Abstract
Introduction
With the resurgence of resurfacing hip arthroplasty complications such as femoral neck fracture and thinning have been identified. We therefore conducted a radiological and biomechanical evaluation of factors affecting femoral neck resorption following resurfacing hip arthroplasty (RHA).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 61 resurfacing hip arthroplasties in 53 patients with a minimum of a 2-year follow-up. Data regarding age, gender, body mass index, indication for surgery, and component size was obtained from case records. Radiographic measurements were made from standardised digital AP pelvic radiographs. The neck shaft angle, stem shaft angle, and the varus–valgus femoral stem alignment were calculated. Changes in abductor/body moment arm, hip ratio, and cup-to-neck ratio were calculated from the pre-op, immediate post-op and 2 year post-operative radiographs.
Results
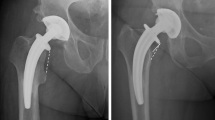
Femoral neck thinning was identified in 98% of cases (60/61) and was greater than 10% in 59% (39/61). The mean change in component-to-neck ratio was 0.12 (0–0.44). No significant relationship was found between the amount of femoral neck resorption and patient age, BMI, gender, diagnosis, component size or orientation. A significant positive correlation was found between a change in abductor moment arm and femoral neck resorption (R = 0.575; p < 0.01). We also calculated that approximately one-third of the change in CNR could be explained by a change in abductor moment arm. From this we formulated the Pillai–Joseph equation to calculate projected thinning at 2 years from the initial post-operative radiograph (CNR difference = 0.094 × AMA difference + 0.129).
Conclusions
RHA significantly alters hip biomechanics and this may result in altered loading patterns with adaptive remodelling causing neck thinning. In order to minimise neck thinning care must be taken not to increase the abductor moment arm.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amstutz HC, Beaule PE, Dorey FJ, Le Duff MJ, Campbell PA, Gruen TA (2004) Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty: two to six-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:28–39
Amstutz HC, Thomas BJ, Jinnah R, Kim W, Grogan T, Yale C (1984) Treatment of primary osteoarthritis of the hip A comparison of total joint and surface replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66(2):228–241
Amstutz HC, Grigoris P, Dorey FJ (1998) Evolution and future of surface replacement of the hip. J Orthop Sci 3:169–186
McMinn D, Treacy RB, Lin K, Pynsent P (1996) Metal on metal surface replacement of the hip. Experience of the McMinn prosthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 329(Suppl):S89–S98
Kishida Y, Sugano N, Nishii T, Miki H, Yamaguchi K, Yoshikawa H (2004) Preservation of the bone mineral density of the femur after surface replacement of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:185–189
Girard J, Lavigne M, Vendittoli PA, Roy AG (2006) Biomechanical reconstruction of the hip: a randomized study comparing total hip resurfacing and total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88-B(6):721–726
Ong KL, Kurtz SM, Manley MT, Rushton N, Mohammed NA, Field RE (2006) Biomechanics of the Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88-B(8):1110–1115
Hart AJ, Scott G (2005) Hip resurfacing following previous proximal femoral osteotomy. Hip Int 15:119–122
Ball ST, Le Duff MJ, Amstutz HC (2007) Early results of conversion of a failed femoral component in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:735–741
Treacy RB, McBryde CW, Pynsent PB (2005) Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty. A minimum follow-up of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:167–170
Shimmin AJ, Back DL (2005) Femoral neck fractures following Birmingham hip resurfacing: a national review of 50 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87-B:463–464
Lilikakis AK, Vowler SL, Villar RN (2005) Hydroxyapatite-coated femoral implant in metal-on-metal resurfacing hip arthroplasty: minimum of two years follow-up. Orthop Clin North Am 36(2):215–222
Amstutz HC, Le Duff MJ (2008) Eleven years of experience with metal-on-metal hybrid hip resurfacing: a review of 1,000 conserve plus. J Arthroplasty 23(6–1):36–43
Shimmin A, Beaule PE, Campbell P (2008) Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:637–654
Spencer S, Carter R, Murray H, Meek RMD (2008) Femoral neck narrowing after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty 23(8):1105–1109
Gill HS, Campbell PA, Murray DW, De Smet KA (2007) Reduction of the potential for thermal damage during hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:16–20
Campbell PA, Wang M, Amstutz HC, Goodman SB (2002) Positive cytokine production in failed metal-on-metal total hip replacements. Acta Orthop Scan 73:506–512
Zeh A, Becker C, Planert M, Lattke P, Wohlrab D (2009) Time-dependent release of cobalt and chromium ions into the serum following implantation of the metal-on-metal Maverick type artificial lumbar disc. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(6):741–746
Daniel J, Ziaee H, Pradhan C, Pynsent PB, McMinn DJ (2007) Blood and urine metal ion levels in young and active patients after Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty: four-year results of a prospective longitudinal study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89-B:169–173
Park YS, Moon YW, Lim SJ, Yang JM, Ahn G, Choi YL (2005) Early osteolysis following second-generation metal-on-metal hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(7):1515–1521
Hing CB, Young DA, Dalziel RE, Bailey M, Back DL, Shimmin AJ (2007) Narrowing of the neck in resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: a radiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(9):1019–1024
McGrory BJ, Morrey BF, Cahalan TD, An KN, Cabanela ME (1995) Effect of femoral offset on range of motion and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77-B:865–869
Charnley J (1979) Low friction arthroplasty of the hip: theory and practice. (Vol 3). Springer, New York
Loughead JM, Chesney D, Holland JP, McCaskie AW (2005) Comparison of offset in Birmingham hip resurfacing and hybrid total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87-B:163–166
Silva M, Lee KH, Heisel C, dela Rosa MA, Schmalzried TP (2004) The biomechanical results of total hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 20 (86) :40–46
Shimmin AJ, Bare J, Back DL (2005) Complications associated with hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 36(2):187–193
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Mr. M. Haddidi, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Wishaw District General Hospital, for providing the patients for this study.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, J., Mullen, M., McAuley, A. et al. Femoral neck resorption following hybrid metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: a radiological and biomechanical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 1433–1438 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1070-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1070-y