Abstract
Purpose
To translate, culturally adapt, and validate the simple shoulder test (SST) and Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS) into Persian language using a cross-sectional and prospective cohort design.
Methods
A standard forward and backward translation was followed to culturally adapt the SST and the OSS into Persian language. Psychometric properties of floor and ceiling effects, construct convergent validity, discriminant validity, internal consistency reliability, test–retest reliability, standard error of the measurement (SEM), smallest detectable change (SDC), and factor structure were determined.
Results
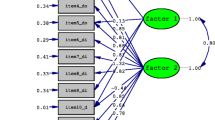
One hundred patients with shoulder disorders and 50 healthy subjects participated in the study. The PSST and the POSS showed no missing responses. No floor or ceiling effects were observed. Both the PSST and POSS detected differences between patients and healthy subjects supporting their discriminant validity. Construct convergent validity was confirmed by a very good correlation between the PSST and POSS (r = 0.68). There was high internal consistency for both the PSST (α = 0.73) and the POSS (α = 0.91 and 0.92). Test–retest reliability with 1-week interval was excellent (ICCagreement = 0.94 for PSST and 0.90 for POSS). Factor analyses demonstrated a three-factor solution for the PSST (49.7 % of variance) and a two-factor solution for the POSS (61.6 % of variance). The SEM/SDC was satisfactory for PSST (5.5/15.3) and POSS (6.8/18.8).
Conclusions
The PSST and POSS are valid and reliable outcome measures for assessing functional limitations in Persian-speaking patients with shoulder disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stevenson JH, Trojlan H (2002) Evaluation of shoulder pain. J Fam Pract 51(7):605–611
Brox JL (2003) Shoulder pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 17(1):33–56
van der Heijden GJ, Leffers P, Bouter LM (2000) Shoulder disability questionnaire design and responsiveness of a functional status measure. J Clin Epidemiol 53(1):29–38
Davatchi F, Tehrani Banihashemi A, Gholami J, Faezi ST, Forouzanfar MH, Salesi M, Karimifar M, Essalatmanesh K, Barghamdi M, Noorolahzadeh E, Dahaghin S, Rasker JJ (2009) The prevalence of musculoskeletal complaints in a rural area in Iran: a WHO-ILAR COPCORD study (stage 1, rural study) in Iran. Clin Rheumatol 28(11):1267–1274
Roy JS, Braën C, Leblond J, Desmeules F, Dionne CE, MacDermid JC, Bureau NJ, Frémont P (2015) Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography, MRI and MR arthrography in the characterisation of rotator cuffdisorders: a meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med (Epub ehead of print)
Vind M, Bogh SB, Larsen CM, Knudsen HK, Søgaard K, Juul-Kristensen B (2011) Inter-examiner reproducibility of clinical tests and criteria used to identify subacromial impingement syndrome. BMJ Open 1(1):e000042
Fitzpatrick R, Fletcher A, Gore S, Jones D, Spiegelhalter D, Cox D (1992) Quality of life measures in health care. I: applications and issues in assessment. BMJ 305(6861):1074–1077
Roy JS, MacDermid JC, Woodhouse LJ (2009) Measuring shoulder function: a systematic review of four questionnaires. Arthritis Rheum 61(5):623–632
Bot SD, Terwee CB, van der Windt DA, Bouter LM, Dekker J, de Vet HC (2004) Clinimetric evaluation of shoulder disability questionnaires: a systematic review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis 63(4):335–341
Schmidt S, Ferrer M, González M, González N, Valderas JM, Alonso J, Escobar A, Vrotsou K, EMPRO Group (2014) Evaluation of shoulder-specific patient-reported outcome measures: a systematic and standardized comparison of available evidence. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 23(3):434–444
Lippitt SB, Harryman DT, Matsen FA (1993) A practical tool for evaluation of function: the simple shoulder test. In: Matsen FA, Fu FH, Hawkins RJ (eds) The shoulder: a balance of mobility and stability. The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, Rosemont, pp 501–559
Angst F, Schwyzer HK, Aeschlimann A, Simmen BR, Goldhahn J (2011) Measures of adult shoulder function: disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand questionnaire (DASH) and its short version (QuickDASH), shoulder pain and disability index (SPADI), American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) Society standardized shoulder assessment form, constant (Murley) score (CS), simple shoulder test (SST), Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS), shoulder disability questionnaire (SDQ), and Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI). Arthritis Care Res 63(S11):S174–S188
Roy JS, Macdermid JC, Faber KJ, Drosdowech DS, Athwal GS (2010) The simple shoulder test is responsive in assessing change following shoulder arthroplasty. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 40(7):413–421
Godfrey J, Hamman R, Lowenstein S, Briggs K, Kocher M (2007) Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the simple shoulder test: psychometric properties by age and injury type. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 16(3):260–267
Rylisˇkis S, Piesˇina E, Kocius M, Marx RG (2008) Cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric properties of the Lithuanian version of the simple shoulder test. Acta med lituanica 15(3):163–168
Marchese C, Cristalli G, Pichi B, Manciocco V, Mercante G, Pellini R, Marchesi P, Sperduti I, Ruscito P, Spriano G (2012) Italian cross-cultural adaptation and validation of three different scales for the evaluation of shoulder pain and dysfunction after neck dissection: University of California—Los Angeles (UCLA) shoulder scale, shoulder pain and disability index (SPADI) and simple shoulder test (SST). Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 32(1):12–17
