Abstract
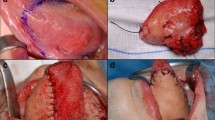
The aim of this study was to evaluate swallowing, speech and quality of life in patients undergoing surgery for malignant tumors involving soft palate. We performed a cross sectional study of 23 patients (aged 32–80 years), submitted to soft palate resection, free of disease for at least 1 year. Primary closure of the surgical defect was performed in 5 patients (21.7 %), adaptation of a palatal obturator prosthesis in 2 (8.7 %), myocutaneous flap in 5 (21.7 %), local flap in 2 (8.7 %) and microsurgical free flap in 9 (39.1 %). All patients were submitted to fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation and completed functional and quality of life questionnaires. Functional evaluation of swallowing showed higher prevalence of pooling of food in the nasopharynx in patients submitted to regional flap reconstruction or primary closure (53.9 %). Swallowing difficulties were predominantly related to solid foods (54.5 %) and were associated with more extensive palatal resections. Most individuals submitted to reconstruction with microsurgical flaps had satisfactory velopharyngeal mobility (87 %). The presence of nasal air escape or velopharyngeal gap was minimal in most of the sample. Hypernasality contributed minimally to imprecisions in speech articulation or intelligibility. Vocal alteration did not impact patients’ quality of life. Pharyngeal phase of swallowing was satisfactory in most patients. However, nasal reflux and penetration were present in a few patients. Most patients had minimal phono-articulatory alterations as a global outcome. Scores of swallowing and speech parameters regarding the questionnaires used were high, demonstrating minor impact on quality of life.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Douglas WG, Rigual NR, Giese W et al (2005) Advanced soft palate cancer: the clinical importance of the parapharyngeal space. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:66–69
Chen J, Pappas L, Moeller JH et al (2007) Treatment or oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma with external beam radiation combined with interstitial brachytherapy. Head Neck 29:362–369
Sakuraba M, Kimata Y, Ota Y et al (2003) Simple maxillary reconstruction using free tissue transfer and prostheses. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:594–600
Brown JS, Rogers SN, Lowe D (2006) A comparison of tongue and soft palate squamous cell carcinoma treated by primary surgery in terms of survival and quality of life outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:208–214
Mariani PB, Kowalski LP, Magrin J (2006) Reconstruction of large defects postmandibulectomy for oral cancer using plates and myocutaneos flaps: a long term follow up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:427–432
Gaziano JE (2002) Evaluation and management of oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer. Cancer Control 9:400–409
Boseley ME, Hartnick CJ (2004) Assessing the outcome of surgery to corret velopharyngeal insufficiency with the pediatric voive outcomes survey. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68:1429–1433
Gillespie MB, Brodsky MB, Day TA et al (2005) Laryngeal penetration and aspiration during swallowing after the treatment of advanced oropharyngeal cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:615–619
Thomas L, Jones TM, Tandon S, Katre C, Lowe D, Rogers SN (2007) An evaluation of the University of Washington quality of life swallowing domain following oropharyngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265(Suppl 1):S29–S37
Tschudi D, Stoeckli S, Schmid S (2003) Quality of life after different treatment modalities for carcinoma of the oropharynx. Laryngoscope 113:1949–1954
Vartanian JG, Carvalho AL, Yueh B et al (2004) Long-term quality-of-life evaluation after head and neck cancer treatment in a developing country. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:1209–1213
Zuydam AC, Lowe D, Brown JS, Vaughan ED, Rogers SN (2005) Predictors of speech and swallowing function following primary surgery for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Clin Otolaryngol 30:428–437
Crary MA, Mann GD, Groher ME (2005) Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehab 86(8):1516–1520
Golding-Kushner KJ, Argamaso RV, Cotton RT et al (1990) Standardization for the reportingof nasopharyngoscopy and multiview videofluoroscopy: a report from an international working group. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 27:337–347
Camargo LOS, Rodrigues CM, Avelar JA (2001) Velopharyngeal oclusion in people who were submitted to nasoendoscopy at The Center of Health Education (CEPS). Salusvita Bauru 20:49–60
Isshiki N, Okamura H, Tanabe M, Morimoto M (1969) Differential diagnosis of hoarseness. Folia Phonetica 21:9–19
Hirano M (1981) Clinical examination of voice. Springer, New York
Dejonckere PH, Remacle M, Fresnel-Elbaz et al (1996) Differentiated. Perceptual evaluation of pathological voice quality: reliability and correlations with acoustic measurements. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 117(3):219–24
Aviv JE (2000) Prospective, randomized outcome study of endoscopy versus modified barium swallow in patients with dysphagia. Laryngoscope 110:563–574
Sie KCY, Chen EY (2007) Management of velopharyngeal insufficiency: development of a protocol and modifications of sphincter pharyngoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 23:128–139
Jacobson BH, Grywalski C, Silbergleit A, Jacobson G, Benninger MS, Newman CW (1997) The voice handicap index (VHI): development and validation. Am J Speech Lang Pathol 6(3):66–70
Chen AY, Frankowski R, Bishop-Leone J et al (2001) The development and validation of a dysphagia-specific quality-of-life questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer: the M. D. Anderson dysphagia inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:870–876
Vartanian JG, Carvalho AL, Yueh B et al (2006) Brazilian-portuguese validation of the University of Washington quality of life questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 28:1115–1121
Hu KS, Harrison LB, Culliney B et al (2004) Cancer of the oropharynx. In: Harrison LB, Sessions RB, Hong WK (eds) Head and neck: a multidisciplinary approach, 2nd edn. Lippincott Williams e Wilkins, Philadelphia Pa, pp 306–351
Osborne RF, Brown JJ (2004) Carcinoma of the oral pharynx: an analysis of subsite treatment heterogeneity. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 13(1) 71–80
Brown JS, Rogers SN, Lowe D (2006) A comparison of tongue and soft palate squamous cell carcinoma treated by primary surgery in terms of survival and quality of life outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35(3):208–214
Seikaly H, Rieger J, Wolfaardt J, Moysa G, Harris J, Jha N (2003) Functional outcomes after primary oropharyngeal cancer resection and reconstruction with the radial forearm free flap. Laryngoscope 133:897–904
Ortiz KL, Jaques B, Monnier P, Alfaro GE, Ruiz AA, Pasche P (2000) Utilizaciónm del colgajo antebraquial en la reconstrucción de la orofaringe posterior a reseccón por cáncer. Rev Inst Nal Cancerol (Mex) 46:85–89
Keuning KHDM, Meijer A, Van der Bilt A, Koole R (2009) Revisional surgery following the superiorly based posterior pharyngeal wall flap historical perspectives and current considerations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:1137–1142
Rich JT, Liu J, Haughey BH (2011) Swallowing function after transoral laser microsurgery (TLM) ± adjuvant therapy for advanced-stage oropharyngeal cancer. Laryngoscope 121(11):2381–2390
Smith GI, Brennan PA, Scott PJ, Ilankovan V (2002) Outcome after radial forearm, gastro-omental, and jejunal free flaps in oral and oropharyngeal reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40:330–333
Gurney TA, Eisele DW, Orloff LA, Wang SJ (2008) Predictors of quality of life after treatment for oral cavity and oropharyngeal carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139:262–267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barata, L.F., de Carvalho, G.B., Carrara-de Angelis, E. et al. Swallowing, speech and quality of life in patients undergoing resection of soft palate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 305–312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2006-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2006-7