Abstract
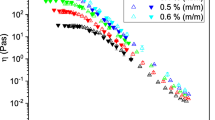
Mixtures of xanthan and guar gum in aqueous solution were studied in two flow situations: simple shear and porous media. In addition, solids transport in vertical annular flow of sand suspensions was explored. The zero shear rate viscosity of the solutions displayed a pronounced synergy: the viscosity of the mixture is higher than that of the polymer solutions in a wide range of relative concentrations of the two polymers, in agreement with previous literature. However, at relatively high shear rates, the viscosity approaches the value of the more viscous xanthan gum solutions at mass fractions of xanthan gum between 0.1 and 0.15, and the degree of synergy substantially decreases. Stress relaxation experiments in simple shear indicate that the polymer mixtures exhibit a well-defined yield stress after relaxation that is absent in solutions of pure polymers. In porous media flow experiments, a synergistic behavior mimicking the shear flow results was obtained for the polymer mixtures at low shear rates. However, at a critical shear rate, the apparent viscosity in porous media flows exceeds the shear viscosity due to the elongational nature of flow in the pores. The solids transport capacity in annular flows is well-represented by trends in shear viscosity and stress relaxation behavior. However, the lack of viscosity synergy at high shear rates limits the applicability of the mixtures as a way to improve solids suspension capacity in annular flows.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloodworth BR, Keely GL, Clark PE (1992) Mud relaxations measurements help predict hole cleaning ability. Oil Gas J 90:73–78
Cairns P, Miles MJ, Morris VJ (1986) Intermolecular binding of xanthan gum and carob gum. Nature 322:89–90
Casas JA, Mohedano A, García-Ochoa F (2000) Viscosity of guar gum and xanthan/guar gum mixture solutions. J Sci Food Agric 80:1722–1727
Chien SF (1994) Settling velocity of irregularly shaped particles. SPE Drill Complet 9:281–289
Fernandes PB (1995) Influence of galactomannan on the structure and thermal behaviour of xanthan/galactomannan mixtures. J Food Eng 24:269–283
González JM, Müller AJ, Torres MF, Sáez AE (2005) The role of shear and elongation in the flow of semi-flexible polymers through porous media. Rheol Acta 44:396–405
Lopes L, Andrade CT, Milas H, Rinaudo M (1992) Role of conformation and acetylation of xanthan on xanthan–guar interaction. Carbohydr Polym 17:121–126
Lundin L, Hermansson AM (1995) Supermolecular aspects of xanthan–locust bean gum gels based on rheology and electron microscopy. Carbohydr Polym 26:129–140
Milas M, Rinaudo M (1990) Flow and viscoelastic properties of xanthan gum solutions. Macromolecules 23:2506–2511
Mothé CG, Correia DZ, de França FP, Riga AT (2006) Thermal and rheological study of polysaccharides for enhanced oil recovery. J Therm Anal Calorim 85:31–36
Müller AJ, Sáez AE (1999) The rheology of polymer solutions in porous media. In: Nguyen TQ, Kausch HH (eds) Flexible polymer chain dynamics in elongational flow: theory and experiment. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 335–393
Patruyo LG, Müller AJ, Sáez AE (2002) Shear and extensional rheology of solutions of modified hydroxyethylcelluloses and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Polymer 43:6481–6493
Pérez RM, Siquier S, Ramírez N, Müller AJ, Sáez AE (2004) Non-Newtonian annular vertical flow of sand suspensions in aqueous solutions of guar gum. J Pet Sci Eng 44:317–331
Rodríguez S, Romero C, Sargenti ML, Müller AJ, Sáez AE, Odell JA (1993) Flow of polymer solutions through porous media. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 49:63–85
Schorsch C, Garnier C, Doublier JL (1995) Microscopy of xanthan/ galactomannan mixtures. Carbohydr Polym 28:319–323
Schorsch C, Garnier C, Doublier JL (1997) Viscoelastic properties of xanthan/galactomannan mixtures: comparison of guar gum with locust bean gum. Carbohydr Polym 34:165–175
Shah SN, Lord DL (1991) Critical velocity correlations for slurry transport with non-Newtonian fluids. AIChE J 37:863–870
Sifferman TR, Myers GM, Haden EL, Wahl HA (1974) Drill-cutting transport in full-scale vertical annuli. J Pet Technol 26:1295–1302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amundarain, J.L., Castro, L.J., Rojas, M.R. et al. Solutions of xanthan gum/guar gum mixtures: shear rheology, porous media flow, and solids transport in annular flow. Rheol Acta 48, 491–498 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-008-0337-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-008-0337-5