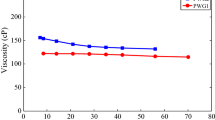
Abstract
This work deals with in situ visualisation of deformation and breakup of a copolymer modified single Newtonian drop immersed in a Newtonian homogenous matrix. The experiments were carried out on a model system made of poly-isobutylene as the suspending fluid and two poly-dimethylsiloxanes with different molecular weights as the drop phase with viscosity ratios 0.036 and 1.13, below and above but close to unity. Three weight concentrations 0.5%, 2% and 10% of the block copolymer laying below, close to and above the critical concentration of the total drop surface coverage were examined. Single drop deformation experiments were carried out in a home-designed Couette quartz cell connected to a home-modified Paar Physica Rheometer. The variation in the length-to-diameter ratio (L/D) versus shear rate and capillary number was measured both in steady and in transient regimes till breakup. The results indicated a weaker resistance of copolymer modified drops against hydrodynamic stresses at both viscosity ratios as compared to the clean drop. However, the drop deformation was found to be complex and depends on the copolymer concentration and the viscosity ratio.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbassi-Sourki F, Huneault MA, Bousmina M (2009) Effect of compatibilization on the deformation and breakup of drops in step-wise increasing shear flow. Polymer 50:645–653
Almusallam AS, Larson RG, Solomon MJ (2000) A constitutive model for the prediction of ellipsoidal droplet shapes and stresses in immiscible polymer blends. J Rheol 44:1055–1083
Bazhlekov IB, Anderson PD, Meijer MEH (2004) Boundary integral method for deformable interfaces in the presence of insoluble surfactants. Lect Notes Comput Sci 2907:355–362
Bazhlekov IB, Anderson PD, Meijer MEH (2006) Numerical investigation of the effect of insoluble surfactants on drop deformation and breakup in simple shear flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 298:369–394
Bentley BJ, Leal LG (1986) An experimental investigation of drop deformation and breakup in steady, two-dimensional linear flows. J Fluid Mech 167:241–283
Bousmina M, Aouina M, Chaudhry B, Guenette R, Bretas RES (2001) Rheology of polymer blends: non-linear model for viscoelastic emulsions undergoing high deformation flows. Rheol Acta 40:538–551
Bousmina M, Mechbal N, Gagne S (2007) US Patent, WO/033479
Cardinaels R, Verhulst K, Moldenaers P (2009) Influence of confinement on the steady state behavior of single droplets in shear flow for immiscible blends with one viscoelastic component. J Rheol 53:1403–1424
Chen J, Stebe KJJ (1996) Marangoni retardation of the terminal velocity of a settling droplet: the role of surfactant physico-chemistry. J Colloid Interface Sci 178:144–155
Deyrail Y, El Mesri Z, Huneault M, Zeghloul A, Bousmina M (2007) Note on the morphology determination in emulsions via rheology. J Rheol 51:781–797
Deyrail Y, Huneault M, Bousmina M (2009) Rheo-optical study of nonlinear effects in an immiscible Newtonian polymer blend under large amplitude oscillatory shear flow. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 15:1467–1480
Eggleton CD, Tsai TM, Stebe K (2001) Tip streaming from a drop in the presence of surfactants. Phys Rev Lett 87:1–4
Grace HP (1982) Dispersion in high viscosity immiscible fluid systems and application of static mixers as dispersion devices in such systems. Chem Eng Commun 14:225–277
Gu JF, Grmela M, Bousmina M (2008) A mesoscopic rheological model of immiscible blends with the interface covered with a surface active agent. Phys Fluids 20:043102–1
Guido S, Greco F (2001) Drop shape under slow steady shear flow and during relaxation. Experimental results and comparison with theory. Rheol Acta 40:176–184
Guido S, Greco F (2004) Dynamics of a liquid drops in a flowing immiscible liquid. Rheol Rev 71:99–142
