Abstract
Introduction
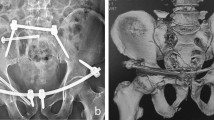
Internal fixation of the traumatic diastasis of symphysis pubis is an integral part of the definitive management of pelvic ring injuries. Both functional outcome and long term physiological effects of plate retention have not been clearly addressed and no specific indications regarding implant removal have been proposed in the literature.
Materials and methods
We reviewed 74 patients (18 females and 56 males), with an average age of 40.6 (16–75) years, who underwent open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of the pubic symphysis. Except from the demographic data many other parameters like suprapubic pain, sexual disturbance, impotence and dyspareunia were taken under consideration. Furthermore, any correlation between implant failure and functional impairment was recorded and the subject of implant removal in pregnant women was examined. Health outcome was assessed according to EuroQol 5-D (EQ-5D) questionnaire. Mean follow up: 41.7 (28–89) months.
Results
Suprapubic pain was present in ten patients. Three men developed neurogenic impotence and one woman had deep dyspareunia. None of these symptoms were related to implant status. Three of the four females who had uncomplicated pregnancy in the post-stabilization period had the plate in situ. Implant failure was seen in four patients but they remained asymptomatic. EQ-5D questionnaire revealed high satisfaction scores among young women and men of all age groups.
Conclusion
This study supports the view that routine removal of the plate is not essential. The issue of whether the implant needs to be removed in women of childbearing age requires further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgower M, Perren S, Matter P (1970) A new plate for internal fixation-the dynamic compression plate (DCP). Injury 2:40–47
Brooks R (1996) EuroQol: the current state of play. Health Policy 37:53–72
Burgess AR, Eastridge BJ, Young JW, Ellison TS, Ellison PS Jr, Poka A, Bathon GH, Brumback RJ (1990) Pelvic ring disruptions: effective classification system and treatment protocols. J Trauma 30:848–856
Cole JD, Blum DA, Ansel LJ (1996) Outcome after fixation of unstable posterior pelvic ring injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res (329):160–179
Copeland CE, Bosse MJ, McCarthy ML, MacKenzie EJ, Guzinski GM, Hash CS, Burgess AR (1997) Effect of trauma and pelvic fracture on female genitourinary, sexual, and reproductive function. J Orthop Trauma 11:73–81
Corriere JN Jr, Rudy DC, Benson GS (1994) Voiding and erectile function after delayed one-stage repair of posterior urethral disruptions in 50 men with a fractured pelvis. J Trauma 37:587–589, discussion 589–590
Dalal SA, Burgess AR, Siegel JH, Young JW, Brumback RJ, Poka A, Dunham CM, Gens D, Bathon H (1989) Pelvic fracture in multiple trauma: classification by mechanism is key to pattern of organ injury, resuscitative requirements, and outcome. J Trauma 29:981–1000, discussion 1000–1002
Deruaz CA, Tschantz P, Groebli Y (2001) Pelvic and acetabular fractures, long term results, retrospective study from Cadolles from 1977 to 1997. Rev Med Suisse Romande 121:351–355
Giannoudis PV (2003) Surgical priorities in damage control in polytrauma. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:478–483
Giannoudis PV, Pape HC (2004) Damage control orthopaedics in unstable pelvic ring injuries. Injury 35:671–677
Hirvensalo E, Lindahl J, Bostman O (1993) A new approach to the internal fixation of unstable pelvic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res (297):28–32
Kamhin M, Ganel A, Salai M, Horoszowski H (1980) Rigid fixation in diastasis of symphysis pubis. J Trauma 20:523–525
Kind P, Dolan P, Gudex C, Williams A (1998) Variations in population health status: results from a United Kingdom national questionnaire survey. BMJ 316:736–741
Kind P, Gudex CM (1994) Measuring health status in the community: a comparison of methods. J Epidemiol Community Health 48:86–91
Kothe S, Keller HW, Heindel W, Rehm KE (1994) Experience with surgical treatment of ruptures of the symphysis pubis. Zentralbl Chir 119:37–43
Lee J, Abrahamson BS, Harrington TG, Singh BV, Lee J, Trocchia AM, Khan SA (2000) Urologic complications of diastasis of the public symphysis: a trauma case report and review of world literature. J Trauma 48:133–136
