Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to identify radiological predictors of early and late instability following conservative treatment of extra-articular distal radius fractures.
Materials and methods
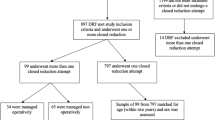
An observational study design was employed using patient records and standardized radiological follow-up examinations as data sources. The database at a single institution was used to identify all patients with extra-articular distal radius fractures over the course of 1 year. A total of 71 patients with extra-articular distal radius fractures (50 dorsally displaced, 21 undisplaced) fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Patients were predominantly female (87%) with a pooled mean age of 64.9 years. All patients with displaced extra-articular distal radius fractures underwent closed reduction with subsequent cast immobilization. Undisplaced fractures were simply treated with cast immobilization. The primary outcomes were early (1 week) and late (6 weeks) instability of the fracture. Instability was defined as: (1) dorsal tilt >15°, (2) volar tilt >20°, (3) ulnar variance >4 mm, (4) radial inclination <10°.
Results
Degree of radial shortening and volar tilt were predictive of early instability (p<0.05), with dorsal comminution also approaching statistical significance (p=0.06). Radial inclination, age, radial shortening, and volar tilt were predictive of late failure (p<0.05). An unexpected result showed that one-third of undisplaced fractures went on to fail, most of which occurred in those patients over the age of 65 years.
Conclusion
An awareness of independent predictors of instability in extra-articular distal radius fractures is helpful in anticipating the final alignment outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaszadegan H, Jonsson U, Sivers K von (1989) Prediction of instability of Colles’ fractures. Acta Orthop Scand 60:646–650
Altissimi M, Mancini G, Azzara A, Ciaffoloni E (1994) Early and late displacement of fractures of the distal radius: the prediction of instability. Int Orthop 18:61–65
Beumer A, McQueen MM (2003) Fractures of the distal radius in low-demand elderly patients: closed reduction of no value in 53 of 60 wrists. Acta Orthop Scand 74:98–100
Cassebaum WH (1950) Colles’ fracture: a study of end results. JAMA 143:963–967
Cooney W, Lindscheid R, Dobyns J (1979) External pin fixation for unstable Colles’ fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 61:840–845
Cooney WP, Agee JM, Hastings H et al (1990) Management of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. Contemp Orthop 21:71–104
Dias JJ, Wray CC, Jones JM, Gregg PJ (1987) The value of early mobilization in the treatment of Colles’ fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:463–467
Dias JJ, Wray CC, Jones JH (1987) The radiological deformity of Colles’ fractures. Injury 18:304–308
Dobyns JH (ed) (1998) The wrist: diagnosis and operative treatment. Mosby, St. Louis
Fernandez DL, Palmer AK (1998) Fractures of the distal radius. In: Green’s operative hand surgery, 4th edn. Churchill-Livingstone, New York
Flish CW, Della Santa DR (1998) Osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures by flexible intramedullary nailing (Geneva experience). Chir Main 17:245–254
Gibson A, Bannister G (1983) Bracing or plaster for Colles’ fractures. A randomized prospective controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 65:221
Hove L, Solhein E, Skjeie R, Sorensen F (1994) Prediction of secondary displacement in Colles fractures. J Hand Surg Br 19:731–736
Jenkins NH, Jones DG, Johnson SR, Mintowt-Czyz WT (1987) External fixation of Colles’ fractures: an anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:207–211
Jenkins NH, Mintowt-Czyz WJ (1988) Mal-union and dysfunction in Colles’ fracture. J Hand Surg Br 13:291–293
Jupiter JB (1991) Current concepts review: fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:461–469
Jupiter JB, Ring D, Weitzel PP (2002) Surgical treatment of redisplaced fractures of the distal radius in patients older than 60 years. J Hand Surg Am 27:714–723
Lafontaine M, Hardy D, Delince P (1989) Stability assessment of distal radius fractures. Injury 20:208–210
McAuliffe TB, Hilliar KM, Coates CJ, Grange WJ (1987) Early mobilization of Colles’ fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:727–729
McQueen MM, Caspers J (1988) Colles’ fracture: does the anatomical result affect the final function? J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:649–651
Owen RA, Melton LJ, Johnson KA, Ilstrup DM, Riggs BL (1982) Incidence of Colles’ fracture in a North American community. J Bone Joint Surg 72:605–607
Porter M, Stockley I (1987) Fractures of the distal radius. Intermediate and end results in relation to radiological findings. Clin Orthop 220:241–252
Sarmiento A, Zagorski JB, Sinclair WF (1980) Functional bracing of Colles’ fractures: a prospective study of immobilization in supination and pronation. Clin Orthop 146:175–183
Schmalholz A (1989) Closed rereduction of axial compression in Colles’ fracture is hardly possible. Acta Orthop Scand 60:57–59
Solgaard S (1986) Early displacement of distal radius fracture. Acta Orthop Scand 57:229–231
Van der Linden W, Ericson R (1981) Colles’ fracture. How should its displacement be measured and how should it be immobilized? J Bone Joint Surg Am 63:1285–1288
Vaughan A, Spencer M, Harrington IJ et al (1985) Treatment of unstable fractures of the distal end radius by external fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 67:385–390
Wilson C, Venner RM (1984) Colles’ fractures: Immobilization in pronation or supination. J R Coll Surg Edinb 29:109–111
Young BT, Vernal UT, Ghazi MR (2000) Outcome following nonoperative treatment of displaced distal radius fractures in low-demand patients older than 60 years. J Hand Surg Am 25:19–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leone, J., Bhandari, M., Adili, A. et al. Predictors of early and late instability following conservative treatment of extra-articular distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124, 38–41 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0597-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0597-6