Abstract
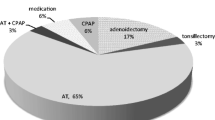
Few data are available about the pattern of upper airway (UA) obstruction in children <2 years with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Also, the role of adenoidectomy versus adenotonsillectomy (AT) is poorly defined in this age group. We performed drug-induced sedation endoscopy (DISE) in young OSAS children to investigate the pattern of UA obstruction and the value of DISE in therapeutic decision making. Retrospective analysis of ≤2-year-old children undergoing DISE-directed UA surgery. OSAS severity and the treatment outcomes were documented by polysomnography. Data are available for 28 patients, age 1.5 years (1.3–1.8), BMI-z score 0.5 (−0.7 to 1.3) with severe OSAS, obstructive apnea/hypopnea index (oAHI) 13.8/hr (7.5–28.3). All but 3 had (>50%) obstruction at the level of the adenoids, and all but 5 had (>50%) tonsillar obstruction. DISE-directed treatment consisted of adenoidectomy (n = 4), tonsillectomy (n = 1), and AT (n = 23). There was a significant improvement in respiratory parameters. Twenty children (71.4%) had a postoperative oAHI <2/hr. None had palatal or tongue base obstruction. Five children had a circumferential UA narrowing (hypotonia), 2 of them had residual OSAS. DISE showed a collapse of the epiglottis in 6 and late-onset laryngomalacia in 4. These findings did not affect surgical outcome. Adenotonsillar hypertrophy is the major cause of UA obstruction, and DISE-directed UA surgery was curative in 71,4% of children ≤2 years. We suggest that DISE may be helpful in surgical decision making. Circumferential UA narrowing may result in less favorable surgical outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaditis AG, Alonso Alvarez ML, Boudewyns A, Alexopoulos EI, Ersu R, Joosten K, Larramona H, Miano S, Narang I, Trang H, Tsaoussoglou M, Vandenbussche N, Villa MP, Van Waardenburg D, Weber S, Verhulst S (2016) Obstructive sleep disordered breathing in 2- to 18-year-old children: diagnosis and management. Eur Respir J 47(1):69–94. doi:10.1183/13993003.00385-2015
Katz ES, Mitchell RB, D’Ambrosio CM (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea in infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185(8):805–816. doi:10.1164/rccm.201108-1455CI
DeHaan KL, Seton C, Fitzgerald DA, Waters KA, MacLean JE (2015) Polysomnography for the diagnosis of sleep disordered breathing in children under 2 years of age. Pediatr Pulmonol. doi:10.1002/ppul.23169
Goldberg S, Shatz A, Picard E, Wexler I, Schwartz S, Swed E, Zilber L, Kerem E (2005) Endoscopic findings in children with obstructive sleep apnea: effects of age and hypotonia. Pediatr Pulmonol 40(3):205–210. doi:10.1002/ppul.20230
Croft CB, Thomson HG, Samuels MP, Southall DP (1990) Endoscopic evaluation and treatment of sleep-associated upper airway obstruction in infants and young children. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 15(3):209–216
Chan DK, Liming BJ, Horn DL, Parikh SR (2014) A new scoring system for upper airway pediatric sleep endoscopy. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140 (7):595–602. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2014.612
Robison JG, Wilson C, Otteson TD, Chakravorty SS, Mehta DK (2013) Analysis of outcomes in treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in infants. Laryngoscope 123(9):2306–2314. doi:10.1002/lary.23685
Cheng J, Elden L (2013) Outcomes in children under 12 months of age undergoing adenotonsillectomy for sleep-disordered breathing. Laryngoscope 123(9):2281–2284. doi:10.1002/lary.23796
Brigance JS, Miyamoto RC, Schilt P, Houston D, Wiebke JL, Givan D, Matt BH (2009) Surgical management of obstructive sleep apnea in infants and young toddlers. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(6):912–916. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2009.01.034
Paradise JL, Smith CG, Bluestone CD (1976) Tympanometric detection of middle ear effusion in infants and young children. Pediatrics 58(2):198–210
Brodsky L (1989) Modern assessment of tonsils and adenoids. Pediatr Clin North Am 36 (6):1551–1569
Boudewyns A, Verhulst S, Maris M, Saldien V, Van de Heyning P (2014) Drug-induced sedation endoscopy in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med 15(12):1526–1531. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2014.06.016
Berry RB, Budhiraja R, Gottlieb DJ, Gozal D, Iber C, Kapur VK, Marcus CL, Mehra R, Parthasarathy S, Quan SF, Redline S, Strohl KP, Davidson Ward SL, Tangredi MM, American Academy of Sleep M (2012) Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. Deliberations of the sleep apnea definitions task force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med 8(5):597–619. doi:10.5664/jcsm.2172
Marcus CL, Moore RH, Rosen CL, Giordani B, Garetz SL, Taylor HG, Mitchell RB, Amin R, Katz ES, Arens R, Paruthi S, Muzumdar H, Gozal D, Thomas NH, Ware J, Beebe D, Snyder K, Elden L, Sprecher RC, Willging P, Jones D, Bent JP, Hoban T, Chervin RD, Ellenberg SS, Redline S, Childhood Adenotonsillectomy T (2013) A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 368(25):2366–2376. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1215881
Chan DK, Liming BJ, Horn DL, Parikh SR (2014) A New Scoring System for Upper Airway Pediatric Sleep Endoscopy. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2014.612
Richter GT, Rutter MJ, deAlarcon A, Orvidas LJ, Thompson DM (2008) Late-onset laryngomalacia: a variant of disease. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(1):75–80. doi:10.1001/archoto.2007.17
Revell SM, Clark WD (2011) Late-onset laryngomalacia: a cause of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75(2):231–238. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.11.007
Galluzzi F, Pignataro L, Gaini RM, Garavello W (2015) Drug induced sleep endoscopy in the decision-making process of children with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 16(3):331–335. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2014.10.017
Caldwell P, Hensley R, Machaalani R, Cheng A, Waters K (2011) How effective is adenoidectomy alone for treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea in a child who presents with adenoid hypertrophy? J Paediatr Child Health 47(8):568–571. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1754.2011.02154.x
Nolan J, Brietzke SE (2011) Systematic review of pediatric tonsil size and polysomnogram-measured obstructive sleep apnea severity. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(6):844–850. doi:10.1177/0194599811400683
Kay DJ, Bryson PC, Casselbrant M (2005) Rates and risk factors for subsequent tonsillectomy after prior adenoidectomy: a regression analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131(3):252–255. doi:10.1001/archotol.131.3.252
Baugh RF, Archer SM, Mitchell RB, Rosenfeld RM, Amin R, Burns JJ, Darrow DH, Giordano T, Litman RS, Li KK, Mannix ME, Schwartz RH, Setzen G, Wald ER, Wall E, Sandberg G, Patel MM, American Academy of O-H, Neck Surgery F (2011) Clinical practice guideline: tonsillectomy in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(1 Suppl):S1–S30. doi:10.1177/0194599810389949
Gross JB, Bachenberg KL, Benumof JL, Caplan RA, Connis RT, Cote CJ, Nickinovich DG, Prachand V, Ward DS, Weaver EM, Ydens L, Yu S, American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative M (2006) Practice guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology 104 (5):1081–1093 (quiz 1117–1088)
Mitchell RB, Kelly J (2005) Outcome of adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea in children under 3 years. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132(5):681–684. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2004.12.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boudewyns, A., Van de Heyning, P. & Verhulst, S. Drug-induced sedation endoscopy in children <2 years with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: upper airway findings and treatment outcomes. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 2319–2325 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4481-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4481-3