Abstract
Introduction
Nerve damage is a rare but serious complication after THA. There exist only little data about the outcome of these patients particularly regarding the long-term results later than 2 years postoperatively. Aim of this study is to answer the following questions: Is the recovery to be expected for light nerve lesions different from the severe ones? Is there a possibility of nerve recovery more than 2 years after THA? Is the potential of nerve recovery depending on the affected nerve?
Materials and methods
This study investigates 2,255 primary THA as well as revision surgeries performed from 1988 to 2003 relating to iatrogenic nerve lesion. We classified the nerve lesion according to the core muscle strength in severe (M0–M2) and light (M3–M4) nerve damage and differentiated between femoral, sciatic and superior gluteal nerve, according to the electromyography.
Results
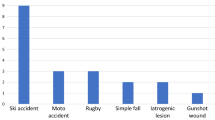
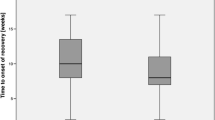
We found 34 cases of iatrogenic nerve damage representing an incidence of 1.5 %. 17 of 34 (50 %) patients showed a complete recovery after 2 years. Out of the remaining 17 patients, six out of seven patients with a final examination after a median time of 93 months achieved further improvement. The different nerves showed no significant different potential of recovery.
Conclusions
In contrast to the literature, an improvement beyond the limit of 2 years is probable and independent of the nerve affected.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer R, Kerschbaumer F, Poisel S, Oberthaler W (1979) The transgluteal approach to the hip joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg Archiv fur orthopadische und Unfall-Chirurgie 95(1–2):47–49
Brown GD, Swanson EA, Nercessian OA (2008) Neurologic injuries after total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop 37(4):191–197
Daniels LWC (1986) Muscle testing: techniques of manual examination, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia
DeHart MM, Riley LH Jr (1999) Nerve injuries in total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 7(2):101–111
Farrell CM, Springer BD, Haidukewych GJ, Morrey BF (2005) Motor nerve palsy following primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(12):2619–2625
Fox AJ, Bedi A, Wanivenhaus F, Sculco TP, Fox JS (2012) Femoral neuropathy following total hip arthroplasty: review and management guidelines. Acta Orthop Belg 78(2):145–151
Goetz MB, Seybold D, Gosse F, Muhr G, Roetman B (2010) The risk of nerve lesions in hip alloarthroplasty. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Unfallchirurgie 148(2):163–167
Holzapfel BM, Heinen F, Holzapfel DE, Reiners K, Noth U, Rudert M (2012) Nerve lesions after minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. Der Orthopade 41(5):354–364
Kirschner S, Goronzy J, Storch A, Gunther KP, Hartmann A (2011) Avoidance, diagnostics and therapy of nerve lesions after total hip arthroplasty. Der Orthopade 40(6):491–499
Navarro RA, Schmalzried TP, Amstutz HC, Dorey FJ (1995) Surgical approach and nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 10(1):1–5
Ochsner P, Brunazzi M (2003) Die Hüfttotalprothese: Implantationstechnik und lokale Komplikationen; eine Darstellung auf der Basis des Systems nach M. E. Müller unter Einbezug einer Langzeitkontrolle; mit 24 Tabellen. Springer, Berlin [u.a.]
Oldenburg M, Muller RT (1997) The frequency, prognosis and significance of nerve injuries in total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 21(1):1–3
Paterson D (1993) The International Documentation and Evaluation System (IDES). Orthopedics 16(1):11–14
Pekkarinen J, Alho A, Puusa A, Paavilainen T (1999) Recovery of sciatic nerve injuries in association with total hip arthroplasty in 27 patients. J Arthroplasty 14(3):305–311
Schoellner C, Schoellner D (2003) Nerve injuries in total hip arthroplasty—prophylactic strategies—quality assurance and risk management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 141(3):289–295
Sendtner E, Borowiak K, Schuster T, Woerner M, Grifka J, Renkawitz T (2011) Tackling the learning curve: comparison between the anterior, minimally invasive (Micro-hip(R)) and the lateral, transgluteal (Bauer) approach for primary total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. Archiv fur orthopadische und Unfall-Chirurgie 131(5):597–602
Simmons C Jr, Izant TH, Rothman RH, Booth RE Jr, Balderston RA (1991) Femoral neuropathy following total hip arthroplasty. Anatomic study, case reports, and literature review. J Arthroplasty 6(Suppl):S57–S66
Solheim LF, Hagen R (1980) Femoral and sciatic neuropathies after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand 51(3):531–534
Weber ER, Daube JR, Coventry MB (1976) Peripheral neuropathies associated with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58(1):66–69
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Susanna Häfliger for the data research and support.
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethical standard
This study was approved by the local ethical committee (Ref. 192/13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zappe, B., Glauser, P.M., Majewski, M. et al. Long-term prognosis of nerve palsy after total hip arthroplasty: results of two-year-follow-ups and long-term results after a mean time of 8 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 1477–1482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2038-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2038-0