Abstract
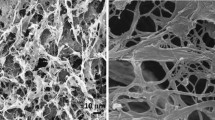
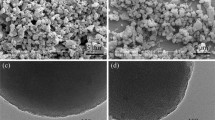
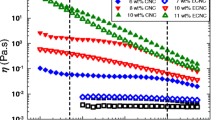
In the present work, we investigated the role of cellulose beads as additive for tuning of shear thickening (ST) behavior of traditional colloidal silica-based shear thickening fluids (STFs). STFs were synthesized with colloidal silica in liquid polyethylene glycol (PEG-200). The ST behavior of cellulose-based STF was compared with silica-based STF in terms of the steady-state and dynamic rheological studies while keeping the same total mass loading in PEG-200 polymer matrix. The ST behavior of cellulose-based STF was found to be more than three times higher than the silica-based STF at the same concentration. It can be expected that the cellulose beads with dense surface hydroxyl groups are a prime reason for improved interfacial interaction between the liquid PEG chains and the PEG-coated silica nanoparticles through strong hydrogen bonding. Both the steady-state and dynamic rheological analyses confirmed the better shear thickening and strain thickening behavior, respectively, as well as higher energy absorption property for cellulose-based STFs. The improved ST behavior of porous cellulose-based STF is definitely due to the cluster formation. This has been justifiably complemented by SEM and in situ rheological microscopy analyses.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes HA (1989) Shear-thickening (“Dilatancy”) in suspensions of nonaggregating solid particles dispersed in Newtonian liquids. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 33:329–366. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550017
Bender J, Wagner NJ (1996) Reversible shear thickening in monodisperse and bidisperse colloidal dispersions. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 40:899–916. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550767
Brady J, Bossis G (1985) The rheology of concentrated suspensions of spheres in simple shear flow by numerical simulation. J Fluid Mech 155:105
Hoffman RL (1972) Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. I. Observation of a flow instability. Trans Soc Rheol 161:155–173
Catherall AA, Melrose JR, Ball RC (2000) Shear thickening and order–disorder effects in concentrated colloids at high shear rates. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 44:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.551072
Bossis G, Brady JF (1989) The rheology of Brownian suspensions. J Chem Phys 91:1866–1874. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.457091
Bender JW, Wagner NJ (1995) Optical measurement of the contributions of colloidal forces to the rheology of concentrated suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 172:171–184. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1995.1240
Farr RS, Melrose JR, Ball RC (1997) Kinetic theory of jamming in hard-sphere startup flows. Phys Rev E 55:7203–7211. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.55.7203
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2002) Flow-small angle neutron scattering measurements of colloidal dispersion microstructure evolution through the shear thickening transition. J Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1519253
Helber R, Doncker F, Bung R (1990) Vibration attenuation by passive stiffness switching mounts. J Sound Vib 138:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(90)90703-3
Laun HM (1991) Rheology of extremely shear thickening polymer (dispersionsa) (passively viscosity switching fluids). J Rheol (N Y N Y) 35:999–1034. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550257
Fischer C, Braun SA, Bourban P-E et al (2006) Dynamic properties of sandwich structures with integrated shear-thickening fluids. Smart Mater Struct 15:1467–1475. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/15/5/036
Zhang XZ, Li WH, Gong XL (2008) The rheology of shear thickening fluid (STF) and the dynamic performance of an STF-filled damper. Smart Mater Struct 17:35027. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/17/3/035027
Jiang W, Gong X, Xuan S, Jiang W, Ye F, Li X, Liu T (2013) Stress pulse attenuation in shear thickening fluid. Appl Phys Lett 102:101901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4795303
Afeshejani SHA, Sabet SAR, Zeynali ME, Atai M (2014) Energy absorption in a shear-thickening fluid. J Mater Eng Perform 23:4289–4297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1217-z
Chu B, Brady AT, Mannhalter BD, Salem DR (2014) Effect of silica particle surface chemistry on the shear thickening behaviour of concentrated colloidal suspensions. J Phys D Appl Phys 47:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/33/335302
