Abstract
Purpose
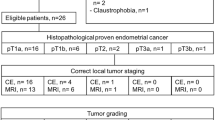
The aim of this study was to evaluate the staging accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with an endorectal surface coil on patients with endometrial cancer compared to results obtained using the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classification and histopathology.
Methods
In this prospective study, patients with biopsy-proven endometrial cancer were staged clinically using the FIGO classification before undergoing 1.5 T MRI with an endorectal surface coil (eMRI). The staging results from the FIGO classification and from eMRI were compared with the histopathological results after surgery. Furthermore, each patient was given a questionnaire designed by the authors to evaluate the patients’ opinions on eMRI. The responses were examined using the methods of descriptive analysis.
Results
A total of 33 consecutive patients were recruited and clinically staged before undergoing eMRI. Subsequently, 21 patients underwent primary surgery and 12 patients primary radiochemotherapy. The FIGO stages were identical to the histopathological results in 17 (81 %) cases, and those of eMRI were identical in 15 (71 %). In 13 (62 %) cases, FIGO and eMRI staged identically. In 12 (57 %) of the 21 cases, all three staging modalities diagnosed the same tumor stage. eMRI overstaged the tumor in four patients and understaged it in two. All T1a tumors were staged correctly by eMRI. Eighteen patients answered the questionnaire, of whom 11 (61 %) patients stated that their experience with eMRI was overall positive.
Conclusions
It seems feasible in principle to employ eMRI for diagnosing patients with endometrial cancer stage T1a. Yet, the results of eMRI for our study population were not better than the results obtained using the FIGO classification or than those from using MRI without an endorectal surface coil. eMRI thus does not meet the expectations based on its use in other pelvic tumor entities.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CE:
-
Clinical examination
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- eMRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging using an endorectal surface coil
- ESC:
-
Endorectal surface coil
- FIGO:
-
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
- FOV:
-
Field of view
References
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Neyman N, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds) (2013) SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2010. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2010/
Garcia M, Jemal A, Ward EM, Center MM, Hao Y et al (2007) Global cancer facts and figures 2007. Atlanta, GA
Baekelandt MM, Castiglione M (2009) Endometrial carcinoma: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 20(Suppl 4):29–31. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp120
Waldmann A, Eisemann N, Katalinic A (2013) Epidemiology of malignant cervical, corpus uteri and ovarian tumours—current data and epidemiological trends. Geburtsh Frauenheilk 73(2):123–129. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1328266
Horner MJ, Ries LAG, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Howlader N, Altekruse SF, Feuer EJ, Huang L, Mariotto A, Miller BA, Lewis DR, Eisner MP, Stinchcomb DG, Edwards BK (eds) (2009) SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2006. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2006/
Chaudhry S, Reinhold C, Guermazi A, Khalili I, Maheshwari S (2003) Benign and malignant diseases of the endometrium. Top Magn Reson Imaging 14(4):339–357
Peungjesada S, Bhosale PR, Balachandran A, Iyer RB (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging of endometrial carcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33(4):601–608. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e31818d427900004728-200907000-00023
Beddy P, O’Neill AC, Yamamoto AK, Addley HC, Reinhold C et al (2012) FIGO staging system for endometrial cancer: added benefits of MR imaging. Radiographics 32(1):241–254. doi:32/1/24110.1148/rg.321115045
Alt CD, Brocker KA, Eichbaum M, Sohn C, Kopp-Schneider A et al (2012) Accuracy of MRI with an endorectal coil for staging endometrial cancer. Acta Radiol 53(5):580–585. doi:ar.2012.11061710.1258/ar.2012.110617
Frei Bonel KA, K K (2007) Endometrial carcinoma. In: Bernd Hamm RF, Ernst Beindner (ed) MRI and CT of the female pelvis. Springer Verlag
Delahanty RJ, Xiang YB, Spurdle A, Beeghly-Fadiel A, Long J et al (2013) Polymorphisms in inflammation pathway genes and endometrial cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 22(2):216–223. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0903