Guido S, Greco F, Villone M (1999) Experimental determination of drop shape in slow steady flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 219:298–309
Guido S, Minale M, Maffettone PL (2000) Drop shape dynamics under shear-flow reversal. J Rheol 44:1385–1399
Guido S, Simeone M, Greco F (2003) Effects of matrix viscoelasticity on drop deformation in dilute polymer blends under slow shear flow. Polymer 44:467–471
Hu TY, Pine DJ, Leal LG (2000) Drop deformation, breakup, and coalescence with compatibilizer. Phys Fluids 12:484–489
Iza M, Bousmina M (2000) Nonlinear rheology of immiscible polymer blends: step strain experiments. J Rheol 44:1363–1384
Iza M, Bousmina M, Jerome R (2001) Rheology of compatibilized immiscible viscoelastic polymer blends. Rheol Acta 40:10–22
Janssen PJA, Anderson PD (2007) Boundary-integral method for drop deformation between parallel plates. Phys Fluids 19:043602
Janssen PJA, Anderson PD (2008) Surfactant-covered drops between parallel plates. Chem Eng Res Des 86:1388–1396
Janssen JMH, Meijer HEH (1993) Droplet breakup mechanisms: stepwise equilibrium versus transient dispersion. J Rheol 37:597–608
Jeon HK, Macosko CW (2003) Visualization of block copolymer distribution on a sheared drop. Polymer 44:5581–5386
Karam HJ, Bellinger JC (1968) Deformation and breakup of liquid droplets in a simple shear field. Ind Engng Chem Fund 7:576–581
Keestra BJ, Van Puyvelde P, Anderson PD, Meijer HEH (2003) Diffuse interface modeling of the morphology and rheology of immiscible polymer blends. Phys. Fluids 15:2567–2575
Levitt LC, Macosko CW (2009) Shearing of polymer drops with interface modification. Macromolecules 32:6270–6277
Li X, Pozrikidis C (1997) The effect of surfactant on the drop deformation and on the rheology of dilute emulsions in Stokes flow. J Fluid Mech 341:165–194
Macosko CW (2000) Morphology development and control in immiscible polymer blends. Macromol Symp 149:171–184
Macosko CW, Guegan P, Khandpur AK, Nakayama A, Marechal P, Inoue T (1996) Compatibilizers for melt blending: premade block copolymers. Macromolecules 29:5590–5598
Maffettone PL, Minale M (1998) Equation of change foe ellipsoidal drops in viscous flow. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 78:227–241
Mark JE (1996) Physical properties of polymers handbook. AIP, New York
Mechbal N, Bousmina M (2007) Effect of copolymer addition on drop deformation during uniaxial elongation and during relaxation after cessation of flow. Macromolecules 40:967–975
Mechbal N, Bousmina M (2009) In situ observation of unusual drop deformation and wobbling in simple shear flow. Rheol Acta 6:653–663
Milliken WJ, Stone HA, Leal LG (1993) The effect of surfactant on the transient motion of Newtonian drops. Phys Fluids A 5:69–79
Pawar Y, Stebe KJ (1996) Marangoni effects on drop deformation in extensional flow: the role of surfactant physical chemistry 1. Insoluble surfactants. Phys Fluids 8:1738–1751
Rumscheidt FD, Mason SG (1961) Particle motion in sheared suspentions, XII. Deformation and burst of fluid drops in shear and hyperbolic flow. J Colloid Sci 16:238–261
Stone HA (1994) Dynamics of drop deformation and breakup in viscous fluids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 26:65–102
Stone HA, Leal LG (1989) The influence of initial deformation on drop breakup in subcritical time-dependent flows at low Reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 206:223–263
Stone HA, Leal LG (1990) The effects of surfactants on drop deformation and breakup. J Fluid Mech 220:161–86
Sundararaj U, Macosko CW (1992) Morphology development in polymer r blends. Polym Eng Sci 32:1814–1823
Taylor GI (1932) The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another fluid. Proc R Soc London Ser A 138:41–48
Taylor GI (1934) The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow. Proc R Soc London Ser A 146:501–523
Tucker III CL, Moldenaers P (2002) Microstructural evolution in polymer blends. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 34:177–210
