Abstract
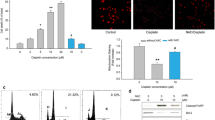
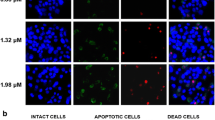
Silibinin is an anticancer and chemopreventive natural compound, which is extracted from milk thistle (Silybum marianum). It is reported that silibinin has anticancer efficacy in many malignant tumors. Laryngeal carcinoma is the second most common head and neck squamous carcinoma. In the present work, we investigated the effects of silibinin on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) cell line Hep-2 cells. We found that silibinin induced the decrease of cell viability in Hep-2 cells with a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Moreover, silibinin resulted in the apoptosis of Hep-2 cells and had synergy effects with arsenic trioxide. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation increased because of silibinin exposure. ROS scavenger NAC alleviated the cytotoxicity of silibinin to Hep-2 cells. The mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was lost in Hep-2 cells treated with silibinin. Subsequently, silibinin induced the activation of caspase-3 in Hep-2 cells and caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK inhibited the cytotoxicity of silibinin in Hep-2 cells. The survivin expression decreased after Hep-2 cells were treated with silibinin. In conclusion, silibinin induced the apoptosis of Hep-2 cells via oxidative stress and down-regulating survivin expression. Therefore, silibinin is a potential therapeutical agent against LSCC in future.








Similar content being viewed by others
Rererences
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300
Karatzanis AD, Psychogios G, Zenk J et al (2009) Comparison among different available surgical approaches in T1 glottic cancer. The Laryngoscope 119:1704–1708
Elsheikh MN, Rinaldo A, Hamakawa H et al (2006) Importance of molecular analysis in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 28:842–849
Gazak R, Walterova D, Kren V (2007) Silybin and silymarin—new and emerging applications in medicine. Curr Med Chem 14:315–338
Deep G, Agarwal R (2010) Antimetastatic efficacy of silibinin: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential against cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:447–463
Wu KJ, Zeng J, Zhu GD et al (2009) Silibinin inhibits prostate cancer invasion, motility and migration by suppressing vimentin and MMP-2 expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1162–1168
Kim S, Choi JH, Lim HI et al (2009) Silibinin prevents TPA-induced MMP-9 expression and VEGF secretion by inactivation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 16:573–580
Li L, Gao Y, Zhang L, Zeng J, He D, Sun Y (2008) Silibinin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis by caspase activation, down-regulating survivin and blocking EGFR-ERK activation in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 272:61–69
Singh RP, Tyagi A, Sharma G, Mohan S, Agarwal R (2008) Oral silibinin inhibits in vivo human bladder tumor xenograft growth involving down-regulation of survivin. Clin Cancer Res 14:300–308
Bang CI, Paik SY, Sun DI, Joo YH, Kim MS (2008) Cell growth inhibition and down-regulation of survivin by silibinin in a laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 117:781–785
Kong Q, Lillehei KO (1998) Antioxidant inhibitors for cancer therapy. Med Hypotheses 51:405–409
Duan W, Jin X, Li Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2010) Silibinin induced autophagic and apoptotic cell death in HT1080 cells through a reactive oxygen species pathway. J Pharmacol Sci 113:48–56
Fan S, Li L, Chen S et al (2011) Silibinin induced-autophagic and apoptotic death is associated with an increase in reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in HeLa cells. Free Radic Res 45:1307–1324
Jiang YY, Huang H, Wang HJ et al (2011) Interruption of mitochondrial complex IV activity and cytochrome c expression activated O(2). (-)-mediated cell survival in silibinin-treated human melanoma A375–S2 cells via IGF-1R-PI3K-Akt and IGF-1R-PLC gamma-PKC pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 668:78–87
Noh EM, Yi MS, Youn HJ et al (2011) Silibinin enhances ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in mcf-7 human breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer 14:8–13
Ryan BM, Konecny GE, Kahlert S et al (2006) Survivin expression in breast cancer predicts clinical outcome and is associated with HER2, VEGF, urokinase plasminogen activator and PAI-1. Ann Oncol 17:597–604
Sah NK, Khan Z, Khan GJ, Bisen PS (2006) Structural, functional and therapeutic biology of survivin. Cancer Lett 244:164–171
Jha K, Shukla M, Pandey M (2012) Survivin expression and targeting in breast cancer. Surg Oncol 21:125–131
Wang Y, Kong W, Xiong X, Zhang S, Sun D (2005) [The expressions of survivin and VEGF in squamous cell carcinoma of larynx and the correlation between the two marks]. Lin chuang er bi yan hou ke za zhi. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol 19:838–841
Shen Z, Ren Y, Ye D, Guo J, Kang C, Ding H (2011) Significance and relationship between DJ-1 gene and surviving gene expression in laryngeal carcinoma. Eur J Histochem 55:e9
Cheng B, Yang X, Han Z, An L, Liu S (2008) Arsenic trioxide induced the apoptosis of laryngeal cancer via down-regulation of survivin mRNA. Auris Nasus Larynx 35:95–101