Long J, Zheng W, Xiang YB, Lose F, Thompson D et al (2012) Genome-wide association study identifies a possible susceptibility locus for endometrial cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21(6):980–987. doi:1055-9965.EPI-11-116010.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-1160
Lurie G, Gaudet MM, Spurdle AB, Carney ME, Wilkens LR et al (2011) The obesity-associated polymorphisms FTO rs9939609 and MC4R rs17782313 and endometrial cancer risk in non-Hispanic white women. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16756. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016756
Spurdle AB, Thompson DJ, Ahmed S, Ferguson K, Healey CS et al (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies a common variant associated with risk of endometrial cancer. Nat Genet 43(5):451–454. doi:ng.81210.1038/ng.812
Hornemann AFD, Diedrich K, Altgassen C (2007) Operative therapie des endometriumkarzinoms. Gynäkologe 40(1):21–26
Koyama T, Tamai K, Togashi K (2007) Staging of carcinoma of the uterine cervix and endometrium. Eur Radiol 17(8):2009–2019. doi:10.1007/s00330-006-0555-0
Emons G, Kimmig R (2009) Interdisciplinary S2 k guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of endometrial carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135(10):1387–1391. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0581-9
Lien HH, Blomlie V, Trope C, Kaern J, Abeler VM (1991) Cancer of the endometrium: value of MR imaging in determining depth of invasion into the myometrium. AJR 157(6):1221–1223
Hricak H, Rubinstein LV, Gherman GM, Karstaedt N (1991) MR imaging evaluation of endometrial carcinoma: results of an NCI cooperative study. Radiology 179(3):829–832
Hirano Y, Kubo K, Hirai Y, Okada S, Yamada K et al (1992) Preliminary experience with gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging for uterine neoplasms. Radiographics 12(2):243–256
Sauer GHD, Kurzeder C, Bäuerle M, Jäger C, Kreienberg R (2007) Diagnostische verfahren beim endometriumkarzinom. Gynäkologe 40(1):14–20
Rockall AG, Meroni R, Sohaib SA, Reynolds K, Alexander-Sefre F et al (2007) Evaluation of endometrial carcinoma on magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17(1):188–196. doi:IJG80510.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.00805.x
Chung HH, Kang SB, Cho JY, Kim JW, Park NH et al (2007) Accuracy of MR imaging for the prediction of myometrial invasion of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 104(3):654–659. doi:S0090-8258(06)00803-110.1016/j.ygyno.2006.10.007
Ortashi O, Jain S, Emannuel O, Henry R, Wood A et al (2008) Evaluation of the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging for staging endometrial cancer. A prospective study of 100 cases at the Dorset Cancer Centre. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 137(2):232–235. doi:S0301-2115(07)00186-810.1016/j.ejogrb.2007.02.029
Messiou C, Spencer JA, Swift SE (2006) MR staging of endometrial carcinoma. Clin Radiol 61(10):822–832. doi:S0009-9260(06)00168-110.1016/j.crad.2006.05.008
Barwick TD, Rockall AG, Barton DP, Sohaib SA (2006) Imaging of endometrial adenocarcinoma. Clin Radiol 61(7):545–555. doi:S0009-9260(06)00099-710.1016/j.crad.2006.03.011
Manfredi R, Gui B, Maresca G, Fanfani F, Bonomo L (2005) Endometrial cancer: magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 30(5):626–636. doi:10.1007/s00261-004-0298-9
Tamai K, Koyama T, Saga T, Umeoka S, Mikami Y et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of uterine endometrial cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(3):682–687. doi:10.1002/jmri.20997
Beddy P, Moyle P, Kataoka M, Yamamoto AK, Joubert I et al (2011) Evaluation of depth of myometrial invasion and overall staging in endometrial cancer: comparison of diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 262(2):530–537. doi:radiol.1111098410.1148/radiol.11110984
Gualdi GF, Casciani E, Guadalaxara A, d’Orta C, Polettini E et al (2000) Local staging of rectal cancer with transrectal ultrasound and endorectal magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with histologic findings. Dis Colon Rectum 43(3):338–345
Vogl TJ, Pegios W, Hunerbein M, Mack MG, Schlag PM et al (1998) Use and applications of MRI techniques in the diagnosis and staging of rectal lesions. Recent Results Cancer Res 146:35–47
Kim MJ, Chung JJ, Lee YH, Lee JT, Yoo HS (1997) Comparison of the use of the transrectal surface coil and the pelvic phased-array coil in MR imaging for preoperative evaluation of uterine cervical carcinoma. AJR 168(5):1215–1221
Kaji Y, Sugimura K, Kitao M, Ishida T (1994) Histopathology of uterine cervical carcinoma: diagnostic comparison of endorectal surface coil and standard body coil MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18(5):785–792
