Abstract
Purpose
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exhibit dysregulated expression in human cancer and play an important role in carcinogenesis. The aim of this study was to identify a distinct miRNA expression signature for cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and to investigate the function of deregulated miRNAs in cervical carcinoma.
Methods
A miRNA microarray was used to compare miRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer, CIN and normal cervical tissues. Real-time RT-PCR was used to validate the expression of 9 miRNAs in 103 cervical tissues. Bioinformatics programs were used to predict potential target genes and their function. Functional studies were performed to characterize the effect on cervical cancer cells by overexpression of miR-218 and miR-21.
Results
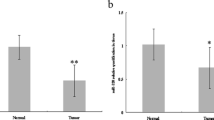
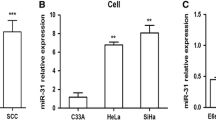
We identified deregulated miRNAs in cervical cancer and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). MiR-218 was the most downregulated (0.175-fold decrease) miRNA, and miR-21 was the most upregulated (5.67-fold increase) miRNA. In addition, the expression patterns of 9 miRNAs were validated by real-time RT-PCR. Bioinformatics analyses and functional studies indicated that miR-218 and miR-21 may be involved in cancer invasion and metastasis.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that miRNAs are aberrantly expressed in cervical cancer and cervical preneoplastic lesions. These miRNAs may be involved in the progression of cervical neoplasm as potential tumor suppressor genes or oncogenes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howell LP, Zhou H, Wu W, Davis R (2004) Significance of subclassifying high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions into moderate dysplasia/CIN II versus severe dysplasia/CIN III/CIS in the Bethesda System terminology. Diagn Cytopathol 30:362–366
Clifford G, Franceschi S, Diaz M, Munoz N, Villa LL (2006) Chapter 3: HPV type-distribution in women with and without cervical neoplastic diseases. Vaccine 24(Suppl 3):S3–S26
Thomison JR, Thomas LK, Shroyer KR (2008) Human papillomavirus: molecular and cytologic/histologic aspects related to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and carcinoma. Hum Pathol 39:154–166
Sassen S, Miska EA, Caldas C (2008) MicroRNA: implications for cancer. Virchows Arch 452:1–10
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2999–3004
Banno K, Yanokura M, Kisu I, Yamagami W, Susumu N, Aoki D (2013) MicroRNAs in endometrial cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 18:186–192
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC (2006) Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9:189–198
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ (2010) Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg 251:499–505
Sotlar K, Diemer D, Dethleffs A, Hack Y, Stubner A, Vollmer N, Menton S, Menton M, Dietz K, Wallwiener D, Kandolf R, Bultmann B (2004) Detection and typing of human papillomavirus by e6 nested multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 42:3176–3184
Barreto CL, Martins DB, de Lima FJ, Magalhaes V (2013) Detection of human Papillomavirus in biopsies of patients with cervical cancer, and its association with prognosis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288:643–648
Lee JW, Choi CH, Choi JJ, Park YA, Kim SJ, Hwang SY, Kim WY, Kim TJ, Lee JH, Kim BG, Bae DS (2008) Altered MicroRNA expression in cervical carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 14:2535–2542
Rao Q, Shen Q, Zhou H, Peng Y, Li J, Lin Z (2012) Aberrant microRNA expression in human cervical carcinomas. Med Oncol 29:1242–1248
Cheung TH, Man KN, Yu MY, Yim SF, Siu NS, Lo KW, Doran G, Wong RR, Wang VW, Smith DI, Worley MJ, Berkowitz RS, Chung TK, Wong YF (2012) Dysregulated microRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cervical neoplasm. Cell Cycle 11:2876–2884
Huang L, Lin JX, Yu YH, Zhang MY, Wang HY, Zheng M (2012) Downregulation of six microRNAs is associated with advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in small cell carcinoma of the cervix. PLoS One 7:e33762
Pereira PM, Marques JP, Soares AR, Carreto L, Santos MA (2010) MicroRNA expression variability in human cervical tissues. PLoS One 5:e11780
Venkataraman S, Birks DK, Balakrishnan I, Alimova I, Harris PS, Patel PR, Handler MH, Dubuc A, Taylor MD, Foreman NK, Vibhakar R (2013) MicroRNA 218 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting multiple cancer phenotype-associated genes in medulloblastoma. J Biol Chem 288:1918–1928
