Abstract
Objective
To investigate a cohort of adult single-sided deafness (SSD) patients who received a cochlear implant and to determine the impact of underlying causes of etiology and duration of deafness on outcome
Study design
Retrospective data analysis
Setting
Tertiary referral centre with a large cochlear implant program
Subjects and methods
A demographic description of 55 adult patients implanted between 2009 and 2016. The best available speech perception score in every patient using the Freiburg Numbers, Freiburg Monosyllables and the Hochmair-Schulz-Moser (HSM) sentence test measured at the 1-, 3-, 6- and 12-month intervals, and the yearly follow-up appointments were examined. A multivariate regression analysis was conducted on the variables speech test, duration of deafness and etiology. Patients were split into four groups according to their duration of deafness (shorter duration of 10 years or less versus longer duration of more than 10 years) and etiology (inflammatory disease versus other causes).
Results
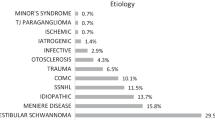
The median word reception score for the Monosyllables at 65 dB SPL were 43.75% (IQR: 29.38) and 67.50% (IQR: 25.63) at 80 dB SPL at 1 year following cochlear implantation. The median percentage score correct for the HSM sentence test was 80% (IQR: 62.95). Etiology of the reviewed patient cohort revealed that most frequent causes for deafness were sudden hearing losses and inflammatory etiologies, e.g. otitis media, labyrinthitis, meningitis, cholesteatoma or mumps. The duration of deafness was not significantly associated with poor speech perception outcome. A significant correlation was found for inflammatory diseases and duration of deafness of longer than 10 years.
Conclusion
The etiology and duration of deafness are important factors for the estimated outcome in speech perception in SSD patients. Presented data reveal that an inflammatory disease leading to deafness in combination with a long duration of deafness (10 + years) lead to poorer speech perception outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vincent C et al (2015) Identification and evaluation of cochlear implant candidates with asymmetrical hearing loss. Audiol Neurotol 20(suppl 1):87–89
Vermeire K, Van De Heyning P (2009) Binaural hearing after cochlear implantation in subjects with unilateral sensorineural deafness and tinnitus. Audiol Neurotol 14(3):163–171
Vermeire K, De Ridder D, Van de Heyning P, Anderson I, Nopp P, Diebl M (2014) Incapacitating unilateral tinnitus in single-sided deafness treated by cochlear implantation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 117(9):645–652
Döge J, Baumann U, Weissgerber T, Rader T (2017) Single-sided deafness: impact of cochlear implantation on speech perception in complex noise and on auditory localization accuracy. Otol Neurotol 38(10):e563–e569
Zeitler DM, Dorman MF, Natale SJ, Loiselle L, Yost WA, Gifford RH (2015) Sound source localization and speech understanding in complex listening environments by single-sided deaf listeners after cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol 36(9):1467–1471
Snapp HA, Holt FD, Liu X, Rajguru SM (2017) Comparison of speech-in-noise and localization benefits in unilateral hearing loss subjects using contralateral routing of signal hearing AIDS or bone-anchored implants. Otol Neurotol 38(1):11–18
Mertens G, Kleine Punte A, De Bodt M, Van De Heyning P (2015) “Binaural auditory outcomes in patients with postlingual profound unilateral hearing loss: 3 years after cochlear implantation,”. Audiol Neurotol 20(suppl 1):67–72
Rahne T, Plontke SK (2016) Functional result after cochlear implantation in children and adults with single-sided deafness. Otol Neurotol 37(9):e332–e340
Boisvert I, McMahon CM, Dowell RC, Lyxell B (2015) Long-term asymmetric hearing affects cochlear implantation outcomes differently in adults with pre- and postlingual hearing loss. PLoS ONE 10(6):1–11
Távora-Vieira D, Boisvert I, McMahon CM, Maric V, Rajan GP (2013) Successful outcomes of cochlear implantation in long-term unilateral deafness: brain plasticity? NeuroReport 24(13):724–729
Arndt S, Prosse S, Laszig R, Wesarg T, Aschendorff A, Hassepass F (2015) Cochlear implantation in children with single-sided deafness: does aetiology and duration of deafness matter? Audiol Neurotol 20(suppl 1):21–30
Tavora-Vieria D, De Ceulaer G, Govaerts PJ, Rajan GP (2015) Cochlear implantation improves localization ability in patients with unilateral deafness. Ear Hear 36(3):93–98
Shinagawa J et al (2017) Etiology of single-sided deafness and asymmetrical hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 137(sup565):S2–S7
Hahlbrock K (1953) Speech audiometry and new word-tests. Arch Ohren Nasen Kehlkopfheilkd 162(5):394–431
Hochmair-Desoyer I, Schulz E, Moser L, Schmidt M (1997) HSM originalartikel.pdf. Am J Otol 18:83
Holden LK et al (2013) Factors affecting open-set word recognition in adults with cochlear implants. Ear Hear 34(3):342–360
Moon IS et al (2014) Is there a deafness duration limit for cochlear implants in post-lingual deaf adults? Acta Otolaryngol 134(2):173–180
Medina MDM et al (2017) Cochlear implantation in postlingual adult patients with long-term auditory deprivation. Otol Neurotol 38(8):e248–e252
Cohen SM, Svirsky MA (2019) Duration of unilateral auditory deprivation is associated with reduced speech perception after cochlear implantation: a single-sided deafness study. Cochlear Implants Int 20(2):51–56
Helmstaedter V, Buechner A, Stolle S, Goetz F, Lenarz T, Durisin M (2018) Cochlear implantation in children with meningitis related deafness: the influence of electrode impedance and implant charge on auditory performance—a case control study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 113:102–109
Katsushika M et al (2018) Outcomes of cochlear implantations for mumps deafness: A report of four pediatric cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 114:76–79
Hassepass F et al (2013) Clinical outcome after cochlear implantation in patients with unilateral hearing loss due to labyrinthitis ossificans. Otol Neurotol 34(7):1278–1283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors received funding in relation to this article. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with ethical standards of the institutional and /or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration. Because of the retrospective study design, formal consent was not required. The study was approved by the Ethical Commission of the Medical University of Würzburg, Germany (Nr. 20180808 02).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurz, A., Grubenbecher, M., Rak, K. et al. The impact of etiology and duration of deafness on speech perception outcomes in SSD patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 3317–3325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05644-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05644-w