Abstract
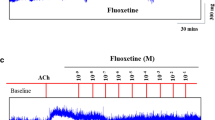
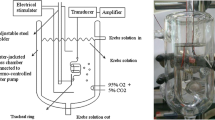
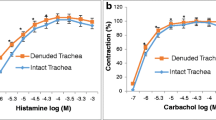
Oxymetazoline is often used as a decongestant in rhinitis patients who are suffering from nasal obstruction. It is used as a nasal drop or spray solution. The effect on nasal mucosa in vitro or in vivo is well known. However, the effect of the drug on tracheal smooth muscle has rarely been explored. During administration of the drug to the nose, it might affect the trachea via inhalation. We used our preparation to test the effectiveness of oxymetazoline on isolated rat’s tracheal smooth muscle. A 5 mm long portion of rat trachea was submersed in 30 ml Kreb’s solution in a muscle bath at 37°C. Changes in tracheal contractility in response to the application of parasympathetic mimetic agents were measured using a transducer connected to a Pentium III computer equipped with polygraphy software. The following assessments were performed: (1) effect on tracheal smooth muscle resting tension; (2) effect on contraction caused by 10−6 M methacholine as a parasympathetic mimetic; (3) effect of oxymetazoline on electrically induced tracheal smooth muscle contractions. Addition of parasympathetic mimetics to the incubation medium caused the trachea to contract in a dose-dependent manner. Addition of oxymetazoline induced a significant relaxation response when the preparation was up to 10−4 M. At the same concentration, the drug also could inhibit EFS induced spike contraction. Oxymetazoline had negligible effect on the basal tension of trachea as the concentration increased. The degree of drug-induced tracheal contraction or relaxation was dose-dependent. The study indicated that high concentrations of oxymetazoline might actually antagonize cholinergic receptors of the trachea.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beny J, Pacicca C (1994) Bidirectional electrical communication between smooth muscle and endothelial cells in the pig coronary artery. Am J Physiol 266:H1465–H1472
Ichimura K, Jackson RT (1983) Calcium, calcium blockers, and nasal smooth muscle. Arch Otolaryngol 109:593–597
Bratton DL, Tanaka DT, Grunstein MM (1987) Effects of temperature on cholinergic contractility of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol 63:1933–1941
Gonzalez O, Santacana GE (2001) Effect of low temperature on tracheal smooth muscle contractile and relaxing responses evoked by electrical field stimulation. Phys Res 20:237–243
Yau KI, Ko FN, Chien CH (1999) Effects of prokinetic agents on contractile responses to electrical field stimulation of isolated guinea pig trachea. J Formos Med Assoc 98:567–572
Yau KI, Hwang TL (2002) The nonadrenergic noncholinergic system can modulate the effect of prokinetic agents on contractile response of isolated guinea pig trachea segments to electrical field stimulation. J Formos Med Assoc 101:695–699
Hoffman BB (2001) Adrenergic-activating and other sympathomimetic drugs. In: Katzung BG (ed) Basic and clinical pharmacology, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, San Francisco, pp 120–154
Wang H-W, Jackson RT (1988) Do cholinergic neurons directly innervate nasal blood vessels? Rhinology 26:139–146
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Tri-Service General Hospital (TSGH C96-27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HW., Wu, CC. Effects of oxymetazoline on isolated rat’s tracheal smooth muscle. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265, 695–698 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0509-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0509-4