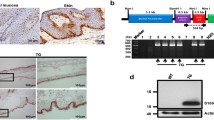
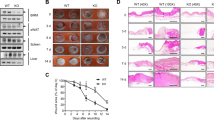
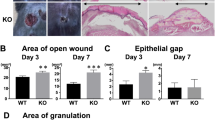
Abstract
We examined the effects of lacking tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) on the healing process of a cutaneous wound in mice using TNFα-deficient mice. A full-thickness circular cutaneous wound 5.0 mm in diameter was produced in the dorsal skin of wild-type (WT) or TNFα-null (KO) mice. After specific intervals of healing, the healing pattern was evaluated by macroscopic observation, histology, immunohistochemistry, or real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Effect of Smad7 gene transfer on the healing phenotype of KO mice was also examined. The results showed that loss of TNFα promotes granulation tissue formation and retards reepithelialization in a circular wound in mouse dorsal skin. Immunohistochemistry showed that distribution of macrophages and myofibroblasts in newly generated granulation tissue seemed similar between WT and KO mice. However, lacking TNFα enhanced mRNA expression of TGFβ1 and collagen Iα2 in such tissue. Smad7 gene transfer counteracted excess granulation tissue formation in KO mice. In conclusion, lacking TNFα potentiates Smad-mediated fibrogenic reaction in healing dermis and retards reepithelialization in a healing mouse cutaneous wound.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham DJ, Shiwen X, Black CM, Sa S, Xu Y, Leask A (2000) Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses the induction of connective tissue growth factor by transforming growth factor-beta in normal and scleroderma fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 275:15220–15225. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.20.15220
Ashcroft GS, Yang X, Glick AB, Weinstein M, Letterio JL, Mizel DE, Anzano M, Greenwell-Wild T, Wahl SM, Deng C, Roberts AB (1999) Mice lucking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat Cell Biol 1:260–266. doi:10.1038/12971
Campbell IK, O’Donnell K, Lawlor KE, Wicks IP (2001) Severe inflammatory arthritis and lymphadenopathy in the absence of TNF. J Clin Invest 107:1519–1527. doi:10.1172/JCI12724
Cohen BJ, Danon D, Roth GS (1987) Wound repair in mice as influenced by age and antimacrophage serum. J Gerontol 42:295–301
Desmoulière A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:103–111. doi:10.1083/jcb.122.1.103
Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Long-Fox A, Charles P, Katsikis P, Brennan FM, Walker J, Bijl H, Ghrayeb J et al (1993) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum 36:1681–1690. doi:10.1002/art.1780361206
Fujita M, Shannon JM, Morikawa O, Gauldie J, Hara N, Mason RJ (2003) Overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha diminishes pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin or transforming growth factor-beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:669–676. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2002-0046OC
Gabbiani G (2003) The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive disease. J Pathol 200:500–503. doi:10.1002/path.1427
Gabbiani G, Hirschel BJ, Ryan GB, Statkov PR, Majno G (1972) Granulation tissue as a contractile organ. A study of structure and function. J Exp Med 135:719–734. doi:10.1084/jem.135.4.719
Gallucci RM, Lee EG, Tomasek JJ (2006) IL-6 modulates alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in dermal fibroblasts from IL-6-deficient mice. J Invest Dermatol 126:561–568. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700109
Goldberg MT, Han YP, Yan C, Shaw MC, Garner WL (2007) TNF-alpha suppresses alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in human dermal fibroblasts: an implication for abnormal wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 127:2645–2655. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700890
Goren I, Müller E, Pfeilschifter J, Frank S (2006) Severely impaired insulin signaling in chronic wounds of diabetic ob/ob mice: a potential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Pathol 168:765–777. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.050293
Grinnell F (1994) Fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and wound contraction. J Cell Biol 124:401–404. doi:10.1083/jcb.124.4.401
Haisa M, Okochi H, Grotendorst GR (1994) Elevated levels of PDGF alpha receptors in keloid fibroblasts contribute to an enhanced response to PDGF. J Invest Dermatol 103:560–563. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12396856
