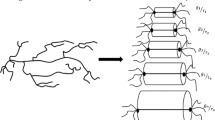
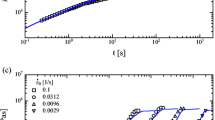
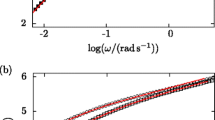
Abstract
The constitutive equation as reported by Rasmussen and Huang (Rheologica Acta 53:199–208, 2014b), explaining the flow dynamics of oligomer (containing a least two Kuhn step)-diluted narrow molecular weight-distributed polymers were extended to general bi-disperse polymer melt system. It was assumed that the Rouse time of a particular polymer chain is dependent on the total number of Kuhn steps of the polymers in direct contact with the considered polymer chain. This number of Kuhn steps is proportional to the weight average molecular weight, M w , replacing the involved molecular weight in the equation as reported by Rasmussen and Huang (Rheologica Acta 53:199–208, 2014b). Two separate stretch evolution equations for the long and the short polymer respectively, were introduced to handle the two involved Rouse times. Experimentally, the bi-disperse polystyrene systems of Nielsen et al. (J Rheol 50:453–476, 2006) and polyisoprene systems as reported by Read et al. (J Rheol 56:823–873, 2012) were within quantitatively agreement with the derived model. This included both startup of extension as well as shear flow. One exception was observed. In the most diluted polyisoprene blend, the measured extensional viscosities were under predicted by the model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auhl D, Chambon P, McLeish TCP, Read DJ (2009) Elongational flow of blends of long and short polymers: effective stretch relaxation time. Phys Rev Lett 103:136001
Auhl D, Ramirez J, Likhtman AE, Chambon P, Fernyhough C (2008) Linear and nonlinear shear flow behavior of monodisperse polyisoprene melts with a large range of molecular weights. J Rheol 52 (3):801–835
Bach A, Almdal K, Rasmussen HK, Hassager O (2003) Elongational viscosity of narrow molar mass distribution polystyrene. Macromolecules 36(14):5174–5179
Baumgaertel M, Schausberger A, Winter HH (1990) The relaxation of polymers with linear flexible chains of uniform length. Rheol Acta 29(5):400–408
Bhattacharjee PK, Oberhauser JP, McKinley GH, Leal LG, Sridhar T (2002) Extensional rheometry of entangled solutions. Macromolecules 35(27):10131–10148
Boukany PE, Wang SQ, Wang XR (2009) Universal scaling behavior in startup shear of entangled linear melts. J Rheol 53(3):617–629
Desai PS, Larson RG (2014) Constitutive model that shows extension thickening for entangled solutions and extension thinning for melts. J Rheol 58(1):255–279
des Cloizeaux J (1988) Double reptation vs. simple reptation in polymer melts. Europhys Lett 5 (5):437–442
Dhole S, Leygue A, Bailly C, Keunings R (2009) A single segment differential tube model with interchain tube pressure effect. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 161(1-3):10–18
Desai PS, Larson RG (2014) Constitutive model that shows extension thickening for entangled solutions and extension thinning for melts. J Rheol 58(1):255–279
Doi M, Edwards SF (1986) The theory of polymer dynamics. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Doi M, Pearson D., Kornfield J, Fuller G (1989) Effect of nematic interaction in the orientational relaxation of polymer melts. Macromolecules 22(3):1488–1490
Doi M, Watanabe HA (1991) Effect of nematic interaction on the Rouse dynamics. Macromolecules 24 (3):740–744
Fetters LJ, Lohsey DJ, Colby R H (2007) Chain dimensions and entanglement spacings: physical properties of polymers Handbook, 2nd ed. Springer Science, New York, pp 445–452
Huang Q, Mednova O, Rasmussen HK, Alvarez NJ, Skov AL, Almdal K, Hassager O (2013a) Concentrated polymer solutions are different from melts: role of entanglement molecular weight. Macromolecules 46(12):5026–5035
Huang Q, Alvarez NJ, Matsumiya Y, Rasmussen HK, Watanabe H, Hassager O (2013b) Extensional rheology of entangled polystyrene solutions suggests importance of nematic interactions. ACS Macro Lett 2(8):741–744
Huang Q, Rasmussen HK, Skov AL, Hassager O (2012) Stress relaxation and reversed flow of low-density polyethylene melts following uniaxial extension. J Rheol 56(6):1535–1554
Jackson JK, Winter HH (1995) Entanglement and flow behavior of bidisperse blends of polystyrene and polybutadiene. Macromolecules 28(9):3146–3155
Khaliullin RN, Schieber JD (2010) Application of the slip-link model to bidisperse systems. Macromolecules 43(14):6202–6212
Kolte MI, Rasmussen HK, Hassager O (1997) Transient filament stretching rheometer II: numerical simulation. Rheol Acta 36(3):285–302
Krishnamoorti R, Graessley WW, Zirkel A, Richter D, Hadjichristidis N, Fetters LJ, Lohse D J (2002) Melt-state polymer chain dimensions as a function of temperature. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 40(16):1768–1776
