Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess the first outcomes of a fully implantable active middle ear device.
Methods
Retrospective observational nonrandomized group study. Settings: Private hospital. Fifteen patients underwent device implantation between December 2014 and June 2017. The pre-operative and post-operative air conduction (AC) and bone conduction (BC) thresholds were evaluated. The functional gain, speech perception in silence and in noise, and localization abilities were also analyzed.
Results
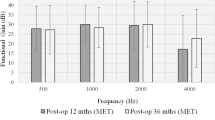
Sixteen active middle ear implantations were performed. Post-operatively, the mean pure tone thresholds were 50.5 dB ( ± 12.64) for BC and 64.9 dB ( ± 15.36) for AC. No differences were found between the post-operative and pre-operative audiometric thresholds before activating the system (p > 0.05). Post-operatively, the mean thresholds in the free field after the device was activated were 46.8 dB, 45.75 dB, 42.6 dB, and 43.38 dB at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, respectively. The global results of speech understanding in silence were 50.7 dB, 47.18 dB, 42 dB, and 42 dB for 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, respectively. Patients with mixed hearing loss had better results than those with sensorineural hearing loss. Speech discrimination in noise and localization was improved.
Conclusions
Despite the small number of patients, our results confirmed that this fully implantable active middle ear device is a viable treatment for patients with moderate-to-severe sensorineural hearing loss who cannot or do not want to use traditional hearing aids for clinical or cosmetic reasons.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ernst A, Todt I, Wagner J (2015) Safety and effectiveness of the Vibrant Soundbridge in treating conductive and mixed hearing loss: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 126:1451–1457
Bruschini L, Forli F, Santoro A et al (2009) Fully implantable Otologics MET CarinaTM device for the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss. Preliminary surgical and clinical results. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 29:79–85
Bittencourt AG, Burke PR, Jardim IS et al (2014) Implantable and semi-implantable hearing aids: a review of history, indications, and surgery. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 18:303–310
Zwartentok JW, Mulder JJS, Snik Ad FM et al (2016) Active middle ear implantation: long-term medical and technical follow-up, implant survival, and complications. Otol Neurotol 37:513–519
Traynor RM, Fredrickson JM (2007) The future is here: the otologics fully implantable hearing system https://www.audiologyonline.com/articles/future-here-otologics-fully-implantable-928. Accessed 1 Jan 2017.
George L (2006) Report of the medical technology assessment working group. Duke University, Durham, New York
Fredrickson JM, Coticchia JM, Khosla S (1996) Current status in the development of implantable middle ear hearing aids. Adv Otol 10:189–204
Bruschini L, Forli F, Passetti S et al (2010) Fully implantable Otologics MET Carina™ device for the treatment of sensorineural and mixed hearing loss: audio-otological results. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 130:1147–1153
Jenkins HA, Atkins JS, Horlbeck D et al (2008) Otologics fully implantable hearing system: phase I trial 1-year results. Otol Neurotol 29:534–541
Fredrickson J, Cotcchia J, Kohosla S (1995) Investigations into an implantable electromagnetic hearing device for moderate to severe sensorineural loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 28:107–120
Rameh C, Meller R, Lavieille JP et al (2010) Long-term patient satisfaction with different middle ear hearing implants in sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 31:883–892
Lefebvre PP, Gisbert J, Cuda D et al (2017) A retrospective multicentre cohort review of patient characteristics and surgical aspects versus the long-term outcomes for recipients of a fully implantable active middle ear implant. Audiol Neurootol 21:333–345
Jenkins HA, Pergola N, Kasic J (2007) Intra-operative ossicular loading with the Otologics fully implantable hearing device. Acta Otolaryngol 127:360–364
Debeaupte M, Decullier E, Tringali S et al (2015) Evolution of the reliability of the fully implantable middle ear transducer over successive generations. Otol Neurotol 36:625–630
Klein K, Nardelli A, Stafinski T (2012) A systematic review of the safety and effectiveness of fully implantable middle ear hearing devices: the carina and esteem systems. Otol Neurotol 33:916–992
Funding
No financial disclosures to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peixoto, M.d., Miranda, C., Bento, M. et al. The first results of a totally implanted active middle ear device. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2775–2781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05557-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05557-8