Abstract
Objectives
This study investigated the hypothesized beneficial effect of low-dose irradiation (LDI) on fracture callus mineralization in a rat model.
Methods
Seventy-two male Sprague–Dawley rats were averagely randomized into LDI group (rats treated with LDI) and SHAM group (rats treated with sham irradiation). Right after either LDI or sham irradiation, a standardized closed fracture on the right femur was established. At 2, 3 and 4 weeks postfracture, 12 rats in each group were euthanized. Fracture callus was assessed by using radiography and MicroCT for callus bridging, peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) for quantifying bone mineral content (BMC) and cross sectional area (CSA), confocal laser scanning microscopy for measuring area fraction of fluorescence labeling (AFFL) and four-point bending test for examining mechanical properties.
Results
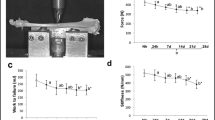
The CSA and AFFL were found to be 22 and 33% smaller in the LDI group compared to the SHAM group at 2 weeks (P < 0.05 for both), whereas the BMC and AFFL were 15 and 34% higher in the LDI group at 3 weeks (P < 0.05 for both). The changing patterns were consistent with the findings in 3-D MicroCT reconstructions. The mechanical parameters (Max-Load, Stiffness and Energy) were also 18, 30 and 24% higher in the LDI group than in the SHAM group at 3 weeks (P < 0.05 for all). At 4 weeks, there was no difference found for all assessments between the two groups.
Conclusion
The results indicated LDI promoted mineralization at the stage of hard callus formation in a rat fracture model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spittler AW, Batch JW, Rutledge BA (1954) Whole body irradiation on the healing of fresh fractures. AMA Arch Surg 68:93–104
Woodard HQ (1970) The influence of X-rays on the healing of fractures. Health Phys 19:791–799
Markbreiter LA, Pelker RR, Friedlaender GE, Peschel R, Panjabi MM (1989) The effect of radiation on the fracture repair process. A biomechanical evaluation of a closed fracture in a rat model. J Orthop Res 7:178–83
Widmann RF, Pelker RR, Friedlaender GE, Panjabi MM, Peschel RE (1993) Effects of prefracture irradiation on the biomechanical parameters of fracture healing. J Orthop Res 11:422–8
Pelker RR, Friedlaender GE (1997) The Nicolas Andry Award—1995. Fracture healing. Radiation induced alterations. Clin Orthop Relat Res (341):267–282.
Heissig B, Rafii S, Akiyama H, Ohki Y, Sato Y, Rafael T et al (2005) Low-dose irradiation promotes tissue revascularization through VEGF release from mast cells and MMP-9-mediated progenitor cell mobilization. J Exp Med 202:739–50
Schindl A, Heinze G, Schindl M, Pernerstorfer-Schon H, Schindl L (2002) Systemic effects of low-intensity laser irradiation on skin microcirculation in patients with diabetic microangiopathy. Microvasc Res 64:240–246
Moeller BJ, Cao Y, Li CY, Dewhirst MW (2004) Radiation activates HIF-1 to regulate vascular radiosensitivity in tumors: role of reoxygenation, free radicals, and stress granules. Cancer Cell 5:429–441
Polytarchou C, Gligoris T, Kardamakis D, Kotsaki E, Papadimitriou E (2004) X-rays affect the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis. Anticancer Res 24:2941–2945
Laukkanen MO, Kuramoto K, Calmels B, Takatoku M, von Kalle C, Donahue RE et al (2005) Low-dose total body irradiation causes clonal fluctuation of primate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood 105:1010–1015
Gerber HP, Vu TH, Ryan AM, Kowalski J, Werb Z, Ferrara N (1999) VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Nat Med 5:623–628
Street J, Winter D, Wang JH, Wakai A, McGuinness A, Redmond HP (2000) Is human fracture hematoma inherently angiogenic? Clin Orthop Relat Res (378):224–237
Street J, Bao M, de Guzman L, Bunting S, Peale FV Jr et al (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9656–9661
Eckardt H, Ding M, Lind M, Hansen ES, Christensen KS, Hvid I (2005) Recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor enhances bone healing in an experimental nonunion model. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:1434–1438
Bonnarens F, Einhorn TA (1984) Production of a standard closed fracture in laboratory animal bone. J Orthop Res 2:97–101
Zhou XZ, Dong QR, Zhang J (2007) Establishment and evaluation of a standard closed fracture model on rat femur. J Southeast Univ (Med Sci Ed) 26:60–62
Warden SJ, Fuchs RK, Kessler CK, Avin KG, Cardinal RE, Stewart RL (2006) Ultrasound produced by a conventional therapeutic ultrasound unit accelerates fracture repair. Phys Ther 86:1118–127
Zhang G, Qin L, Hung WY, Shi YY, Leung PC, Yeung HY et al (2006) Flavonoids derived from herbal Epimedium Brevicornum Maxim prevent OVX-induced osteoporosis in rats independent of its enhancement in intestinal calcium absorption. Bone 38:818–825
Chan CW, Qin L, Lee KM, Cheung WH, Cheng JC, Leung KS (2006) Dose-dependent effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on callus formation during rapid distraction osteogenesis. J Orthop Res 24:2072–2079
