Abstract
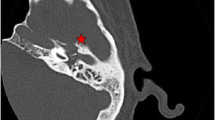
Necrotizing external otitis is a potentially life-threatening infection involving the temporal and adjacent bones. The most frequent pathogen is attributed to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, but is rarely caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Recently, we encountered a 47-year-old diabetic man with a swollen obliterated external ear canal with granulation tissue on the right ear. Image study demonstrated skull base osteomyelitis, epidural abscess and cerebral venous sinus thrombi. It was later proved to be necrotizing external otitis caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. He then underwent craniotomy for drainage of the epidural abscess, followed by intravenous ciprofloxacin and metronidazole for 2 consecutive weeks until both pus and blood cultures depicted no growth of pathogens. Based on this case, synergistic antibiotic therapy using a third-generation cephalosporin or quinolone (ciprofloxacin), accompanied by metronidazole, and even a short-term aminoglycoside is recommended for the treatment of severe Klebsiella-induced necrotizing external otitis. Surgical intervention should be limited without shedding of the pathogens.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giamarellou H (1992) Malignant otitis externa: the therapeutic evolution of a lethal infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 30:745–751
Slattery WH, Brackmann DE (1996) Skull base osteomyelitis. Malignant external otitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 29:795–806
Ress BD, Luntz M, Telischi FF, Balkany TJ, Whiteman ML (1997) Necrotizing external otitis in patients with AIDS. Laryngoscope 107:456–460
Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW (1999) Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. New Engl J Med 341:1906–1912
Podschun R, Ullmann U (1998) Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:589–603
Chang SC, Fang CT, Hsueh PR, Chen YC, Luh KT (2000) Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing liver abscess in Taiwan. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 37:279–284
Allroggen H, Abbott RJ (2000) Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Postgrad Med J 76:12–15
Syms MJ, Tsai PD, Holtel MR (1999) Management of lateral sinus thrombosis. Laryngoscope 109:1616–1620
Gherini SG, Brackmann DE, Bradley WG (1986) Magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography in malignant external otitis. Laryngoscope 96:542–548
Fekete T, Tumah H, Woodwell J, Satishchandran V, Truant A, Axelrod P (1996) Comparative susceptibilities of Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to 11 antimicrobial agents in a tertiary-care university hospital. Am J Med 100 [Suppl 6A]:20s–25s
Brisse S, Milatovic D, Fluit AC, Verhoef J, Schmitz FJ (2000) Epidemiology of quinolone resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca in Europe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 19:64–68
Paterson DL, Mulazimoglu L, Casellas JM, Ko WC, Goossens H, Von Gottberg A, Mohapatra S, Trenholme GM, Klugman KP, McCormack JG, Yu VL (2000) Epidemiology of ciprofloxacin resistance and its relationship to extended-spectrum beta-lactamase production in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 30:473–478
Kimmelman CP, Lucente FE (1989) Use of ceftazidime for malignant external otitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 98:721–725
Levenson MJ, Parisier SC, Dolitsky J, Bindra G (1991) Ciprofloxacin: drug of choice in the treatment of malignant external otitis. Laryngoscope 101:821–824
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grant no. NSC 93-2314-B002-114 from the National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, TH., Kuo, ST. & Young, YH. Necrotizing external otitis in a patient caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263, 344–346 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-0998-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-0998-y