Abstract
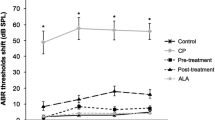
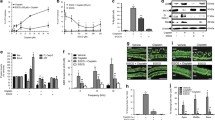
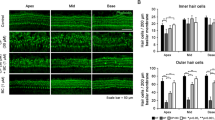
Cis-diammineedichloroplatinum (cisplatin) is a chemotherapeutic agent that is widely used in the treatment of many cancers. Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity and neurotoxicity are dose-limiting adverse effects for cisplatin. The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying cisplatin-induced ototoxicity aren’t fully understood. It has been proposed that cisplatin primarily cause damage at the cochlea, outer hair cells in particular, leading to excessive production of free oxygen radicals in the organ of Corti, stria vascularis, spiral ligament, and spiral ganglionic cells. The cytotoxicity is associated with the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS); thus, there is an increasing interest on antioxidants with an effort to discover the established protection against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity over time. Misoprostol (MP) has gained considerable interest as a reactive oxygen species scavenger in recent years. To best of our knowledge, there is no study about protective effect of MP, a prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) analogue, on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. In our study, we show that protective effects of misoprostol on cisplatin-induced ototoxcity on rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Womer RB, Silber JH (2004) Predicting cisplatin ototoxicity in children: the influence of age and the cumulative dose. Eur J Cancer 40:2445–2451
Sluyter S, Klis SF, de Groot JC, Smoorenburg GF (2003) Alterations in the stria vascularis in relation to cisplatin ototoxicity and recovery. Hear Res 185:49–56
Erdem T, Bayindir T, Filiz A, Iraz M, Selimoglu E (2012) The effect of resveratrol on the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(10):2185–2188
Yumusakhuylu AC, Yazici M, Sari M, Binnetoglu A, Kosemihal E, Akdas F, Sirvanci S, Yuksel M, Uneri C, Tutkun A (2012) Protective role of resveratrol against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:404–408
Laurell G, Bagger-Sjoback D (1991) Dose-dependent inner ear changes after I.V. administration of cisplatin. J Otolaryngol 20:158–167
Siddik ZH (2003) Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 22:7265–7279
Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Oh GS, Moon HD, Kwon KB, Park C, Park BH, Lee HK, Chung SY, Park R, So HS (2010) Roles of NADPH oxidases in cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and ototoxicity. J Neurosci 30:3933–3946
Lynch ED, Gu R, Pierce C, Kil J (2005) Reduction of acute cisplatin ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats by oral administration of allopurinol and ebselen. Hear Res 201:81–89
Salam OM, Saleem AA, Omara EA, Hassan NS (2009) Hepatoprotective effects of MP and silymarin on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 23(2):179–188
Yang H, Majno P, Morel P et al (2002) Prostaglandin E(1) protects human liver sinusoidal endothelial cell from apoptosis induced by hypoxia reoxygenation. Microvasc Res 64:94–103
Sostres C, Gargallo CJ, Arroyo MT, Lanas A (2010) Adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, aspirin and coxibs) on upper gastrointestinal tract. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 24(2):121–132. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2009.11.005
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (2009) Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med 219:177–186
Williams CJ, Whitehouse JM (1979) Cis-platinum: a new anticancer agent. Br Med J 1:1689–1691
Hartmann JT, Lipp HP (2003) Toxicity of platinum compounds. Expert Opin Pharmacother 4:889–901
Lopez-Gonzalez MA, Guerrero JM, Rojas F, Delgado F (2000) Ototoxicity caused by cisplatin is ameliorated by melatonin and other antioxidants. J Pineal Res 28:73–80
Daldal A, Odabasi O, Serbetcioglu B (2007) The protective effect of intratympanic dexamethasone on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:747–752
Kalkanis JG, Whitworth C, Rybak LP (2004) Vitamin E reduces cisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 114:538–542
Campbell KC, Meech RP, Rybak LP, Hughes LF (1999) D-Methionine protects against cisplatin damage to the stria vascularis. Hear Res 138:13–28
Feghali JG, Liu W, Van De Water TR (2001) l-n-acetyl-cysteine protection against cisplatin-induced auditory neuronal and hair cell toxicity. Laryngoscope 111:1147–1155
Huang X, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (2007) Ginkgo bilobaextract (EGb 761) protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Otol Neurotol 28:828–833
