Abstract
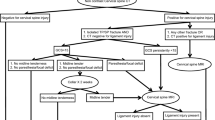
We studied both the clinical features and computed tomography (CT) findings in 25 patients with a cervical spinal injury related to diving. In all patients the X-rays, including anteroposterior, lateral and open mouth views, were normal. The clinical features included headache, dizziness, without an alteration in the state of consciousness. In 5 patients, the CT spinal scan revealed cervical spinal injury unrecognised on X-ray. In 4 of them, the mechanism of the trauma was a direct injury to the head when it hit the bottom of the pool; in 1 patient, the mechanism was indirect injury transmitted from the stretched hands to the cervical spine. We conclude that the cervical spinal injury caused by diving should be evaluated selectively by CT spinal scan in patients with direct cervical injury, even if the clinical and roentgenographic results appear negative.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kligman, M., Vasili, C. & Roffman, M. The role of computed tomography in cervical spinal injury due to diving. Arch Orth Traum Surg 121, 139–141 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020000198
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020000198