Kauntz H, Bousserouel S, Gosse F, Raul F (2011) Silibinin triggers apoptotic signaling pathways and autophagic survival response in human colon adenocarcinoma cells and their derived metastatic cells. Apoptosis 16:1042–1053
Cheung CW, Taylor PJ, Kirkpatrick CM et al (2007) Therapeutic value of orally administered silibinin in renal cell carcinoma: manipulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 levels. BJU Int 100:438–444
Kauntz H, Bousserouel S, Gosse F, Raul F (2012) The flavonolignan silibinin potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma and in derived TRAIL-resistant metastatic cells. Apoptosis 17:797–809
Son YG, Kim EH, Kim JY et al (2007) Silibinin sensitizes human glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via DR5 up-regulation and down-regulation of c-FLIP and survivin. Cancer Res 67:8274–8284
Dizaji MZ, Malehmir M, Ghavamzadeh A, Alimoghaddam K, Ghaffari SH (2012) Synergistic effects of arsenic trioxide and silibinin on apoptosis and invasion in human glioblastoma U87MG cell line. Neurochem Res 37:370–380
Flaig TW, Gustafson DL, Su LJ et al (2007) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of silybin-phytosome in prostate cancer patients. Invest New Drugs 25:139–146
Pradhan SC, Girish C (2006) Hepatoprotective herbal drug, silymarin from experimental pharmacology to clinical medicine. Indian J Med Res 124:491–504
Zhou B, Wu LJ, Li LH et al (2006) Silibinin protects against isoproterenol-induced rat cardiac myocyte injury through mitochondrial pathway after up-regulation of SIRT1. J Pharmacol Sci 102:387–395
Wang MJ, Lin WW, Chen HL et al (2002) Silymarin protects dopaminergic neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglia activation. Eur J Neurosci 16:2103–2112
Lu P, Mamiya T, Lu L et al (2010) Silibinin attenuates cognitive deficits and decreases of dopamine and serotonin induced by repeated methamphetamine treatment. Behav Brain Res 207:387–393
Lu P, Mamiya T, Lu LL et al (2009) Silibinin prevents amyloid beta peptide-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in mice. Br J Pharmacol 157:1270–1277
Marrazzo G, Bosco P, La Delia F et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of silibinin in diabetic mice. Neurosci Lett 504:252–256
Pallauf K, Rimbach G (2013) Autophagy, polyphenols and healthy ageing. Ageing Res Rev 12:237–252
Liu B, Yang P, Ye Y et al (2011) Role of ROS in the protective effect of silibinin on sodium nitroprusside-induced apoptosis in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Free Radic Res 45:835–847
Duan WJ, Li QS, Xia MY, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2011) Silibinin activated p53 and induced autophagic death in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells via reactive oxygen species-p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 34:47–53
Kim KW, Choi CH, Kim TH, Kwon CH, Woo JS, Kim YK (2009) Silibinin inhibits glioma cell proliferation via Ca2+/ROS/MAPK-dependent mechanism in vitro and glioma tumor growth in vivo. Neurochem Res 34:1479–1490
Zeng J, Sun Y, Wu K et al (2011) Chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effects of intravesical silibinin against bladder cancer by acting on mitochondria. Mol Cancer Ther 10:104–116
Tiwari P, Kumar A, Balakrishnan S, Kushwaha HS, Mishra KP (2011) Silibinin-induced apoptosis in MCF7 and T47D human breast carcinoma cells involves caspase-8 activation and mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Invest 29:12–20
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE, Adjei AA (2005) Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin 55:178–194
Agarwal C, Singh RP, Dhanalakshmi S et al (2003) Silibinin upregulates the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma HT-29 cells. Oncogene 22:8271–8282
Tyagi A, Agarwal C, Harrison G, Glode LM, Agarwal R (2004) Silibinin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cells by regulating CDKI-CDK-cyclin cascade, and caspase 3 and PARP cleavages. Carcinogenesis 25:1711–1720
Kumar S (1999) Mechanisms mediating caspase activation in cell death. Cell Death Differ 6:1060–1066
Tyagi A, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Agarwal R (2006) Silibinin activates p53-caspase 2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: evidence for a regulatory loop between p53 and caspase 2. Carcinogenesis 27:2269–2280
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev 8:61–70
Zhao H, Ren J, Zhuo X, Ye H, Zou J, Liu S (2008) Prognostic significance of Survivin and CD44v6 in laryngeal cancer surgical margins. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134:1051–1058
Chen XM, Luan XY, Lei DP et al (2008) Suppression of survivin expression by short hairpin RNA induces apoptosis in human laryngeal carcinoma cells. ORL Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Relat Spec 70:168–175
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by Youth Fund of Jining Medical University (No. JYQ2011KZ005), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (ZR2010HL057, ZR2010HL045) and a Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (No. J12LE10).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X. Yang, X. Li and L. An contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Li, X., An, L. et al. Silibinin induced the apoptosis of Hep-2 cells via oxidative stress and down-regulating survivin expression. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2289–2297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2444-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2444-x