Lynch ED, Gu R, Pierce C, Kil J (2005) Reduction of acute cisplatin ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats by oral administration of allopurinol and ebselen. Hear Res 201:81–89
Church MW, Blakley BW, Burgio DL, Gupta AK (2004) WR-2721 (Amifostine) ameliorates cisplatin-induced hearing loss but causes neurotoxicity in hamsters: dose-dependent effects. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5:227–237
Hyppolito MA, de Oliveira JA, Rossato M (2006) Cisplatin ototoxicity and otoprotection with sodium salicylate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263:798–803
Yazici ZM, Meric A, Midi A, Arınc YV, Kahya V, Hafız G (2012) Reduction of cisplatin ototoxicity in rats by oral administration of pomegranate extract. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:45–52
Halliwell B (1994) Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet 344:721–724
Xu O, Liu Y, Li X, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Wang N, Zhang Y, Lu H (2011) Protective effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza against cisplatininduced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Am J Otolaryngol 32:228–234
Sagit M, Korkmaz F, Akcadag A, Somdas MA (2013) Protective effect of thymoquinone against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:2231–2237. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2254-6
Kapusuz Z, Ozkırıs M, Kala M, Saydam L. Protective Role of Bilberry Extract Against Cisplatin Induced Ototoxicity in Rats. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65(4):339–344. doi:10.1007/s12070-013-0642-x
Çiçek MT, Kalcioglu MT, Bayindir T, Toplu Y, Iraz M (2014) The effect of lycopene on the ototoxicity induced by cisplatin. Turk J Med Sci 44:582–585. doi:10.3906/sag-1304-66 ©TÜBİTAK
Kelles M, Tan M, Kalcioglu MT, Toplu Y, Bulam N (2013) The protective effect of Chrysin against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1007/s12070-013-0695-x
- Ozturk M, Ucar S, Sarı F, Erdogan S, Topdag M, Iseri M.(2013) Possible protective effect of sertraline against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: an experimental study. Hindawi Publ Corp Sci World J vol, Article ID 523480, 5 pages 10.1155/2013/523480
Toplu Y, Parlakpinar H, Sapmaz E, Karatas E, Polat A, Kizilay A (2014) The protective role of Molsidomine on the cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (July–Sept 2014) 66(3):314–319. doi:10.1007/s12070-014-0718-2
Bayindir T, Iraz M, Kelles M, Kaya S, Tan M, Filiz A, Toplu Y, Kalcioglu MT (2014) The effect of beta glucan on cisplatin ototoxicity. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (Apr–Jun 2014) 66(2):131–134. doi:10.1007/s12070-013-0623-0
Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KI (2006) Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Mc Graw Hill Companies, New York
Gana TJ, Koo J, MacPherson BR (1992) Gross and histologic effects of topical misoprostol on canine gastric mucosa. Exp Toxicol Pathol 44:40–46
Asako H, Kubes P, Wallace J, Wolf RE, Granger DN (1992) Modulation of leukocyte adhesion in rat mesenteric venules by aspirin and salicylate. Gastroenterology 103:146–152
Andrews FJ, Malconenti-Wilson C, O’Brien PE (1994). Effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on LFA-1 and ICAM-1 expression in gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol 266(4 pt 1):G657–G664
Widomski DL, Walsh RE, Baron DA et al (1991) Effects of the prostaglandin analogue misoprostol on inflammatory mediator release by human monocytes. Agents Actions 34:30–31
Kim HJ, Kwak JY (1996) Effects of misoprostol on renal function and plasma enothelin-1 levels during early postoperative stage of living donor renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 1996(28):1207–1209
Kawata R, Urade Y, Tachibana M, Mizukoshi O (1988) Prostaglandin synthesis by the cochlea. Prostaglandins 1988(35):173–184
Briner W, House J, O’Leary M (1993) Synthetic prostaglandin E1 misoprostol as a treatment for tinnitus. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:652–654
Davies NM, Longstreth J, Jamali F (2001) Misoprostol therapeutics revisited. Pharmacotherapy 21(1):60–73
Ozer MK, Halil A, Moncu MC, Savran M, Calapoglu M, Yesilot S, Candan IA et al (2011) Effects of misoprostol on cisplatininduced renal damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1556–1559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Funding
This study was funded by Kayseri Training and Research Hospital.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doğan, M., Polat, H., Yaşar, M. et al. Protective role of misoprostol against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273, 3685–3692 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4031-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4031-4