Van Kampen DA, Van Beers LW, Scholtes VA, Terwee CB, Willems WJ (2012) Validation of the Dutch version of the simple shoulder test. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(6):808–814
Neto JO, Gesser RL, Steglich V, Bonilauri Ferreira AP, Gandhi M, Vissoci JR, Pietrobon R (2013) Validation of the Simple Shoulder Test in a Portuguese-Brazilian population. Is the latent variable structure and validation of the Simple Shoulder Test Stable across cultures? PLoS One 8(5): e62890
Membrilla-Mesa MD, Tejero-Fernández V, Cuesta-Vargas AI, Arroyo-Morales M (2015) Validation and reliability of a Spanish version of simple shoulder test (SST-Sp). Qual Life Res 24(2):411–416
Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A (1996) Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about shoulder surgery. J Bone Jt Surg Br 78(4):593–600
Dawson J, Rogers K, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A (2009) The Oxford Shoulder Score revisited. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(1):119–123
Huber W, Hofstaetter JG, Hanslik-Schnabel B, Posch M, Wurnig C (2004) The German version of the Oxford Shoulder Score: cross-cultural adaptation and validation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124(8):531–536
Berendes T, Pilot P, Willems J, Verburg H, te Slaa R (2010) Validation of the Dutch version of the Oxford Shoulder Score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 19(6):829–836
Murena L, Vulcano E, D’Angelo F, Monti M, Cherubino P (2010) Italian cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Oxford shoulder score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 19(3):335–341
Frich LH, Noergaard PM, Brorson S (2011) Validation of the Danish version of Oxford Shoulder Score. Dan Med Bull 58(11):A4335
Tuğay U, Tuğay N, Gelecek N, Özkan M (2011) Oxford Shoulder Score: cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Turkish version. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(5):687–694
Roh YH, Noh JH, Kim W, Oh JH, Gong HS, Baek GH (2012) Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Korean version of the Oxford shoulder score. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(1):93–99
Terwee CB, Bot SD, de Boer MR, van der Windt DA, Knol DL, Bouter LM, de Vet HC (2007) Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol 60(1):34–42
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guilhemin F, Ferraz MB (2000) Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 25(24):3186–3191
Ansari NN, Feise RJ, Naghdi S, Ebadi S, Yoosefinejad AK (2011) The functional rating index: reliability and validity of the Persian language version in patients with low back pain. Spine 36(24):E1573–E1577
Ansari NN, Feise RJ, Naghdi S, Mohseni A, Rezazadeh M (2012) The functional rating index: reliability and validity of the Persian language version in patients with neck pain. Spine 37(14):E844–E848
Nakhostin Ansari N, Naghdi S, Mohammadi R, Hasson S (2015) Multiple sclerosis walking scale-12, translation, adaptation and validation for the Persian language population. Gait Posture 41(2):420–424
Feise RJ, Michael Menke J (2001) Functional rating index: a new valid and reliable instrument to measure the magnitude of clinical change in spinal conditions. Spine 26(1):78–86
Costello AB, Osborne J (2005) Best practices in exploratory factor analysis: four recommendations for getting the most from your analysis. Pract Assess Res Eval 10(7):1–9
Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC (2003) Statistical methods for rates and proportions, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Bruton A, Conway JH, Holgate ST (2000) Reliability: what is it, and how is it measured? Physiotherapy 86(2):94–99
Beaton DE, Richards RR (1996) Measuring function of the shoulder: a cross-sectional comparison of five questionnaires. J Bone Jt Surg Am 78(6):882–890
Skutek M, Fremerey RW, Zeichen J, Bosch U (2000) Outcome analysis following open rotator cuff repair: early effectiveness validated using four different shoulder assessment scales. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 120(7–8):432–436
Getahun TY, MacDermid JC, Patterson SD (2000) Concurrent validity of patient rating scales in assessment of outcome after rotator cuff repair. J Musculoskelet Res 4(2):119–127
Beaton DE, Richards RR (1998) Assessing the reliability and responsiveness of 5 shoulder questionnaires. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 7(6):565–572
Roddey TS, Olson SL, Cook KF, Gartsman GM, Hanten W (2000) Comparison of the University of California-Los Angeles shoulder scale and the simple shoulder test with the shoulder pain and disability index: single-administration reliability and validity. Phys Ther 80(8):759–768
Dawson J, Hill G, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A (2001) The benefits of using patient based methods of assessment: medium-term results of an observational study of shoulder surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(6):877–882
Cloke DJ, Lynn SE, Watson H, Steen IN, Purdy S, Williams JR (2005) A comparison of functional, patient-based scores in subacromial impingement. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14(4):380–384
Placzek JD, Lukens SC, Badalanmenti S, Roubal PJ, Freeman DC, Walleman KM, Parrot A, Wiater JM (2004) Shoulder outcome measures: a comparison of 6 functional tests. Am J Sports Med 32(5):1270–1277
Acknowledgments
We thank subjects for their participation in this study. The authors thank Research Deputy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghdi, S., Nakhostin Ansari, N., Rustaie, N. et al. Simple shoulder test and Oxford Shoulder Score: Persian translation and cross-cultural validation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135, 1707–1718 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2330-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2330-7