Abstract
Introduction
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL) is an otologic urgency whose treatment is still controversial. Its etiology remains largely unknown in most cases and predicting its prognosis is still a challenge. Cardiovascular risk factors (CVRF) have been implicated in the etiopathogenesis of this entity.
Objectives
Application of the SCORE (Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation) risk scale in patients with SSHL and evaluation of its potential prognostic value in recovery in patients with CVRF.
Materials and methods
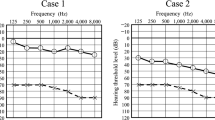
Prospective analysis of patients with SSHL admitted for protocol treatment including intravenous corticosteroid therapy associated to weekly intratympanic injection in the event of therapeutic failure or severe hearing loss at admission. Demographic, audiometric, clinical and imaging data were assessed. The SCORE risk scale was applied and the audiometric recovery was compared among different risk groups.
Results
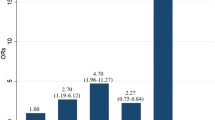
Our overall complete and partial recovery rates were 35.9% and 26%, respectively. More than a half of our patients had at least one CVRF. Of these, overweight/obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypertension were the most common. In our sample, patients with CVRF and higher SCORE risk presented higher PTA at admission and also worse hearing outcome, although these results were not statically significant.
Conclusion
This preliminary study could not confirm the validity for SCORE scale for cardiovascular risk assessment in predicting audiometric recovery in patients with SSHL with multiple comorbidities. Further research with larger samples are needed to elucidate the etiology of SSHL and the exact role of cardiovascular risk factors in the pathophysiology of SSHL.
Level of evidence
4


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSHL:
-
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- CVRF:
-
Cardiovascular risk factors
- SCORE:
-
Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation
- PTA:
-
Pure-tone average
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Wu CS, Lin HC, Chao PZ (2006) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: evidence from Taiwan. Audiol Neurootol 11(3):151–156
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Arlinger S, Hultcrantz E (2007) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: results drawn from the Swedish national database. Acta Otolaryngol 127(11):1168–1175
Stachler RJ et al (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146(1S):S1–S35
Conlin AE, Parnes LS (2007) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, I: a systematic review. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(6):573–581
Mattox DE, Simmons FB (1977) Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86(4 Pt 1):463–480
Fetterman BL, Saunders JE, Luxford WM (1996) Prognosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol 17(4):529–536
Haynes DS, O’Malley M, Cohen S, Watford K, Labadie RF (2007) Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 117(1):3–15
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V et al (2007) Genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 117(3):547–551
Aimoni C, Bianchini C, Borin M et al (2010) Diabetes, cardiovascular risk factors and idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case–control study. Audiol Neurootol 15(2):111–115
Arjun D, Neha G, Surinder KS, Ravi K (2015) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss; prognostic factors. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 27(82):355–359
Chang YS et al (2017) Framingham risk score as a prognostic predictor of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a preliminary study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 126:382–387
Conroy RM, Pyörälä K, Fitzgerald AP, Sans S, Menotti A, De Backer G et al (2003) Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: the SCORE project. Eur Heart J 24(11):987–1003
Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H et al (2012) European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012): the Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur Heart J 33:1635–1701
Haremza C, Klopp-Dutote N, Strunski V, Page C (2017) Evaluation of cardiovascular risks and recovery of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in hospitalised patients: comparison between complete and partial sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Laryngol Otol 131(10):919–924
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD (2010) Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 120(5):1011–1021
Ullrich D, Aurbach G, Drobik C (1992) A prospective study of hyperlipidemia as a pathogenic factor in sudden hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 249:273–276
Ballesteros F, Alobid I, Tassies D, Reverter JC, Scharf RE, Guilemany JM et al (2009) Is there an overlap between sudden neurosensorial hearing loss and cardiovascular risk factors? Audiol Neurotol 14:139–145
Chang IJ, Kang CJ, Yueh CY, Fang KH, Yeh RM, Tsai YT (2015) The relationship between serum lipids and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(4):e0121025
Funding
The authors did not receive any specific financial or material support from agencies from the public sector, commercial sector or non-profit entities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ASM takes full responsibility for the integrity of the data presented. AL contributed to the collection of data. All the other authors contributed to the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of the data for the work. DR and DM had full access to all data and made substantial contributions to the analysis and interpretation of data. JG and LD were also responsible for the study supervision. ASM was responsible for the drafting of the manuscript and all the authors for revising it for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have read and understood the policy on declaration of interests of this magazine and have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menezes, A.S., Ribeiro, D., Lima, A. et al. SCORE risk scale as a prognostic factor after sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2739–2745 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05518-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05518-1