Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study is to assess if an application of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) gel would improve the mechanical properties of rabbit’s patellar tendon after resecting its central portion.
Materials and methods
Forty skeletally mature New Zealand White rabbits were used. Two groups ten rabbits each (PRP and control group) were used to evaluate mechanical properties and histology after 14 days and two groups ten rabbits each (PRP and control groups) were used to evaluate mechanical properties and histology after 28 days.
Results
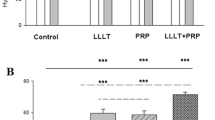
At 14 days, PRP group showed a 72.2% increase in force at failure, a 39.1% increase in ultimate stress, and a 53.1% increase in stiffness, as compared with controls. These changes were statistically significant (P < 0.05). At 28 days, there was no longer any significant difference between PRP and control groups (P > 0.05).
Discussion
In our study, the mechanical properties of the regenerated tendon in the PRP group were significantly improved in relation to the control group. It appears that PRP has a strong effect in the early phase of tendon healing. This effect is probably due to the growth factors that are released from the platelets during activation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed IM, Lagopoulos M, McConnell P, Soames RW, Sefton GK (1998) Blood supply of the Achilles tendon. J Orthop Res 16(5):591–596
Akeda K, An HS, Pichika R, Attawia M, Thonar EJ, Lenz ME, Uchida A, Masuda K (2006) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) stimulates the extracellular matrix metabolism of porcine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus cells cultured in alginate beads. Spine 31:959–966
Anaguchi Y, Yasuda K, Majima T, Tohyama H, Minami A, Hayashi K (2005) The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on mechanical properties of the fibrous tissue regenerated in the patellar tendon after resecting the central portion. Clin Biomech 20(9):959–965
Aspenberg P, Virchenko O (2004) Platelet concentrate injection improves Achilles tendon repair in rats. Acta Orthop Scand 75(1):93–99
Evans CH (1999) Cytokines and the role they play in the healing of ligaments and tendons. Sports Med 28(2):71–76
Ferraz FH, Schellini SA, Schellini RC, Pellizon CH, Hirai FE, Padovani CR (2008) BMP implant associated with platelet-rich plasma in orbit fracture repair. Curr Eye Res 33(3):293–301
Harnack L, Boedeker RH, Kurtulus I, Boehm S, Gonzales J, Meyle J (2008) Use of platelet-rich plasma in periodontal surgery-a prospective randomised double blind clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig [Epub ahead of print]
Kazakos K, Lyras DN, Tilkeridis K, Verettas D, Tryfonidis M (2008) The use of autologous PRP gel as an aid in the management of acute trauma wounds. Injury [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 18703188
Lucarelli E, Fini M, Beccheroni A, Giavaresi G, Di Bella C, Aldini NN, Guzzardella G, Martini L, Cenacchi A, Di Maggio N, Sangiorgi L, Fornasari PM, Mercuri M, Giardino R, Donati D (2005) Stromal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma improve bone allograft integration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 435:62–68
Maffulli N, Moller HD, Evans CH (2002) Tendon healing: can it be optimised? Growth factors may be useful in tendon healing, possibly introduced using gene therapy. Br J Sports Med 36:315–316
Mariconda M, Cozzolino F, Cozzolino A, D’Agostino E, Bove A, Milano C (2008) Platelet gel supplementation in long bone nonunions treated by external fixation. J Orthop Trauma 22(5):342–345
Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR (1998) Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 85:638–646
McGrath MH (1990) Peptide growth factors and wound healing. Clin Plast Surg 17(3):421–432
Molloy T, Wang Y, Murrell G (2003) The roles of growth factors in tendon and ligament healing. Sports Med 33(5):381–394
Murray MM, Spindler KP, Devin C, Snyder BS, Muller J, Takahashi M, Ballard P, Nanney LB, Zurakowski D (2006) Use of a collagen-platelet rich plasma scaffold to stimulate healing of a central defect in the canine ACL. J Orthop Res 24(4):820–830
Murray MM, Spindler KP, Abreu E, Muller JA, Nedder A, Kelly M, Frino J, Zurakowski D, Valenza M, Snyder BD, Connolly SA (2007) Collagen-platelet rich plasma hydrogel enhances primary repair of the porcine anterior cruciate ligament. J Orthop Res 25(1):81–91
Nagae M, Ikeda T, Mikami Y, Hase H, Ozawa H, Matsuda KI, Sakamoto H, Tabata Y, Kawata M, Kubo T (2007) Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng 13:147–158
Roldan JC, Jepsen S, Miller J, Freitag S, Rueger DC, Acil Y, Terheyden H (2004) Bone formation in the presence of platelet-rich plasma vs. bone morphogenetic protein-7. Bone 34:80–90
Smith JJ, Ross MW, Smith RK (2006) Anabolic effects of acellular bone marrow, platelet rich plasma, and serum on equine suspensory ligament fibroblasts in vitro. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 19:43–47
Werner S, Grose R (2003) Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev 83(3):835–870
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyras, D.N., Kazakos, K., Verettas, D. et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma gel in the early phase of patellar tendon healing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129, 1577–1582 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0935-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0935-4