Abstract
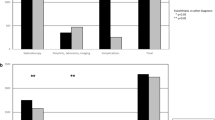
Sialendoscopy is an established, minimally invasive technique to diagnose and treat obstructive disorders of major salivary glands. Knowledge about patient satisfaction and quality of life is limited. All patients who underwent sialendoscopy were prospectively followed and evaluated. To determine the quality of life after sialendoscopy, an established questionnaire was evaluated (Short-Form-36 Health Survey-SF-36). To determine patient satisfaction, a self-made questionnaire was applied and evaluated. Furthermore, postoperative follow-up examination and the amount of patients who could be saved from sialadenectomy were determined. Main reasons for sialendoscopy were recurrent or permanent swelling of the affected salivary gland. 46 patients were included, 52 sialendoscopies were performed. Immediately after sialendoscopy operative ablation of the respective gland was averted in 98.1 % of the patients. After the follow-up period of 225.4 ± 79.0 days operative ablation of the respective gland was avoided in 89.9 % of the patients. Overall, 85.2 % reported an improvement of symptoms during follow-up, however, values for role-physical functioning (p = 0.025) and bodily pain (p = 0.011) still showed a significant difference when compared to a matched reference group of healthy individuals. Significant negative influence factors towards the outcome were younger age, long-term duration of symptoms and selected SF-36 items (vitality, social functioning, and mental health). Operative ablation of major salivary glands can be avoided by means of sialendoscopy in high percentages during short-term. There seems to be a high patient satisfaction in these selected cases. The duration of preoperative symptoms appears to be an important factor predisposing towards poor satisfaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gundlach P, Scherer H, Hopf J, Leege N, Müller G, Hirst L, Scholz C (1990) Endoscopic-controlled laser lithotripsy of salivary calculi. In vitro studies and initial clinical use. HNO 38:247–250
Katz P (1991) Endoscopy of the salivary glands. Ann Radiol 34:110–113
Nahlieli O, Neder A, Baruchin AM (1994) Salivary gland endoscopy: a new technique for diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:1240–1242
Marchal F, Dulguerov P, Lehmann W (1999) Interventional sialendoscopy. N Engl J Med 341:1242–1243
Faure F, Froehlich P, Marchal F (2008) Paediatric sialendoscopy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:60–63
Iro H, Zenk J, Koch M (2010) Modern concepts for the diagnosis and therapy of sialolithiasis. HNO 58:211–217
Koch M, Iro H, Zenk J (2010) Stenosis and other non-sialolithiasis-related obstructions of the major salivary gland ducts. Modern treatment concepts. HNO 58:218–224
Walvekar RR, Razfar A, Carrau RL, Schaitkin B (2008) Sialendoscopy and associated complications: a preliminary experience. Laryngoscope 118:776–779
Marchal F (2007) A combined endoscopic and external approach for extraction of large stones with preservation of parotid and submandibular glands. Laryngoscope 117:373–377
Katz P (1991) Endoscopy of the salivary glands. Ann Radiol (Paris) 34(1–2):110–113
Kroll T, Finkensieper M, Hauk H, Guntinas-Lichius O, Wittekindt C (2012) Sialendoscopy—learning curve and nation-wide survey in German ENT-departments. Laryngorhinootologie 91(9):561–5.
Gopinath B, McMahon CM, Rochtchina E, Karpa MJ, Mitchell P (2010) Risk factors and impacts of incident tinnitus in older adults. Ann Epidemiol 20(2):129–135
Soler ZM, Hwang PH, Mace J, Smith TL (2010) Outcomes after middle turbinate resection: revisiting a controversial topic. Laryngoscope 120(4):832–837
Chu DW, Chow TL, Lim BH, Kwok SP (2003) Endoscopic management of submandibular sialolithiasis. Surg Endosc 17(6):876–879
Nahlieli O, Baruchin AM (1997) Sialoendoscopy: three years’ experience as a diagnostic and treatment modality. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55 (9):912–918 (discussion 919–920)
Capaccio P, Toretta S, Ottavian F, Sambataro G, Pignataro L (2007) Modern management of obstructive salivary diseases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 27(4):161–172
Marchal F, Kurt AM, Dulguerov P, Becker M, Oedman M, Lehmann W (2001) Histopathology of submandibular glands removed for sialolithiasis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110(5 Pt 1):464–469
Makdissi J, Escudier MP, Brown JE, Osailan S, Drage N, McGurk M (2004) Glandular function after intraoral removal of salivary calculi from the hilum of the submandibular gland. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42(6):538–541
Quenin S, Plouin-Gaudon I, Marchal F, Froehlich P, Distant F, Faure F (2008) Juvenile recurrent parotitis: sialendoscopic approach. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(7):715–719
Schmitz S, Zengel P, Alvir I, Andratschke M, Berghaus A, Lang S (2008) Long-term evaluation of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in the treatment of salivary stones. J Laryngol Otol 122(1):65–71
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kroll, T., Finkensieper, M., Sharma, S.J. et al. Short-term outcome and patient satisfaction after sialendoscopy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2939–2945 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2418-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2418-z