Van Hemelrijck E, Van Puyvelde P, Velankar S, Macosko CW, Moldenaers P (2004) Interfacial elasticity and coalescence suppression in compatibilized polymer blends. J Rheol 48:143–158
Van Hemelrijck E, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2006) Rheology and morphology of highly compatibilized polymer blends. Macromol Symp 233:51–58
Vananroye A, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2006) Structure development in confined polymer blends: steady state shear flow and relaxation. Langmuir 22:2273–2280
Vananroye A, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2007) Effect of confinement on the steady-state behavior of single droplets during shear flow. J Rheol 51:139–153
Vananroye A, Janssen PJA, Anderson PD, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2008) Microconfined equiviscous droplet deformation: comparison of experimental and numerical results. Phys Fluids 20:013101–1
Van Puyvelde P, Velankar S, Moldenaers P (2001) Rheology and morphology of compatibilized polymer blends. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 6:457–463
Van Puyvelde P, Velankar S, Mewis J, Moldenaers P (2002) Effect of Marangoni stresses on the deformation and coalescence in compatibilized immiscible polymer blends. Polym Eng Sci 42:1956–1964
Velankar S, Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2001) Effect of compatibilization on the breakup of polymeric drops in shear flow. J Rheol 45:1007–1019
Verhulst K, Moldenaers P, Minale M (2007) Drop shape dynamics of a Newtonian drop in a non-Newtonian matrix during transient and steady shear flow. J Rheol 51:261–273
Verhulst K, Cardinaels R, Moldenaers P, Afkhami S, Renardy Y (2009) Influence of viscoelasticity on drop deformation and orientation in shear flow. Part 2: dynamics. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 156:44–57
Vinckier I, Mewis J, Moldenaers P (1997) Stress relaxation as a microstructural probe for immiscible polymer blends. Rheol Acta 36:513–523
Vinckier I, Mewis J, Moldenaers P (1999a) Elastic recovery of immiscible blends part 2: transient flow histories. Rheol Acta 38:198–205
Vinckier I, Minale M, Mewis J, Moldenaers P (1999b) Rheology of semi-dilute emulsions: viscoelastic effects caused by the interfacial tension. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 150:217–228
Vinckier I, Moldenaers P, Mewis J (1999c) Elastic recovery of immiscible blends part 1. Analysis after steady state shear flow. Rheol Acta 38:65–72
Yamane H, Takahashi M, Okamoto K, Masuda T (1998) Observation of deformation and recovery of PIB droplet in a PIB/PDMS blend after application of step shear strain. J Rheol 42:567–580
Yeo LY, Matar OK, Perez de Oritz ES, Hewitt GFJ (2001) The dynamics of Marangoni-driven local film drainage between two drops. J Colloid Interface Sci 241:233–247
Yu W, Bousmina M (2003) Ellipsoidal model for droplet deformation in emulsions. J Rheol 47:1011–1039
Yu W, Bousmina M, Zhou C, Tucker III CL (2004) Theory for drop deformation in viscoelastic systems. J Rheol 48:417–438
Yu W, Zhou C, Bousmina M (2005) Theory of morphology evolution in mixtures of viscoelastic immiscible blends. J Rheol 49:215–236
Yu W, Bousmina M, Zhou C (2006) Note on the morphology determination in emulsions via rheology. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 133:57–62
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the NSERC (Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada) and Canada Research Chair on Polymer Physics and Nanomaterials and Steacie fellowship grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbassi-Sourki, F., Bousmina, M. & Huneault, M.A. Effect of interfacial modifier on single drop deformation and breakup in step increasing shear flow. Rheol Acta 51, 111–126 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0602-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0602-x