Abstract
Background
A retrospective analysis of the records of all the patients of pulmonary arterial hypertension with pregnancy at AIIMS, New Delhi, India, to study maternal and perinatal outcome and to compare outcome between severe and mild pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Materials and methods
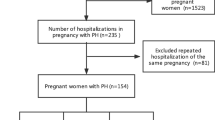
A retrospective analysis was carried out of 30 pregnancies in women with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) who delivered at ≥28 weeks of gestation from July 2006 through July 2012 at a tertiary care center in India. Pulmonary artery blood pressure (PABP) during the first trimester of pregnancy or before pregnancy was considered to define PABP as severe or mild, with severe cases having systolic PABP >50 mmHg on echocardiography.
Results
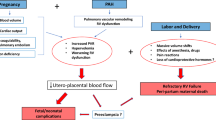
Out of 30 patients, 14 patients had severe PAH and 16 patients had mild PAH. Women with severe PAH had a significantly higher incidence of preterm delivery (11 vs. 3, P < 0.05), small for gestational age infants (10 vs. 2, P < 0.05) and cardiac complications (6 vs. 1, P < 0.05) compared to women with mild PAH. There was maternal mortality in a patient with Eisenmenger syndrome. In women with severe PAH and mild PAH, PABP increased in later pregnancy from 63.14 ± 7.6 to 71.57 ± 7.9 mmHg (P < 0.05) and from 40.37 ± 3.6 to 41.69 ± 4.1 mmHg (P < 0.05), respectively.
Conclusions
Pregnancy in women with severe PAH is associated with higher maternal morbidity and adverse fetal outcome compared to pregnancy in women with mild PAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badesch DB, Champion HC, Sanchez Gomez, Hoeper MM, Loyd JE, Manes A (2009) Diagnosis and assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:S55–S66
McGoon MD, Kane GC (2009) Pulmonary hypertension: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc 84:191–207
Duffels MG, Engelfriet PM, Berger RM, Van loon RL, Hoendermis ES et al (2007) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease: an epidemiologic perspective from a Dutch registry. Int J Cardiol 120:198–204
Katsuragi S, Yamanaka K, Neki R, Kamiya C, Sasaki Y, Osato K (2012) Maternal outcome in pregnancy complicated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ J 76:2249–2254
Weiss BM, Zemp L, Seifert B, Hess OM (1998) Outcome of pulmonary vascular disease in pregnancy: a systematic overview from 1978 through 1996. J Am Coll Cardiol 31:1650–1657
Curry R, Swan L, Steer PJ (2009) Cardiac disease in pregnancy. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 21:508–513
Benza RL, Miller DP, Gomberg-Maitland M, Frantz RP, Foreman AJ, Coffey CS (2010) Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights from the registry to evaluate early and long-term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management (REVEAL). Circulation 122:164–172
Bedard E, Dimopoulos K, Gatzoulis MA (2009) Has there been any progress made on pregnancy outcomes among women with pulmonary arterial hypertension? Eur Heart J 30:256–265
Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA (2009) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European society of cardiology (ESC) and the European respiratory society (ERS). Eur Heart J 30:2493–2537
Bonnin M, Mercier FJ, Sitbo O, Roger Christoph S, Jais X, Humbert M (2005) Severe pulmonary hypertension during pregnancy: mode of delivery and anesthetic management of 15 consecutive cases. Anesthesiology 102:1133–1137
Curry R, Fletcher C, Gelson E, Gatzoulis M, Woolnough M, Richards N (2012) Pulmonary hypertension and pregnancy-a review of 12 pregnancies in nine women. BJOG 119:752–761
Tacoy G, Ekim NN, Cengel A (2010) Dramatic response of a patient with pregnancy induced idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension to sildenafil treatment. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 36:414–417
Goland S, Tsai F, Habib M, Janmohamed M, Goodwin TM, Elkayam U (2010) Favorable outcome of pregnancy with an elective use of epoprostenol and sildenafil in women with severe pulmonary hypertension. Cardiology 115:205–208
Smedstad KG, Cramb R, Morison DH (1994) Pulmonary hypertension and pregnancy. A series of 8 cases. Canad J Anaesth 41:502–512
Yentis SM, Steer PJ, Plaat F (1998) Eisenmenger’s syndrome in pregnancy: maternal and fetal mortality in the 1990 s. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 105:921–922
Lin JH, Zhoa WX, Su Y, Shi J, Jiang GJ, Wu ZM (2006) Perinatal management and pregnancy outcome in pregnant women with pulmonary hypertension complicating cardiac disease. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 41:99–102
Fisher MR, Forfia PR, Chamera E, Housten-Harris T, Champion HC, Girgis RE, Corretti MC, Hassoun PM (2009) Accuracy of Doppler echocardiography in the hemodynamic assessment of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 179:615–621
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subbaiah, M., Kumar, S., Roy, K.K. et al. Pregnancy outcome in women with pulmonary arterial hypertension: single-center experience from India. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288, 305–309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-2761-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-2761-8