Abstract
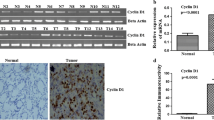
The aim of the research was to evaluate the expression levels of cyclin E/A and CDC25A/B during laryngeal carcinogenesis. The expression was demonstrated using immunohistochemistry in 46 cases of laryngeal cancer (LSCC), 23 epithelial dysplasias (ED) and 21 samples of normal mucosa (NM). The mean labeling indices (LI) for cyclin E in LSCC, ED and NM were 10.6, 4.9 and 0%; for cyclin A 27.2, 17.5 and 7%; for CDC25A 73.9, 53 and 32% and for CDC25B 36.5, 25.9 and 0%, respectively. A gradual increase in cyclin A and CDC25A expression levels from mild through moderate and severe dysplasia to in situ carcinoma were noted. Cyclin A LI significantly increased also from NM through ED to LSCC. Cyclin A and CDC25A LI significantly increased from NM to ED. Overexpression of cyclin A and CDC25A was significantly associated with proliferation among ED. Linear interdependency was detected in ED between the expression of CDC25A and cyclin A. Cyclin E and CDC25B overexpression occurs as a late event in neoplastic transformation. The progressive expression of proteins supports the multistep model of laryngealcarcinogenesis. The results indicate a possible role of cyclin A as a marker reflecting cell proliferation. The enhanced immunoexpression of cyclin A and CDC25A suggests the potential for malignant formation in preneoplastic lesions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cordon-Cardo C (1995) Mutation of cell cycle regulators, biological and clinical applications for human neoplasm. Am J Pathol 147:545–560
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI (1999) Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature 401:297–300
Geng Y, Yu Q, Sicinska E, Das M, Schneider JE, Bhattacharya S (2003) Cyclin E ablation in the mouse. Cell 114:431–443
Galaktionov K, Beach D (1991) Specific activation of cdc25 tyrosine phosphatases by B-type cyclins: evidence for multiple roles of mitotic cyclins. Cell 67:1181–1194
Blomberg I, Hoffman I (1999) Ectopic expression of Cdc25A accelerates the G1/S transition and lead to the premature activation of cyclin E and A-dependent kinases. Moll Cell Biol 19:6183–6194
Chen X, Prywes R (1999) Serum-induced expression of the cdc25A gene by relief of E2F-mediated repression. Mol Cell Biol 19:4695–4702
Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC, Helin K (1999) CDC25A phosphatase is a target of E2F and is required for efficient E2Finduced S phase. Mol Cell Biol 10:6379–6395
Dong Y, Sui L, Watanabe Y, Sugimoto K, Tokuda M (2002) Aberrant expression of cyclin A in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 22:83–90
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA, Callister M, Ding Y, Hortobagyi GN, Bedrosian I, Knickerbocker C, Toyofuku W, Lowe M, Herliczek TW, Bacus SS (2002) Cyclin E and survival in patients with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1566–1575
Ngan ESW, Hashimoto Y, Ma ZQ, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY (2003) Overexpression of Cdc25B, an androgen receptor coactivator, in prostate cancer. Oncogene 22:734–739
Xu X, Yamamoto H, Sakon M, Yasui M, Ngan CY, Fukunaga H, Morita T, Ogawa M, Nagano H, Nakamori S, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, Monden M (2003) Overexpression of CDC25 phosphatase is associated with hypergrowth activity and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 5:1764–1772
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61(5):759–767
Joachim E, Peschos D, Goussia A, Mittari E, Charalabopoulos K, Michale M, Salmas M, Vougiouklakis Th, AssimakopoulosD, Agnantis NJ (2004) Expression patterns of cyclins D1, E in laryngeal epithelial lesions: correlation with other cell cycle regulators (p53, pRb, Ki-67 and PCNA) and clinicopathological features. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 23(2):277–283
Lonardo F, Rusch V, Langenfeld J, Dmitrovsky E, Klimstra DS (1999) Overexpression of cyclin D1 and E is frequent in bronchial preneoplasia and precedes squamous cell carcinoma development. Cancer Res 59:2470–2476
Jeannon JP, Soames JV, Aston V, Stafford FW, Wilson JA (2004) Molecular markers in dysplasia of the larynx: expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21, p27 and p53 tumour suppressor gene in predicting cancer risk. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29(6):698–704
Shin DM, Ro JY, Hong WK, Hittelman WN (1994) Dysregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in premalignant lesions during head and neck tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 54(12):3153–3159
Sarbia M, Bektas N, Bektas N, Muller W, Heep H, Borchard F, Gabbert HE (1999) Expression of cyclin E in dysplasia, carcinoma, and nonmalignant lesions of Barrett esophagus. Cancer 86:2597–2601
Scott IS, Morris LS, Bird K, Davies RJ, Vowler SL, Rushbrook SM, Marshall AE, Laskey RA, Miller R, Arends MJ, Coleman N (2003) A novel immunohistochemical method to estimate cell-cycle phase distribution in archival tissue: implications for the prediction of outcome in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 201:187–197
Möröy T, Geisen C (2004) Cyclin E. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1424–1439
Nielsen NH, Emdin SO, Cajander J, Landberg G (1997) Deregulation of cyclin E and D1 in breast cancer is associated with inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene 14:295–304
Jordan RCK, Bradley G, Slingerland J (1998) Reduced levels of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 in epithelial dysplasia and carcinoma of the oral cavity. Am J Pathol 152:585–590
Chen HM, Yen-Ping Kuo M, Lin KH, Lin CY, Chiang CP (2003) Expression of cyclin A is related to progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwan. Oral Oncology 39:476–482
Zindy F, Lamas E, Chenivesse X, Sobczak J, Wang J, Fesquet D, Henglein B, Brechot C (1992) Cyclin A is required in normal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 182:1144–1154
Jinno S, Suto K, Nagata A (1994) Cdc25A is a novel phosphatase functioning early in the cell cycle. EMBO J 13:1549–1556
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI (1999) Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature 401:297–300
Almadori G, Bussu F, Cadoni G, Galli J, Rigante M, Artuso A, Maurizi M (2004) Multistep laryngeal carcinogenesis helps our understanding of the field cancerisation phenomenon: a review. Eur J Cancer 40:2383–2388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fraczek, M., Wozniak, Z., Ramsey, D. et al. Expression patterns of cyclin E, cyclin A and CDC25 phosphatases in laryngeal carcinogenesis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264, 923–928 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0276-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0276-2