Leighton RL (1968) Surgical treatment of some pelvic fractures. J Am Vet Med Assoc 153:1739–1741
Letournel E (1981) Surgical fixation of displaced pelvic fractures and dislocations of the symphysis pubis (excluding acetabular fractures) (author’s transl). Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 67:771–782
Lewis MM, Mayer V (1977) Pubic symphysis diastasis treated by open reduction and internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res (123):37–39
Lindahl J, Hirvensalo E, Bostman O, Santavirta S (1999) Failure of reduction with an external fixator in the management of injuries of the pelvic ring. Long-term evaluation of 110 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:955–962
MacAvoy MC, McClellan RT, Goodman SB, Chien CR, Allen WA, van der Meulen MC (1997) Stability of open-book pelvic fractures using a new biomechanical model of single-limb stance. J Orthop Trauma 11:590–593
Matta JM (1996) Indications for anterior fixation of pelvic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res (329):88–96
Meissner A, Fell M, Wilk R, Boenick U, Rahmanzadeh R (1996) Biomechanics of the pubic symphysis. Which forces lead to mobility of the symphysis in physiological conditions?. Unfallchirurg 99:415–421
Meissner A, Fell M, Wilk R, Boenick U, Rahmanzadeh R (1998) Comparison of internal fixation methods for the symphysis in multi-directional dynamic gait simulation. Unfallchirurg 101:18–25
Monfort J, Le Neel JC, Leborgne J, Lehoux J, Malvy P (1973) Recent disjunctions of the pubic symphysis. Therapeutic indications apropos of 50 cases. Ann Chir 27:601–608
Pohlemann T, Bosch U, Gansslen A, Tscherne H (1994) The Hannover experience in management of pelvic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res (305):69–80
Raman R, Roberts CS, Pape HC, Giannoudis PV (2005) Implant retention and removal after internal fixation of the symphysis pubis. Injury 36:827–831
Sharp IK (1973) Plate fixation of disrupted symphysis pubis. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br 55:618–620
Shenfeld OZ, Kiselgorf D, Gofrit ON, Verstandig AG, Landau EH, Pode D, Jordan GH, McAninch JW (2003) The incidence and causes of erectile dysfunction after pelvic fractures associated with posterior urethral disruption. J Urol 169:2173–2176
Simonian PT, Routt ML Jr, Harrington RM, Tencer AF (1994) Box plate fixation of the symphysis pubis: biomechanical evaluation of a new technique. J Orthop Trauma 8:483–489
Simonian PT, Schwappach JR, Routt ML Jr, Agnew SG, Harrington RM, Tencer AF (1996) Evaluation of new plate designs for symphysis pubis internal fixation. J Trauma 41:498–502
Stuart PR, Talbot D, Milne DD (1990) Internal fixation of pubic symphysis diastasis with a tension banding technique. Injury 21:223–224
Tee SS, Hyzan Y, Razak M (2000) Functional outcome of open reduction and internal fixation of pelvic ring injuries. Med J Malaysia 55(Suppl C):49–58
Tile M (2003) Management of Pelvic ring injuries. In: Fractures of the Pelvis and Acetabulum. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 168–216
Van den Bosch EW, Van der Kleyn R, Hogervorst M, Van Vugt AB (1999) Functional outcome of internal fixation for pelvic ring fractures. J Trauma 47:365–371
Varga E, Hearn T, Powell J, Tile M (1995) Effects of method of internal fixation of symphyseal disruptions on stability of the pelvic ring. Injury 26:75–80
Webb LX, Bosse MJ, Mayo KA, Lange RH, Miller ME, Swiontkowski MF (1990) Results in patients with craniocerebral trauma and an operatively managed acetabular fracture. J Orthop Trauma 4:376–382
Wen Y, Liu X, Ge B, Liu Z, Shiji Z (1998) A newer plate system for internal fixation of un-stable pelvic fractures. Int Surg 83:88–90
Willy C, Schmidt R, Gerngross H, Friemert B (2004) Treatment of trans-symphyseal instability with an internal fixator. Outcome of a surgical technique on the basis of a case report. Unfallchirurg 107:706–708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giannoudis, P.V., Chalidis, B.E. & Roberts, C.S. Internal fixation of traumatic diastasis of pubic symphysis: is plate removal essential?. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128, 325–331 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0429-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0429-1