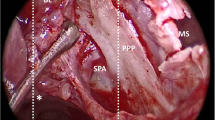
Abstract
This study aims to provide guidance regarding patient selection and timing of intervention with sphenopalatine artery (SPA) ligation by defining ‘severe epistaxis’. An analysis of all patients undergoing SPA ligation (January 2002–2010) was performed. SPA ligation was deemed necessary if at least one of the four identified criteria was fulfilled. The same analysis was also performed on all patients admitted with epistaxis who did not undergo SPA ligation over a 6-month period. All 27 patients who underwent SPA ligation met at least one of the criteria selected. Uncontrolled epistaxis (21/27) was fulfilled most often. In comparison, only 4/71 patients admitted with epistaxis who did not undergo SPA ligation fulfilled any single criterion. All criteria were satisfied in a significantly higher number of cases in the SPA group (p < 0.001) The criteria studied proved helpful in identifying patients admitted to hospital with epistaxis who had failed conservative measures.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker TW, Macfarlane TV, McGarry GW (2007) The epidemiology and chronobiology of epistaxis: an investigation of Scottish hospital admissions 1995–2004. Clin Otolaryngol 32(5):361–365
Rourke T, Tassone P, Philpott C, Bath A (2009) ENT cases seen at a local ‘walk-in centre’: a 1 year review. J Laryngol Otol 123(3):339–342
Petruson B, Rudin R (1975) The frequency of epistaxis in a male population sample. Rhinology 13:129–133
Pope LE, Hobbs CG (2005) Epistaxis: an update on current management. Postgrad Med J 81(955):309–314 Review
Viducich RA, Blanda MP, Gerson LW (1995) Posterior epistaxis: clinical features and acute complications. Ann Emerg Med 25:592–596
Tan LK, Calhoun KH (1999) Epistaxis. Med Clin North Am 83:43–56
Wurtle P (1996) How I do it: emergency nasal packing using an umbilical cord clamp to secure a Foley catheter for posterior epistaxis. J Otolaryngol 25:46–47
Ho EC, Mansell NJ (2004) How we do it: a practical approach to Foley catheter posterior nasal packing. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:754–757
Viehweg TL, Roberson JB, Hudson JW (2006) Epistaxis: diagnosis and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64(3):511–518
Douglas R, Wormold PJ (2007) Update on epistaxis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15(3):180–183
Nouraei SA, Maani T, Hajioff D, Saleh HA, Mackay IS (2007) Outcome of endoscopic sphenopalatine artery occlusion for intractable epistaxis: a 10-year experience. Laryngoscope 117(8):1452–1456
Feusi B, Holzmann D (2005) Steurer posterior epistaxis: systematic review on the effectiveness of surgical therapies. J Rhinology 43(4):300–304
Kumar S, Shetty A, Rockey J, Nilssen E (2003) Contemporary surgical treatment of epistaxis. What is the evidence for sphenopalatine artery ligation? Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 28(4):360–363
O’Flynn PE, Shadaba A (2000) Management of posterior epistaxis by endoscopic clipping of the sphenopalatine artery. Clin Otolaryngol 25:374–377
Simmen DB, Raghavan U, Briner HR, Manestar M, Groscurth P, Jones NS (2006) The anatomy of the sphenopalatine artery for the endoscopic sinus surgeon. Am J Rhinol 20(5):502–505
Gifford TO, Orlandi RR (2008) Epistaxis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 41(3):525–536 viii
Schlosser RJ (2009) Clinical practice. Epistaxis. N Engl J Med 360(8):784–789
Almeyda R, Shahzad A, Bleach N (2007) Silicone Foley catheters outperform latex Foley catheters for post nasal packing: an in vitro study. Clin Otolaryngol 32(6):480–483
Asanau A, Timoshenko AP, Vercherin P, Martin C, Prades JM (2009) Sphenopalatine and anterior ethmoidal artery ligation for severe epistaxis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118(9):639–644
Budrovich R, Saetti R (1992) Microscopic and endoscopic ligation of the sphenopalatine artery. Laryngoscope 1002:1390–1394
Snyderman CH, Goldman SA, Carrau RL, Ferguson BJ, Grandis JR (1999) Endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation is an effective method of treatment for posterior epistaxis. Am J Rhinol 13(2):137–140
Seno S, Arikata M, Sakurai H, Owaki S, Fukui J, Suzuki M, Shimizu T (2009) Endoscopic ligation of the sphenopalatine artery and the maxillary artery for the treatment of intractable posterior epistaxis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23(2):197–199
Wormold PJ, Wee DT, van Hasselt CA (2000) Endoscopic ligation of the sphenopalatine artery for refractory posterior epistaxis. Am J Rhinol 14(4):261–264
Holzmann D, Kaufmann T, Pedrini P, Valavanis A (2003) Posterior epistaxis: endonasal exposure and occlusion of the branches of the sphenopalatine artery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260(8):425–428
Loughran S, Hilmi O, McGarry GW (2005) Endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation—when, why and how to do it. An on-line video tutorial. Clin Otolaryngol 30(6):539–543
Biswas D, Rafferty A, Jassar P (2009) Night emergency cover for ENT in England: a national survey. J Laryngol Otol 123(8):899–902
Abdelkader M, Leong SC, White PS (2007) Endoscopic control of the sphenopalatine artery for epistaxis: long-term results. J Laryngol Otol 121(8):759–762
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhani, R., Syed, I., Qureishi, A. et al. The Wexham Criteria: defining severe epistaxis to select patients requiring sphenopalatine artery ligation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2039–2043 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2318-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2318-7