Abstract
Purpose
Women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus (pGDM) are at high risk for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disorders. In this study, we aimed to compare plasma apelin levels between women with and without pGDM, and to investigate the possible association of apelin with cardiometabolic risk factors.
Methods
Among 252 consecutive Caucasian women with GDM being included in a prospective postpartum follow-up protocol, 141 women eligible for the study protocol were enrolled. Control group consisted of 49 age- and body mass index-matched healthy women without pGDM. Circulating apelin, IL-6 and plasminogen activator inhibitor levels, and carotid intima media thickness (IMT) were measured. To evaluate carbohydrate intolerance, 75-g oral glucose tolerance test was performed. Fasting insulin and lipids were measured, and homeostasis model assessment index was calculated.
Results
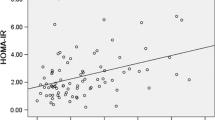
Plasma apelin levels were reduced in women with pGDM (p < 0.001). In multiple regression analysis, apelin was negatively associated with fasting (r 2 0.090, β −0.273, p = 0.001) and post-load glucose (r 2 0.061, β −0.187, p = 0.022), serum IL-6 (r 2 0.082, β −0.234, p = 0.002), and carotid IMT (r 2 0.057, β −0.168, p = 0.033).
Conclusions
Our results suggested that suppressed apelin levels were associated with increased cardiovascular risk in women with pGDM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara A (2007) Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus: a public health perspective. Diabetes Care 30(Suppl 2):S141–S146
Blank A, Grave GD, Metzger BE (1995) Effects of gestational diabetes on perinatal morbidity reassessed. Report of the International Workshop on Adverse Perinatal Outcomes of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, December 3–4, 1992. Diabetes Care 18(1):127–129
American Diabetes Association (2012) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1):S64–S71
Gonzalez-Quintero VH, Istwan NB, Rhea DJ et al (2007) The impact of glycemic control on neonatal outcome in singleton pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes. Diabetes Care 30(3):467–470
Yogev Y, Xenakis EM, Langer O (2004) The association between preeclampsia and the severity of gestational diabetes: the impact of glycemic control. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191(5):1655–1660
Bentley-Lewis R (2009) Late cardiovascular consequences of gestational diabetes mellitus. Semin Reprod Med 27(4):322–329
Versari D, Daghini E, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Taddei S (2009) Endothelial dysfunction as a target for prevention of cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 32(Suppl 2):S314–S321
Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE (1997) Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation 96(5):1432–1437
Brohall G, Oden A, Fagerberg B (2006) Carotid artery intima-media thickness in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance: a systematic review. Diabet Med 23(6):609–616
Bo S, Valpreda S, Menato G et al (2007) Should we consider gestational diabetes a vascular risk factor? Atherosclerosis 194(2):e72–e79
Akinci B, Celtik A, Genc S et al (2011) Evaluation of postpartum carbohydrate intolerance and cardiovascular risk factors in women with gestational diabetes. Gynecol Endocrinol 27(5):361–367
Falcao-Pires I, Leite-Moreira AF (2005) Apelin: a novel neurohumoral modulator of the cardiovascular system. Pathophysiologic importance and potential use as a therapeutic target. Rev Port Cardiol 24(10):1263–1276
Grisk O (2007) Apelin and vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Res 74(3):339–340
Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP (2005) Emerging roles of apelin in biology and medicine. Pharmacol Ther 107(2):198–211
Coustan DR, Carpenter MW (1985) Detection and treatment of gestational diabetes. Clin Obstet Gynecol 28(3):507–515
Aydin S (2010) The presence of the peptides apelin, ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in the human breast milk, and the lowering of their levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 31(12):2236–2240
Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y et al (2004) Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure in vivo. J Biol Chem 279(25):26274–26279
Chandrasekaran B, Dar O, McDonagh T (2008) The role of apelin in cardiovascular function and heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 10(8):725–732
Tatemoto K, Takayama K, Zou MX et al (2001) The novel peptide apelin lowers blood pressure via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Regul Pept 99(2–3):87–92
Chun HJ, Ali ZA, Kojima Y et al (2008) Apelin signaling antagonizes Ang II effects in mouse models of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 118(10):3343–3354
Tao J, Zhu W, Li Y et al (2011) Apelin-13 protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of ER-dependent apoptotic pathways in a time-dependent fashion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(4):H1471–H1486
Li Z, Bai Y, Hu J (2008) Reduced apelin levels in stable angina. Intern Med 47(22):1951–1955
Malyszko J, Malyszko JS, Pawlak K, Wolczynski S, Mysliwiec M (2008) Apelin, a novel adipocytokine, in relation to endothelial function and inflammation in kidney allograft recipients. Transplant Proc 40(10):3466–3469
Tasci I, Dogru T, Naharci I et al (2007) Plasma apelin is lower in patients with elevated LDL-cholesterol. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 115(7):428–432
Tasci I, Erdem G, Ozgur G et al (2009) LDL-cholesterol lowering increases plasma apelin in isolated hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 204(1):222–228
Rittig K, Hildebrandt U, Thamer C et al (2011) Apelin serum levels are not associated with early atherosclerosis or fat distribution in young subjects with increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 119(6):358–361
Graham I, Atar D, Borch-Johnsen K et al (2007) European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: full text. Fourth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts). Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 14(Suppl 2):S1–S113
Tasci I (2011) Apelin, prediabetes and atherosclerosis. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 119(8):457–458
Erdem G, Dogru T, Tasci I, Sonmez A, Tapan S (2008) Low plasma apelin levels in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 116(5):289–292
Zhang Y, Shen C, Li X et al (2009) Low plasma apelin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in Chinese people. Diabetes Care 32(12):e150
Zhong JC, Yu XY, Huang Y, Yung LM, Lau CW, Lin SG (2007) Apelin modulates aortic vascular tone via endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation pathway in diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Res 74(3):388–395
Telejko B, Kuzmicki M, Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek N et al (2010) Plasma apelin levels and apelin/APJ mRNA expression in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87(2):176–183
Castan-Laurell I, Dray C, Attane C, Duparc T, Knauf C, Valet P (2011) Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine 40(1):1–9
Boucher J, Masri B, Daviaud D et al (2005) Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 146(4):1764–1771
Rayalam S, Della-Fera MA, Krieg PA, Cox CM, Robins A, Baile CA (2008) A putative role for apelin in the etiology of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368(3):815–819
Castan-Laurell I, Vitkova M, Daviaud D et al (2008) Effect of hypocaloric diet-induced weight loss in obese women on plasma apelin and adipose tissue expression of apelin and APJ. Eur J Endocrinol 158(6):905–910
Heinonen MV, Laaksonen DE, Karhu T et al (2009) Effect of diet-induced weight loss on plasma apelin and cytokine levels in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 19(9):626–633
Chang CY, Tsai YC, Lee CH, Chan TF, Wang SH, Su JH (2011) Lower serum apelin levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril 95(8):2520–2523
Metzger BE, Gabbe SG, Persson B et al (2010) International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 33(3):676–682
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akinci, B., Celtik, A., Tunali, S. et al. Circulating apelin levels are associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in women with previous gestational diabetes. Arch Gynecol Obstet 289, 787–793 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-3070-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-3070-y