Abstract
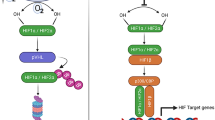
Hemorrhagic shock (HS) initiates an inflammatory response that includes increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and production of prostaglandins. Induction of iNOS during the ischemic phase of HS may involve the activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Increased expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) during HS contributes to prostaglandin production. The aim of this study was to determine whether the ischemic phase of HS results in the activation of HIF-1 and the induction of COX-2. The lungs of rats subjected to HS demonstrated a twofold increase in HIF-1 activation (P < 0.01) and a 7.4-fold increase in expression of COX-2 mRNA (P < 0.01) compared with sham controls. The upregulation of iNOS and COX-2 during ischemia are two important early response genes that promote the inflammatory response and may contribute to organ damage through the rapid and exaggerated production of nitric oxide and prostaglandins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hierholzer, C., Harbrecht, B., Billiar, T. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activation and cyclo-oxygenase-2 induction are early reperfusion-independent inflammatory events in hemorrhagic shock. Arch Orth Traum Surg 121, 219–222 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020000211
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020000211