Larson RG, Sridhar T, Leal LG, McKinley GH, Likhtman AE, McLeish TCB (2003) Definitions of entanglement spacing and time constants in the tube model. J Rheol 47(3):809–818
Likhtman AE, McLeish TCB (2002) Quantitative theory for linear dynamics of linear entangled polymers. Macromolecules 35(16):6332–6343
Marrucci G (1996) Dynamics of entanglements: a nonlinear model consistent with the Cox-Merz rule. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 62(2-3):279–289
Menezes EV, Graessley W W (1982) Nonlinear rheological behavior of polymer systems for several shear-flow histories. J Polym Sci Part B - Polym Phys 20(10):1817–1833
Nielsen JK, Rasmussen HK, Hassager O, McKinley GH (2006) Elongational viscosity of monodisperse and bidisperse polystyrene melts. J Rheol 50(4):453–476
Osaki K, Inoue T, Isomura T (2000) Stress overshoot of polymer solutions at high rates of shear. J Polym Sci Part B - Polym Phys 38(14):1917–1925
Osaki K, Inoue T, Uematsu T, Yamashita Y (2001) Evaluation methods of the longest Rouse relaxation time of an entangled polymer in a semidilute solution. J Polym Sci Part B - Polym Phys 39(14):1704–1712
Park J, Mead DW, Denn MM (2012) Stochastic simulation of entangled polymeric liquids in fast flows: microstructure modification. J Rheol 56(5):1057–1081
Park SJ, Larson RG (2004) Tube dilation and reptation in binary blends of monodisperse linear polymers. Macromolecules 37(2):597–604
Rasmussen HK, Bejenariu AG, Hassager O, Auhl D (2010) Experimental evaluation of the pure configurational stress assumption in the flow dynamics of entangled polymer polymer melts. J Rheol 54(6):1325–1336
Rasmussen HK, Christensen JH, Gøttsche SJ (2000) Inflation of polymer melts into elliptic and circular cylinders. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 93(2-3):245–263
Rasmussen HK, Huang Q (2014a) The missing link between the extensional dynamics of polymer melts and solutions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 204 (1):1–6
Rasmussen HK, Huang Q (2014b) Interchain tube pressure effect in extensional flows of oligomer diluted nearly monodisperse polystyrene melts. Rheol Acta 53 (3):199–208
Read DJ, Jagannathan K, Sukumaran SK, Auhl D (2012) A full-chain constitutive model for bidisperse blends of linear polymers. J Rheol 56(4):823–873
Schweizer T, Meerveld J, Öettinger HC (2004) Nonlinear shear rheology of polystyrene melt with narrow molecular weight distributionexperiment and theory. J Rheol 48(6):1345–1363
Sentmanat ML (2004) Miniature universal testing platform: from extensional melt rheology to solid-state deformation behavior. Rheol Acta 43:657–669
Spiegelberg SH, Ables DC, McKinley GH (1996) The role of end-effects on measurements of extensional viscosity in filament stretching rheometers. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 64 (2-3):229–267
Struglinski MJ, Graessley WW (1985) Effects of polydispersity on the linear viscoelastic properties of entangled polymers I. Experimental observations for binary mixtures of linear polybutadiene. Macromolecules 18(12):2630–2643
Szabo P (1997) Transient filament stretching rheometer part I: force balance analysis. Rheol Acta 36(3):277–284
van Ruymbeke E, Nielsen J, Hassager O (2010) Linear and nonlinear viscoelastic properties of bidisperse linear polymers: mixing law and tube pressure effect. J Rheol 54(5):1155–1172
Vinogradov G V, Malkin A Y, Volosevitch V V (1975) Flow, high-elastic (recoverable) deformation, and rupture of uncured high molecular weight linear polymers in uniaxial extension. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 13(9):1721–1735
Wagner M H, Kheirandish S, Hassager O (2005) Quantitative prediction of transient and steady-state elongational viscosity of nearly monodisperse polystyrene melts. J Rheol 49(6):1317–1327
Wagner M H, Rolon-Garrido V H, Nielsen J K, Rasmussen H K, Hassager O (2008) A constitutive analysis of transient and steady-state elongational viscosities of bidisperse polystyrene blends. J Rheol 52(1):67–86
Wang Y Y, Cheng S W, Wang S Q (2011) Basic characteristics of uniaxial extension rheology: comparing monodisperse and bidisperse polymer melts. J Rheol 5(6):1247–1270
Yaoita T, Isaki T, Masubuchi Y, Watanabe H, Ianniruberto G, Marrucci G (2012) Primitive chain network simulation of elongational flows of entangled linear chains: stretch/orientation-induced reduction of monomeric friction. Macromolecules 45 (6):2773–2782
Ye X, Sridhar T (2005) Effects of the polydispersity on rheological properties of entangled polystyrene solutions. Macromolecules 38(8):3442–3449
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmussen, H.K. Interchain tube pressure effect in the flow dynamics of bi-disperse polymer melts. Rheol Acta 54, 9–18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-014-0816-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-014-0816-9