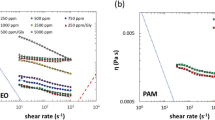
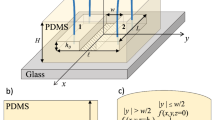
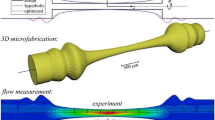
Abstract
Microfluidic devices are ideally suited for the study of complex fluids undergoing large deformation rates in the absence of inertial complications. In particular, a microfluidic contraction geometry can be utilized to characterize the material response of complex fluids in an extensionally-dominated flow, but the mixed nature of the flow kinematics makes quantitative measurements of material functions such as the true extensional viscosity challenging. In this paper, we introduce the ‘extensional viscometer-rheometer-on-a-chip’ (EVROC), which is a hyperbolically-shaped contraction-expansion geometry fabricated using microfluidic technology for characterizing the importance of viscoelastic effects in an extensionally-dominated flow at large extension rates (\(\lambda \dot \varepsilon _a \gg 1\), where \(\lambda \) is the characteristic relaxation time, or for many industrial processes \(\dot \varepsilon _a \gg 1\) s\(^{-1}\)). We combine measurements of the flow kinematics, the mechanical pressure drop across the contraction and spatially-resolved flow-induced birefringence to study a number of model rheological fluids, as well as several representative liquid consumer products, in order to assess the utility of EVROC as an extensional viscosity indexer.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams EB, Whitehead JC, Bogue DC (1965) Stresses in a viscoelastic fluid in converging and diverging flow. AIChE J 11(6):1026–1032
Afonso AM, Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT, Alves MA (2011) Dynamics of high-Deborah-number entry flows: a numerical study. J Fluid Mech 677:272–304
Aguayo JP, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF (2008) Excess pressure-drop estimation in contraction and expansion flows for constant shear-viscosity, extension strain-hardening fluids. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 153(2–3):157–176
Baek SG, Magda JJ (2003) Monolithic rheometer plate fabricated using silicon micromachining technology and containing miniature pressure sensors for N 1 and N 2 measurements. J Rheol 47(5):1249–1260
Bandalusena HCH, Zimmerman WB, Rees JM (2009) Microfluidic rheometry of a polymer solution by micron resolution particle image velocimetry: a model validation study. Meas Sci Technol 20(11):115404
Bandalusena HCH, Zimmerman WB, Rees JM (2010) Creeping flow analysis of an integrated microfluidic device for rheometry. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 165(19–20):1302–1308
Binding DM, Walters K (1988) On the use of flow through a contraction in estimating the extensional viscosity of mobile polymer solutions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 30(2–3):233–250
Bird RB, Armstrong RC, Hassager O (1987) Dynamics of polymeric liquids, Vol 1, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Cates ME, Fielding SM (2006) Rheology of giant micelles. Adv Phys 55(7–8):799–879
Cogswell FN (1972) Converging flow of polymer melts in extrusion dies. Polym Eng Sci 12(1):64–73
Cogswell FN (1978) Converging flow and stretching flow: a compilation. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 4(1–2):23–38
Collier JR, Romanoschi O, Petrovan S (1998) Elongational rheology of polymer melts and solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 69:2357–2367
Dubash N, Cheung P, Shen AQ (2012) Elastic instabilities in a microfluidic cross-slot flow of wormlike micellar solutions. Soft Matter 8:5847–5856
Everage AE, Ballman RL (1978) The extensional flow capillary as a new method for extensional viscosity measurement. Nature 273(5669):213–215
Feigl K, Tanner FX, Edwards BJ, Collier JR (2003) A numerical study of the measurement of elongational viscosity of polymeric fluids in a semihyperbolically converging die. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 115:191–215
Ferer M, Anna SL, Tortora P, Kadambi JR, Oliver M, Bromhal GS, Smith DH (2011) Two-phase flow in porous media: predicting its dependence on capillary number and viscosity ratio. Transp Porous Med 86(1):273–289
Fuller GG (1990) Optical rheometry. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 22:387–417
Galindo-Rosales FJ, Alves MA, Oliveira MSN (2013) Microdevices for extensional rheometry of low viscosity elastic liquids: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid 14(1–2):1–19
Groisman A, Quake SR (2004) A microfluidic rectifier: anisotropic flow resistance at low Reynolds numbers. Phys Rev Lett 92(9):094501
Han CD, Drexler LH (1973a) Studies of converging flows of viscoelastic polymeric melts. 1. Stress-birefringent measurements in entrance region of a sharp-edged slit die. J Appl Polym Sci 17(8):2329–2354
Han CD, Drexler LH (1973b) Studies of converging flows of viscoelastic polymeric melts. 3. Stress and velocity distributions in entrance region of a tapered slit die. J Appl Polym Sci 17(8):2369–2393
Hashimoto T, Kido K, Kaki S, Yamamoto T, Mori N (2006) Effects of surfactant and salt concentrations on capillary flow and its entry flow for wormlike micelle solutions. Rheol Acta 45(6):841–852
Haward SJ, Ober TJ, Oliveira MSN, Alves MA, McKinley GH (2012a) Extensional rheology and elastic instabilities of a wormlike micellar solution in a microfluidic cross-slot device. Soft Matter 8(2):536–555
Haward SJ, McKinley GH (2012) Stagnation point flow of wormlike micellar solutions in a microfluidic cross-slot device: effects of surfactant concentration and ionic environment. Phys Rev E 85:031502
Haward SJ, Oliveira MSN, Alves MA, McKinley GH (2012b) Optimized cross-slot flow geometry for microfluidic extensional rheometry. Phys Rev Lett 109(12):128301