Qin L, Fok PK, Lu HB, Shi SQ, Leng Y, Leung KS (2006) Low intensity pulsed ultrasound increases the matrix hardness of the healing tissues at bone–tendon insertion—a partial patellectomy model in rabbits. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 21:387–394
Siu WS, Qin L, Cheung WH, Leung KS (2004) A study of trabecular bones in ovariectomized goats with micro-computed tomography and peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Bone 35:21–26
Hao YJ, Zhang G, Wang YS, Qin L, Hung WY, Leung KS et al (2007) Changes of microstructure and mineralized tissue in the middle and late phase of osteoporotic fracture healing in rats. Bone 41(4):631–638
Kazama JJ, Gejyo F, Ejiri S, Okada M, Ei I, Arakawa M et al (1993) Application of confocal laser scanning microscopy to the observation of bone biopsy specimens. Bone 14:885–889
Grotz KA, Piepkorn B, Al-Nawas B, Duschner H, Bittinger F, Kann P et al (1999) Confocal laser scanning microscopy: A nondestructive subsurface histotomography of healthy human bone. Calcif Tissue Int 65:8–10
Lu HB, Qin L, Fok PK, Cheung WH, Lee KM, Guo X et al (2006) Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates bone–tendon junction healing: a partial patellectomy model in rabbits. Am J Sports Med 34:1287–1296
Zhang G, Qin L, Sheng H, Yeung KW, Yeung HY, Cheung WH et al (2007) Epimedium-derived phytoestrogen exert beneficial effect on preventing steroid-associated osteonecrosis in rabbits with inhibition of both thrombosis and lipid-deposition. Bone 40:685–692
Regen E, Wilkins W (1936) The influence of roentgen irradiation on the rate of healing of fractures and the phosphatase activity of the callus of adult bone. J Bone Joint Surg 18:69–79
Pelker RR, Friedlaender GE, Panjabi MM, Kapp D, Doganis A (1984) Radiation-induced alterations of fracture healing biomechanics. J Orthop Res 2:90–96
Tam KF, Cheung WH, Lee KM, Qin L, Leung KS (2005) Delayed stimulatory effect of low-intensity shockwaves on human periosteal cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res 438:260–265
Green N, French S, Rodriquez G, Hays M, Fingerhut A (1969) Radiation-induced delayed union of fractures. Radiology 93:635–641
Takahashi S, Sugimoto M, Kotoura Y, Sasai K, Oka M, Yamamuro T (1994) Long-term changes in the haversian systems following high-dose irradiation. An ultrastructural and quantitative histomorphological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:722–738
Dudziak ME, Saadeh PB, Mehrara BJ, Steinbrech DS, Greenwald JA, Gittes GK et al (2000) The effects of ionizing radiation on osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1049–1061
Paris F, Fuks Z, Kang A, Capodieci P, Juan G, Ehleiter D et al (2001) Endothelial apoptosis as the primary lesion initiating intestinal radiation damage in mice. Science 293:293–297
Gridley DS, Loredo LN, Slater JD, Archambeau JO, Bedros AA, Andres ML et al (1998) Pilot evaluation of cytokine levels in patients undergoing radiotherapy for brain tumor. Cancer Detect Prev 22:20–29
Gorski DH, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT, Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM et al (1999) Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 59:3374–3378
Sonveaux P, Brouet A, Havaux X, Gregoire V, Dessy C, Balligand JL et al (2003) Irradiation-induced angiogenesis through the up-regulation of the nitric oxide pathway: implications for tumor radiotherapy. Cancer Res 63:1012–1019
Ausprunk DH, Knighton DR, Folkman J (1974) Differentiation of vascular endothelium in the chick chorioallantois: a structural and autoradiographic study. Dev Biol 38:237–248
O’Keefe RJ, Crabb ID, Puzas JE, Rosier RN (1994) Effects of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and fibroblast growth factor on DNA synthesis in growth plate chondrocytes are enhanced by insulin-like growth factor-I. J Orthop Res 12:299–310
Vu TH, Shipley JM, Bergers G, Berger JE, Helms JA, Hanahan D et al (1998) MMP-9/gelatinase B is a key regulator of growth plate angiogenesis and apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Cell 93:411–422
Einhorn TA (2005) The science of fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma 19:S4–S6
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mrs. Yang Xiao Hong for assistance on confocal laser scanning, Dr. Yeung Hiu Yan for MicroCT support, Prof. Cheung Wing Hoi for constructive advice on project arrangement and Dr. Lee Kwong Man for discussion on and interpretation for some of the research findings. This project was supported by the Research Grant of General Equipment Department of P.L.A. in China (No. 616010305) and Hong Kong Contemporary Orthopaedic Research and Education Fund (COREF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X.Z., Zhang, G., Dong, Q.R. et al. Low-dose X-irradiation promotes mineralization of fracture callus in a rat model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129, 125–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0634-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0634-6