor complex (IL-6RC) in human rapidbrain autopsy tissue. J Neurosci 25:1536
Schöbitz B, De Kloet ER, Sutano W, Holsboer F (1993) Cellular localization of interleukin-6 mRNA and interleukin-6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 5:1426–1435
Schöbitz B, Voorhuis DAM, De Kloet ER (1992) Localization of interleukin-6 mRNA and interleukin-6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 136:189–192
Somers W, Stahl M, Seehra JS (1997) 1.9 A crystal structure of interleukin 6: implications for a novel mode of receptor dimerization and signaling. EMBO J 16:989–997
Sterneck E, Kaplan DR, Johnson PF (1996) Interleukin-6 induces expression of peripherin and cooperates with Trk receptor signaling to promote neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 67:1365–1374
Strauss S, Bauer J,Ganter U, Jonas U, Berger M, Volk B (1992) Detection of Interleukin-6 and α2-macroglobulin immunoreactivity in cortex and hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Lab Invest 66:223–230
Stübner S, Schön T, Padberg F, Teipel SJ, Schwarz MJ, Haslinger A, Buch K, Dukoff R ,Lasser R, Müller N, Sunderland T, Rapoport SI, Möller HJ, Hampel H (1999) Interleukin-6 and the soluble IL-6 receptor are decreased in cerebrospinal fluid of geriatric patients with major depression: no alteration of soluble gp130. Neurosci Lett 259:145–148
Taga T (1997) Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 15:797–819
Taga T, Hibi M, Hirata Y, Yamasaki KY, Yasukawa K, Matsuda T, Hirano T, Kishimoto T (1989) Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell 58:573–581
Van Snick J (1990) Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol 8:253–278
Vandenabeele P, Fiers W (1991) Is amyloidogenesis during Alzheimer’s disease due to an IL-1-/IL-6-mediated acute phase response in the brain? Trends Immunol 12:217–219
Ward LD, Hammacher A, Howlett GJ, Matthews JM, Fabri L, Moritz RL, Nice EC, Weinstock J, Simpson RJ (1996) Influence of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) dimerization on formation of the high affinity hexameric IL-6 receptor complex. J Biol Chem 271:20138–20144
Ward LD, Howlett GJ, Disciolo G, Yasukawa K, Hammacher A, Moritz RL, Simpson R (1994) High affinity interleukin-6 receptor is a hexameric complex consisting of two molecules each of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor and gp130. J Biol Chem 269:23286–23289
Wood JA, Wood PL, Ryan R, Graff-Radford NR, Pilapil C, Robtaille Y, Quirion R (1993) Cytokine indices in Alzheimer’s temporal cortex: no changes in mature IL-1β or IL-1Rα but increases in the associated acute phase proteins IL-6, α2-macroglobulin and C-reactive protein. Brain Res 629:245–252
Woodroofe MN, Sarna GS, Wadhwa M, Hayes GM, Loughlin AJ, Tinker A, Cuzner ML (1991) Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin- 6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol 33:227–236
Xu GY, Yu HA, Stahl M, McDonagh T, Kay LE, Cumming DA (1997) Solution structure of recombinant human interleukin-6. J Mol Biol 368:468–481
Yan SD, Zhu H, Fu J, Yan SF, Roher A, Tourtellotte WW, Rajavashisth T, Chen X, Godman GC, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1997) Amyloid-beta peptide-receptor for advanced glycation endproduct interaction elicits neuronal expression of macrophagecolony stimulating factor: a proinflammatory pathway in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5296–5301
Yan SD, Yan SF, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Kuppusamy P, Smith MA, Perry G, Godman GC, Nawroth P (1995) Non-enzymatically glycated tau in Alzheimer’s disease induces neuronal oxidant stress resulting in cytokine gene expression and release of amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Med 1:693–699
Zarow C, Schlueter KE, Zhang Q (1996) Interleukin-6 mRNA is elevated in Alzheimer disease brain. J Neurosci 22:214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Preliminary parts of this work were presented in abstract form at the 28th Annual Meeting of the Society of Neuroscience, Los Angeles, CA, 1998, at the 29th Annual Meeting of the Society of Neuroscience, Miami, FL, 1999, at the Neuroinflammation Conference, Washington, DC, 2000 and at the 30th Annual Meeting of the Society of Neuroscience, New Orleans, LA, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hampel, H., Haslinger, A., Scheloske, M. et al. Pattern of interleukin-6 receptor complex immunoreactivity between cortical regions of rapid autopsy normal and Alzheimer’s disease brain. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 255, 269–278 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-004-0558-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-004-0558-2