Milestone BN, Schnall MD, Lenkinski RE, Kressel HY (1991) Cervical carcinoma: MR imaging with an endorectal surface coil. Radiology 180(1):91–95
Preidler KW, Tamussino K, Szolar DM, Ranner G, Ebner F (1996) Staging of cervical carcinomas. Comparison of body-coil magnetic resonance imaging and endorectal surface coil magnetic resonance imaging with histopathologic correlation. Invest Radiol 31(7):458–462
Schnall MD, Imai Y, Tomaszewski J, Pollack HM, Lenkinski RE et al (1991) Prostate cancer: local staging with endorectal surface coil MR imaging. Radiology 178(3):797–802
Chelsky MJ, Schnall MD, Seidmon EJ, Pollack HM (1993) Use of endorectal surface coil magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer. J Urol 150(2 Pt 1):391–395
Kinkel K, Forstner R, Danza FM, Oleaga L, Cunha TM et al (2009) Staging of endometrial cancer with MRI: guidelines of the European Society of Urogenital Imaging. Eur Radiol 19(7):1565–1574. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1309-6
Pecorelli S (2009) Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and endometrium. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 105(2):103–104
Frei Bonel KA, KK (2007) Endometrial carcinoma. In: Beindner Ernst, Bernd Hamm RF (eds) MRI and CT of the Female Pelvis. Springer, Berlin, Germany
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2009) TNM classification of malignant tumours, vol 7. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ, USA
Masterson TA, Touijer K (2008) The role of endorectal coil MRI in preoperative staging and decision-making for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. MAGMA 21(6):371–377. doi:10.1007/s10334-008-0116-4
Manfredi R, Mirk P, Maresca G, Margariti PA, Testa A et al (2004) Local-regional staging of endometrial carcinoma: role of MR imaging in surgical planning. Radiology 231(2):372–378. doi:10.1148/radiol23120211842312021184
Nakao Y, Yokoyama M, Hara K, Koyamatsu Y, Yasunaga M et al (2006) MR imaging in endometrial carcinoma as a diagnostic tool for the absence of myometrial invasion. Gynecol Oncol 102(2):343–347. doi:S0090-8258(06)00020-510.1016/j.ygyno.2005.12.028
Rieck GC, Bulman J, Whitaker R, Leeson SC (2005) A retrospective review of magnetic resonance imaging in assessing the extent of myometrial infiltration for patients with endometrial carcinoma. J Obstet Gynaecol 25(8):765–768. doi:V770G62KW036335310.1080/01443610500327951
Savelli L, Ceccarini M, Ludovisi M, Fruscella E, De Iaco PA et al (2008) Preoperative local staging of endometrial cancer: transvaginal sonography vs. magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 31(5):560–566. doi:10.1002/uog.5295
Suh DS, Kim JK, Kim KR, Kim DY, Kim JH et al (2009) Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging in assessing myometrial invasion absence in endometrial carcinoma. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 88(9):990–993. doi:91343986010.1080/00016340903141135
Tong T, Yajia G, Huaying W, Weijun P (2011) Application of 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging in endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. doi:10.1007/s00404-011-2053-0
Vasconcelos C, Felix A, Cunha TM (2007) Preoperative assessment of deep myometrial and cervical invasion in endometrial carcinoma: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and histopathologic evaluation. J Obstet Gynaecol 27(1):65–70. doi:77038510410.1080/01443610601056418
Cunha TM, Felix A, Cabral I (2001) Preoperative assessment of deep myometrial and cervical invasion in endometrial carcinoma: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and gross visual inspection. Int J Gynecol Cancer 11(2):130–136. doi:ijg01004
Pakkal MV, Rudralingam V, McCluggage WG, Kelly BE (2004) MR staging in carcinoma of the endometrium and carcinoma of the cervix. Ulster Med J 73(1):20–24
Shin KE, Park BK, Kim CK, Bae DS, Song SY et al (2011) MR staging accuracy for endometrial cancer based on the new FIGO stage. Acta Radiol 52(7):818–824. doi:ar.2011.10042610.1258/ar.2011.100426
Emons G, Hellriegel M, Hawighorst T (2009) Modern therapy concepts for endometrial cancer. Pathologe 30(4):268–273. doi:10.1007/s00292-009-1149-9
Acknowledgments
KAB received a scholarship of the Medical Faculty of the University of Heidelberg to complete this work.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brocker, K.A., Alt, C.D., Breyer, U. et al. Endometrial cancer: results of clinical and histopathological staging compared to magnetic resonance imaging using an endorectal surface coil. Arch Gynecol Obstet 289, 851–858 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-3061-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-3061-z