Kumar S, Millis AJ, Baglioni C (1992) Expression of interleukin 1-inducible genes and production interleukin 1 by aging human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4683–4687. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4683
Kuroki M, Noguchi Y, Shimono M, Tomono K, Tashiro T, Obata Y, Nakayama E, Kohno S (2003) Repression of bleomycin-induced pneumopathy by TNF. J Immunol 170:567–574
Leask A, Denton CP, Abraham DJ (2004) Insights into the molecular mechanism of chronic fibrosis: the role of connective tissue growth factor in scleroderma. J Invest Dermatol 122:1–6. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202X.2003.22133.x
Liu JY, Sime PJ, Wu T, Warshamana GS, Pociask D, Tsai SY, Brody AR (2001) Transforming growth factor-beta(1) overexpression in tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor knockout mice induces fibroproliferative lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:3–7
Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, Smolen J, Emery P, Harriman G, Feldmann M, Lipsky P (1999) Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 354:1932–1939. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)05246-0
Mori R, Kondo T, Ohshima T, Ishida Y, Mukaida N (2002) Accelerated wound healing in tumor necrosis factor receptor p55-deficient mice with reduced leukocyte infiltration. FASEB J 16:963–974. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0776com
Roth D, Piekarek M, Paulsson M, Christ H, Bloch W, Krieg T, Davidson JM, Eming SA (2006) Plasmin modulates VEGF-A-mediated angiogenesis during wound repair. Am J Pathol 168:670–684. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.050372
Saika S, Ikeda K, Yamanaka O, Flanders KC, Nakajima Y, Miyamoto T, Ohnishi Y, Kao WW, Muragaki Y, Ooshima A (2005) Therapeutic effects of adenoviral gene transfer of bone morphogenic protein-7 on a corneal alkali injury model in mice. Lab Invest 85:474–486. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700247
Saika S, Shiraishi A, Liu CY, Funderburgh JL, Kao CW, Converse RL, Kao WW (2000) Role of lumican in the corneal epithelium during wound healing. J Biol Chem 275:2607–2612. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.4.2607
Saika S, Miyamoto T, Yamanaka O, Kato T, Ohnishi Y, Flanders KC, Ikeda K, Nakajima Y, Kao WW, Sato M, Muragaki Y, Ooshima A (2005) Therapeutic effects of topical administration of SN50, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, in treatment of corneal alkali burns in mice. Am J Pathol 166:1393–1403
Saika S, Ikeda K, Yamanaka O, Miyamoto T, Ohnishi Y, Sato M, Muragaki Y, Ooshima A, Nakajima Y, Kao WW, Flanders KC, Roberts AB (2005) Expression of Smad7 in mouse eyes accelerates healing of corneal tissue after exposure to alkali. Am J Pathol 166:1405–1418
Saika S, Ikeda K, Yamanaka O, Flanders KC, Okada Y, Miyamoto T, Kitano A, Ooshima A, Nakajima Y, Ohnishi Y, Kao WW (2006) Loss of tumor necrosis factor alpha potentiates transforming growth factor beta-mediated pathogenic tissue response during wound healing. Am J Pathol 168:1848–1860. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.050980
Serini G, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Ropraz P, Geinoz A, Borsi L, Zardi L, Gabbiani G (1998) The fibronectin domain ED-A is crucial for myofibroblastic phenotype induction by transforming growth factor-beta1. J Cell Biol 142:873–881. doi:10.1083/jcb.142.3.873
Singer AJ, Clark RA (1999) Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med 341:738–746. doi:10.1056/NEJM199909023411006
Verrecchia F, Tacheau C, Wagner EF, Mauviel A (2003) A central role for the JNK pathway in mediating the antagonistic activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines against transforming growth factor-beta-driven SMAD3/4-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:1585–1593. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206927200
Wang W, Huang XR, Li AG (2005) Signaling mechanism of TGF-beta 1 in prevention of renal inflammation: role of Smad7. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1371–1383. doi:10.1681/ASN.2004121070
Werner S, Grose R (2003) Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev 83:835–870
Werner S, Krieg T, Smola H (2007) Keratinocyte–fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 127:998–1008. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700786
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinozaki, M., Okada, Y., Kitano, A. et al. Impaired cutaneous wound healing with excess granulation tissue formation in TNFα-null mice. Arch Dermatol Res 301, 531–537 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-0969-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-0969-z