Hudson SD, Phelan FR Jr, Handler MD, Cabral JT, Migler KB, Amis EJ (2004) Microuidic analog of the four-roll mill. Appl Phys Lett 85(2):335–337
James DF, Saringer JH (1982) Flow of dilute polymer solutions through converging channels. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 11:317–339
James DF (1991) Flow in a converging channel at moderate Reynolds-numbers. AIChE J 37(1):59–64
Janeschitz-Kriegl H (1983) Polymer melt rheology and flow birefringence. Springer-Verlag, New York
Kang K, Koelling KW, Lee LJ (2006) Microdevice end pressure evaluations with Bagley correction. Microfluid Nanofluid 2(3):223–235
Lee JS, Dylla-Spears R, Teclemariam NP, Muller SJ (2007) Microfluidic four-roll mill for all flow types. Appl Phys Lett 90(7):074103
Lerouge S, Berret J-F (2010) Shear-induced transitions and instabilities in surfactant wormlike micelles. In: Dusek K, Joanny J-F (eds) Polymer characterization of advances in polymer science, vol 230. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–71
Marín-Santibáñez BM, Pérez-González J, de Vargas L, Decruppe JP, Huelsz G (2009) Visualization of shear banding and entry Poiseuille flow oscillations in a micellar aqueous solution. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 157(1–2):117–125
Masselon C, Salmon JB, Colin A (2008) Nonlocal effects in flows of wormlike micellar solutions. Phys Rev Lett 100(3):038301
McKinley GH, Tripathi A (2000) How to extract the Newtonian viscosity from capillary breakup measurements in a filament rheometer. J Rheol 44(3): 653–670
Meinhart CD, Wereley ST, Gray MHB (2000) Volume illumination for two-dimensional particle image velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 11(6):809–814
Nyström M, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Stading M, Webster MF (2012) Numerical simulations of Boger fluids through different contraction configurations for the development of a measuring system for extensional viscosity. Rheol Acta 51:713–727
Ober TJ, Soulages J, McKinley GH (2011) Spatially resolved quantitative rheo-optics of complex fluids in a microfluidic device. J Rheol 55(5):1127–1159
Oliveira MSN, Alves MA, Pinho FT, McKinley GH (2007) Viscous flow through microfabricated hyperbolic contractions. Exp Fluid 43(2–3):437–451
Oliveira MSN, Rodd LE, McKinley GH, Alves MA (2008) Simulations of extensional flow in microrheometric devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 5(6):809–826
Pandey A, Lele A (2007) Exploring the utility of an axisymmetric semi-hyperbolic die for determining the transient uniaxial elongation viscosity of polymer melts. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 144:170–177
Pathak JA, Hudson SD (2006) Rheo-optics of equilibrium polymer solutions: Wormlike micelles in elongational flow in a microfluidic cross-slot. Macromolecules 39(25):8782–8792
Pipe CJ, Majmudar TS, McKinley GH (2008) High shear rate viscometry. Rheol Acta 47(5–6):621–642
Pipe CJ, McKinley GH (2009) Microfluidic rheometry. Mech Res Commun 36(1):110–120
Rajagopalan D (2000) Computational analysis of techniques to determine extensional viscosity from entrance flows. Rheol Acta 39:138–151
Rodd LE, Scott TP, Boger DV, Cooper-White JJ, McKinley GH (2005) The inertio-elastic planar entry flow of low-viscosity elastic fluids in micro-fabricated geometries. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 129(1):1–22
Rodd LE, Cooper-White JJ, Boger DV, McKinley GH (2007) Role of the elasticity number in the entry flow of dilute polymer solutions in micro-fabricated contraction geometries. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 143:170–191
Schuberth S, Münstedt H (2008) Transient elongational viscosities of aqueous polyacrylamide solutions measured with an optical rheometer. Rheol Acta 47(2):139–147
Sousa PC, Pinho FT, Oliveira MSN, Alves A (2011) Extensional flow of blood analog solutions in microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 5:014108
Sousa PC, Pinho FT, Oliveira MSN, Alves MA (2012) High performance microfluidic rectifiers for viscoelastic fluid flow. RSC Adv 2(3):920–929
Stone PA, Hudson SD, Dalhaimer P, Discher DE, Amis EJ, Migler KB (2006) Dynamics of wormlike micelles in elongational flows. Macromolecules 39(20):7144–7148
Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF, Aguayo JP, Manero O (2011) Numerical investigation of transient contraction flows for worm-like micellar systems using Bautista–Manero models. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 166(1–2):102–117
Vasudevan M, Buse E, Lu D, Krishna H, Kalyanaraman R, Shen AQ, Khomami B, Sureshkumar R (2010) Irreversible nanogel formation in surfactant solutions by microporous flow. Nat Mater 9(5):436–441
Wang J, James DF, Park CB (2010) Planar extensional flow resistance of a foaming plastic. J Rheol 54(1):95–116
Wang J, James DF (2011) Lubricated extensional flow of viscoelastic fluids in a convergent microchannel. J Rheol 55(5):1103–1126
White FM (2006) Viscous fluid flow, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Seong-Gi Baek and Dr. Ying-Chih Wang of Rheosense, Inc. for material support in the form of the EVROC chips and associated hardware. We also are grateful to Dr. Mónica Oliveira, Dr. Trushant Majmudar and Dr. Vivek Sharma for helpful discussions. TJO acknowledges the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship for funding. SJH acknowledges funding from NASA Microgravity Fluid Sciences (grant NNX09AV99G) and the European Commission under Marie Curie action FP7-PEOPLE-2011-IIF (grant 298220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ober, T.J., Haward, S.J., Pipe, C.J. et al. Microfluidic extensional rheometry using a hyperbolic contraction geometry. Rheol Acta 52, 529–546 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0701-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0701-y