Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effects of miR-1246 on proliferation, invasion, and migration in the human (CSCC) cell line SiHa.
Methods
SiHa cells were assigned into three groups: miR-1246 analog; miR-1246 antagonist; and control. The MTT, transwell, and wound healing assays were performed to evaluate the proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities of SiHa cells, respectively. Western blot was carried out to detect protein expression of thrombospondin-2 (THBS2) before and after transfection with miR-1246 analog, antagonist, or control. In addition, a THBS2 3′-UTR-containing dual luciferase plasmid was generated and co-transfected with miR-1246, the inhibitor, or non-specific miRNA, into SiHa cells to observe its effects on THBS2-driven luciferase enzyme activity.
Results
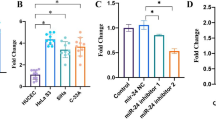
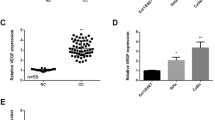
MTT, transwell, and wound healing assays revealed that proliferation, migration, and invasion were all significantly enhanced (P < 0.01) in SiHa cells transfected with miR-1246 analog, but were suppressed in those transfected with the miR-1246 antagonist. Western blot data showed that miR-1246 analog-transfected SiHa cells had significantly decreased THBS2 expression when compared with control-transfected cells (gray value = 6.28 ± 10.22 vs. 9.58 ± 17.58; P = 0.013) while those transfected with the miR-1246 antagonist had significantly increased THBS2 expression (gray value = 12.90 ± 19.81; P = 0.037). Moreover, SiHa cells co-transfected with miR-1246 and the THBS2 3′-UTR-containing plasmid exhibited decreased luciferase enzyme activity compared with the control.
Conclusion
MiR-1246 induced CSCC SiHa cell proliferation, invasion and migration. Preliminary evidence suggests that miR-1246 might promote CSCC tumorigenesis and progression by the suppression of its target gene THBS2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Medina PP, Nolde M, Slack FJ (2010) OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 467:86–90
Pigati L, Yaddanapudi SC, Iyengar R, Kim DJ, Hearn SA, Danforth D, Hastings ML, Duelli DM (2010) Selective release of microRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One 5:e13515
Gillen AE, Gosalia N, Leir SH, Harris A (2011) MicroRNA regulation of expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Biochem J 438:25–32
Zhang Y, Liao JM, Zeng SX, Lu H (2011) p53 downregulates Down syndrome-associated DYRK1A through miR-1246. EMBO Rep 12:811–817
Jaiswal R, Luk F, Gong J, Mathys JM, Grau GE, Bebawy M (2012) Microparticle conferred microRNA profiles––implications in the transfer and dominance of cancer traits. Mol Cancer 11:37
Jones CI, Zabolotskaya MV, King AJ, Stewart HJ, Horne GA, Chevassut TJ, Newbury SF (2012) Identification of circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for use in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer 107:1987–1996
Liao JM, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Lu H (2012) MiR-1246: a new link of the p53 family with cancer and Down syndrome. Cell Cycle 11:2624–2630
Piepoli A, Tavano F, Copetti M, Mazza T, Palumbo O, Panza A, di MFF, Pazienza V, Mazzoccoli G, Biscaglia G, Gentile A, Mastrodonato N, Carella M, Pellegrini F, di SP, Andriulli A (2012) Mirna expression profiles identify drivers in colorectal and pancreatic cancers. PLOS One 7:e33663
Chen J, Yao D, Li Y, Chen H, He C, Ding N, Lu Y, Ou T, Zhao S, Li L, Long F (2013) Serum microRNA expression levels can predict lymph node metastasis in patients with early-stage cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med 32:557–567
Morin RD, O’Connor MD, Griffith M, Kuchenbauer F, Delaney A, Prabhu AL, Zhao Y, McDonald H, Zeng T, Hirst M, Eaves CJ, Marra MA (2008) Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res 18:610–621
Baraniskin A, Nopel-Dunnebacke S, Ahrens M, Jensen SG, Zollner H, Maghnouj A, Wos A, Mayerle J, Munding J, Kost D, Reinacher-Schick A, Liffers S, Schroers R, Chromik AM, Meyer HE, Uhl W, Klein-Scory S, Weiss FU, Stephan C, Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Lerch MM, Tannapfel A, Schmiegel W, Andersen CL, Hahn SA (2013) Circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 132:E48–E57
Baek KH, Zaslavsky A, Lynch RC, Britt C, Okada Y, Siarey RJ, Lensch MW, Park IH, Yoon SS, Minami T, Korenberg JR, Folkman J, Daley GQ, Aird WC, Galdzicki Z, Ryeom S (2009) Down’s syndrome suppression of tumour growth and the role of the calcineurin inhibitor DSCR1. Nature 459:1126–1130
Takeshita N, Hoshino I, Mori M, Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Yoneyama Y, Ikeda N, Isozaki Y, Maruyama T, Akanuma N, Komatsu A, Jitsukawa M, Matsubara H (2013) Serum microRNA expression profile: miR-1246 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 108:644–652
Czekierdowski A, Czekierdowska S, Danilos J, Czuba B, Sodowski K, Sodowska H, Szymanski M, Kotarski J (2008) Microvessel density and CpG island methylation of the THBS2 gene in malignant ovarian tumors. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 4):53–65
Hirose Y, Chiba K, Karasugi T, Nakajima M, Kawaguchi Y, Mikami Y, Furuichi T, Mio F, Miyake A, Miyamoto T, Ozaki K, Takahashi A, Mizuta H, Kubo T, Kimura T, Tanaka T, Toyama Y, Ikegawa S (2008) A functional polymorphism in THBS2 that affects alternative splicing and MMP binding is associated with lumbar-disc herniation. Am J Hum Genet 82:1122–1129
Kim H, Watkinson J, Varadan V, Anastassiou D (2010) Multi-cancer computational analysis reveals invasion-associated variant of desmoplastic reaction involving INHBA, THBS2 and COL11A1. BMC Med Genomics 3:51
Wang Y, Fu W, Xie F, Wang Y, Chu X, Wang H, Shen M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Sun W, Lei R, Yang L, Wu H, Foo J, Liu J, Jin L, Huang W (2010) Common polymorphisms in ITGA2, PON1 and THBS2 are associated with coronary atherosclerosis in a candidate gene association study of the Chinese Han population. J Hum Genet 55:490–494
Muth CA, Steinl C, Klein G, Lee-Thedieck C (2013) Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell behavior by the nanostructured presentation of extracellular matrix components. PLoS One 8:e54778
Yang Z, Kyriakides TR, Bornstein P (2000) Matricellular proteins as modulators of cell-matrix interactions: adhesive defect in thrombospondin 2-null fibroblasts is a consequence of increased levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol Biol Cell 11:3353–3364
Rodder S, Scherer A, Korner M, Eisenberger U, Hertig A, Raulf F, Rondeau E, Marti HP (2010) Meta-analyses qualify metzincins and related genes as acute rejection markers in renal transplant patients. Am J Transplant 10:286–297
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China (2011GXNSFA018184, 2013GXNSFBA019130, 2013GXNSFBA019132. www.gxsti.net), and the Public Health self-financing project research project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Z2012071).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Yao, D., Zhao, S. et al. MiR-1246 promotes SiHa cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through suppression of its target gene thrombospondin 2. Arch Gynecol Obstet 290, 725–732 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3260-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3260-2