Abstract
Aims
The purpose of this study is to investigate the association between proliferation inhibition of cisplatin and aquaporin 5 (AQP5) expression and its regulation in ovarian carcinoma cell CAOV3.
Methods
Cell growth rate was measured by MTT after CAOV3 cells were incubated with cisplatin or NF-κB inhibitor PDTC. Western blot and RT-PCR were used to detect the expression of AQP5 and NF-κB p65.
Results
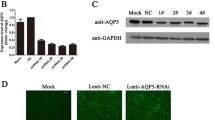
Our results showed that expression of AQP5, NF-κB in cytoplasm and karyon and IκBα in cytoplasm protein in CAOV3 cells can be induced to decrease by cisplatin with concentration-dependent manner, and there is a positive correlation between AQP5 protein and cell growth rate (r = 0.607, P < 0.05). When cells were incubated with 10 μg/ml cisplatin, AQP5, NF-κB p65, and IκBα increased rapidly at 6–12 h, but decreased at 24 h, remain on low level until to 72 h. Expression of AQP5 could be induced to decrease by PDTC, and a positive correlation between AQP5 protein expression and NF-κB p65 and IκBα (r = 0.894, 0.857; P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Proliferation inhibition of cisplatin is related with AQP5 expression, and NF-κB may be involved in mechanism of AQP5 regulation. AQP5 will be potential target for therapy of ovarian carcinoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS (2005) Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature 434:786–792
Hoque MO, Soria JC, Woo J, Lee T, Lee J, Jang SJ, Upadhyay S, Trink B, Monitto C, Desmaze C, Mao L, Sidransky D, Moon C (2006) Aquaporin 1 is overexpressed in lung cancer and stimulates NIH-3T3 cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. Am J Pathol 168:1345–1353
Krane CM, Melvin JE, Nguyen HV, Richardson L, Towne JE, Doetschman T, Menon AG (2001) Salivary acinar cells from aquaporin 5-deficient mice have decreased membrane water permeability and altered cell volume regulation. J Biol Chem 276:23413–23420
Gresz V, Kwon TH, Gong H, Agre P, Steward MC, King LS, Nielsen S (2004) Immunolocalization of AQP-5 in rat parotid and submandibular salivary glands after stimulation or inhibition of secretion in vivo. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G151–G161
Kreda SM, Gynn MC, Fenstermacher DA, Boucher RC, Gabriel SE (2001) Expression and localization of epithelial aquaporins in the adult human lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24:224–234
Burghardt B, Elkaer ML, Kwon TH, Rácz GZ, Varga G, Steward MC, Nielsen S (2003) Distribution of aquaporin water channels AQP1 and AQP5 in the ductal system of the human pancreas. Gut 52:1008–1016
Shen L, Zhu Z, Huang Y, Shu Y, Sun M, Xu H, Zhang G, Guo R, Wei W, Wu W (2010) Expression profile of multiple aquaporins in human gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Biomed Pharmacother 64(5):313–318
Zhang Z, Chen Z, Song Y, Zhang P, Hu J, Bai C (2010) Expression of aquaporin 5 increases proliferation and metastasis potential of lung cancer. J Pathol 221(2):210–220
Watanabe T, Fujii T, Oya T, Horikawa N, Tabuchi Y, Takahashi Y, Morii M, Takeguchi N, Tsukada K, Sakai H (2009) Involvement of aquaporin-5 in differentiation of human gastric cancer cells. J Physiol Sci 59(2):113–122
Yang JH, Shi YF, Cheng Q, Deng L (2006) Expression and localization of aquaporin-5 in the epithelial ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol 100(2):294–299
Sebens S, Arlt A, Schafer H (2008) NF-kappaB as a molecular target in therapy of pancreatic carcinoma. Recent Results Cancer Res 177:152–164
Monazani E, Shtil AA, La Porta CA (2007) The water channels, new druggable targets to combat cancer cell survival, invasiveness and metastasis. Curr Drug Targets 8(10):1132–1137
Xiang Y, Ma B, Li T, Gao JW, Yu HM, Li XJ (2004) Acetazolamide inhibits aquaporin-1 protein expression and angiogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(6):812–816
Nicchia GP, Frigeri A, Liuzzi GM, Svelto M (2003) Inhibition of aquaporin-4 expression in astrocytes by RNAi determines alteration in cell morphology, growth, and water transport and induces changes in ischemia-related genes. FASEB J 17(11):1508–1510
Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS (2008) Prevention of skin tumorigenesis and impairment of epidermal cell proliferation by targeted aquaporin-3 gene disruption. Mol Cell Biol 28:326–332
Kang SK, Chae YK, Woo J, Kim MS, Park JC, Lee J, Soria JC, Jang SJ, Sidransky D, Moon C (2008) Role of human aquaporin 5 in colorectal carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 173(2):518–525
Yao C, Purwanti N, Karabasil MR, Azlina A, Javkhlan P, Hasegawa T, Akamatsu T, Hosoi T, Ozawa K, Hosoi K (2010) Potential down-regulation of salivary gland AQP5 by LPS via cross-coupling of NF-{kappa}B and p-c-Jun/c-Fos. Am J Pathol 177(2):724–734
Ishibashi K, Kuwahara M, Gu Y, Tanaka Y, Marumo F, Sasaki S (1998) Cloning and functional expression of a new aquaporin (AQP9) abundantly expressed in the peripheral leukocytes permeable to water and urea, but not to glycerol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244(1):268–274
King LS, Nielsen S, Agre P (1997) Aquaporins in complex tissues. I. Developmental patterns in respiratory and glandular tissues of rat. Am J Physiol 273(5 Pt 1):C1541–C1548
Hernandez L, Hsu SC, Davidson B, Birrer MJ, Kohn EC, Annunziata CM (2010) Activation of NF-kappaB signaling by inhibitor of NF-kappaB kinase beta increases aggressiveness of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 70(10):4005–4014
Towne JE, Krane CM, Bachurski CJ, Menon AG (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits aquaporin 5 expression in mouse lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 276(22):18657–18664
Ito H, Yamamoto N, Arima H, Hirate H, Morishima T, Umenishi F, Tada T, Asai K, Katsuya H, Sobue K (2006) Interleukin-1beta induces the expression of aquaporin-4 through a nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 99(1):107–118
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 200904435047), and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant number: 20070335047).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Yan, C., Zheng, W. et al. Proliferation inhibition of cisplatin and aquaporin 5 expression in human ovarian cancer cell CAOV3. Arch Gynecol Obstet 285, 239–245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-011-1908-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-011-1908-8