Davidson MR, Larsen JE, Yang IA, Hayward NK, Clarke BE, Duhig EE, Passmore LH, Bowman RV, Fong KM (2010) MicroRNA-218 is deleted and downregulated in lung squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 5:e12560
Gao C, Zhang Z, Liu W, Xiao S, Gu W, Lu H (2010) Reduced microRNA-218 expression is associated with high nuclear factor kappa B activation in gastric cancer. Cancer 116:41–49
Martinez I, Gardiner AS, Board KF, Monzon FA, Edwards RP, Khan SA (2008) Human papillomavirus type 16 reduces the expression of microRNA-218 in cervical carcinoma cells. Oncogene 27:2575–2582
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS, Meyers C, Zheng ZM (2008) Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS One 3:e2557
Li Y, Liu J, Yuan C, Cui B, Zou X, Qiao Y (2010) High-risk human papillomavirus reduces the expression of microRNA-218 in women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Int Med Res 38:1730–1736
Tu HF, Lin SC, Chang KW (2013) MicroRNA aberrances in head and neck cancer: pathogenetic and clinical significance. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21:104–111
Qin X, Yan L, Zhao X, Li C, Fu Y (2012) microRNA-21 overexpression contributes to cell proliferation by targeting PTEN in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett 4:1290–1296
Vosa U, Vooder T, Kolde R, Vilo J, Metspalu A, Annilo T (2013) Meta-analysis of microRNA expression in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 132:2884–2893
Lui WO, Pourmand N, Patterson BK, Fire A (2007) Patterns of known and novel small RNAs in human cervical cancer. Cancer Res 67:6031–6043
Deftereos G, Corrie SR, Feng Q, Morihara J, Stern J, Hawes SE, Kiviat NB (2011) Expression of mir-21 and mir-143 in cervical specimens ranging from histologically normal through to invasive cervical cancer. PLoS One 6:e28423
Gocze K, Gombos K, Juhasz K, Kovacs K, Kajtar B, Benczik M, Gocze P, Patczai B, Arany I, Ember I (2013) Unique microRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer. Anticancer Res 33:2561–2567
Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Nohata N, Kikkawa N, Enokida H, Yoshino H, Yamasaki T, Hidaka H, Nakagawa M, Okamoto Y, Seki N (2012) Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting laminin-332 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 3:1386–1400
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, Wu K, Liu J, Sun S, Guo X, Wang B, Gang Y, Zhang Y, Li Q, Qiao T, Zhao Q, Nie Y, Fan D (2010) MiR-218 inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor. PLoS Genet 6:e1000879
Alajez NM, Lenarduzzi M, Ito E, Hui AB, Shi W, Bruce J, Yue S, Huang SH, Xu W, Waldron J, O’Sullivan B, Liu FF (2011) MiR-218 suppresses nasopharyngeal cancer progression through downregulation of survivin and the SLIT2-ROBO1 pathway. Cancer Res 71:2381–2391
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J, Wang ZX (2013) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem 372:35–45
Chusorn P, Namwat N, Loilome W, Techasen A, Pairojkul C, Khuntikeo N, Dechakhamphu A, Talabnin C, Chan-On W, Ong CK, Teh BT, Yongvanit P (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-21 regulating PDCD4 during tumorigenesis of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma contributes to tumor growth and metastasis. Tumour Biol 34:1579–1588
Yao Q, Xu H, Zhang QQ, Zhou H, Qu LH (2009) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation and down-regulates the expression of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:539–542
Yamamoto N, Kinoshita T, Nohata N, Itesako T, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Shozu M, Seki N (2013) Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting focal adhesion pathways in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 42:1523–1532
Li J, Ping Z, Ning H (2012) MiR-218 impairs tumor growth and increases chemo-sensitivity to cisplatin in cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci 13:16053–16064
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81060219) and Natural Science Fundation of Guangxi (No. 2014GXNSFAA118266)
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Kangkang Zeng and Wenjing Zheng have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, K., Zheng, W., Mo, X. et al. Dysregulated microRNAs involved in the progression of cervical neoplasm. Arch Gynecol Obstet 292, 905–913 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3702-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3702-5