Petel OE, Ouellet S, Loiseau J, Marr BJ, Frost DL, Higgins AJ (2013) The effect of particle strength on the ballistic resistance of shear thickening fluids. Appl Phys Lett 102:064103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4791785
Petel OE, Ouellet S, Loiseau J, Frost DL, Higgins AJ (2015) A comparison of the ballistic performance of shear thickening fluids based on particle strength and volume fraction. Int J Impact Eng 85:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.06.004
Lee YS, Wetzel ED, Wagner NJ (2003) The ballistic impact characteristics of Kevlar?? Woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fluid. J Mater Sci 38:2825–2833. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024424200221
Egres Jr RG, Decker MJ, Halbach CJ, Lee YS, Kirkwood JE, Kirkwood KM, Wagner NJ, Wetzel ED (2006) Stab resistance of shear thickening fluid (STF)–Kevlar composites for body armor applications. Transformational Science and Technology for the Current and Future Force. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812772572_0034
Decker MJ, Halbach CJ, Nam CH, Wagner NJ, Wetzel ED (2007) Stab resistance of shear thickening fluid (STF)-treated fabrics. Compos Sci Technol 67:565–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.08.007
Rosen BA, Laufer CN, Kalman DP et al (2007) Multi-threat performance of kaolin-based shear thickening fluid (STF)-treated fabrics. Proc. SAMPE (Baltimore, MD, 3–7 June)
Hassan TA, Rangari VK, Jeelani S (2010) Synthesis, processing and characterization of shear thickening fluid (STF) impregnated fabric composites. Mater Sci Eng A 527:2892–2899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.01.018
Majumdar A, Butola BS, Srivastava A (2014) Development of soft composite materials with improved impact resistance using Kevlar fabric and nano-silica based shear thickening fluid. Mater Des 54:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.086
Hunt W III, Phelps C (1991) Method to reduce movement of a CPF device via a shear-thickening fluid. US Pat 4,982,792
Williams T, Day J, Pickard S (2007) Surgical and medical garments and materials incorporating shear thickening fluids. US Pat. App. 12/440,086
Galindo-Rosales FJ, Martínez-Aranda S, Campo-Deaño L (2015) CorkSTFμfluidics – a novel concept for the development of eco-friendly light-weight energy absorbing composites. Mater Des 82:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.12.025
Bettin G (2007) High-rate deformation behavior and applications of fluid filled reticulated foams. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Genovese DB (2012) Shear rheology of hard-sphere, dispersed, and aggregated suspensions, and filler-matrix composites. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 171:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.12.005
Raghavan SR, Walls HJ, Khan SA (2000) Rheology of silica dispersions in organic liquids: new evidence for solvation forces dictated by hydrogen bonding. Langmuir 16:7920–7930. https://doi.org/10.1021/la991548q
Osman MA, Atallah A (2006) Interfacial adhesion and composite viscoelasticity. Macromol Rapid Commun 27:1380–1385. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200600294
Xu Y-L, Gong X-L, Peng C, Sun YQ, Jiang WQ, Zhang Z (2010) Shear thickening fluids based on additives with different concentrations and molecular chain lengths. Chin J Chem Phys 23:342–346. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-0068/23/03/342-346
Yu K, Cao H, Qian K et al (2012) Shear thickening behavior of modified silica nanoparticles in polyethylene glycol. J Nanopart Res 14:747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0747-2
Sha X, Yu K, Cao H, Qian K (2013) Shear thickening behavior of nanoparticle suspensions with carbon nanofillers. J Nanopart Res 15:1816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1816-x
Gürgen S, Kushan MC, Li W (2016) The effect of carbide particle additives on rheology of shear thickening fluids. Korea Aust Rheol J 28:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0011-x
He Q, Gong X, Xuan S, Jiang W, Chen Q (2015) Shear thickening of suspensions of porous silica nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 50:6041–6049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9151-5
Gericke M, Trygg J, Fardim P (2013) Functional cellulose beads: preparation, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev 113:4812–4836. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300242j
Chen LF, Tsao GT (1977) Chemical procedures for enzyme immobilization on porous cellulose beads. Biotechnol Bioeng 19:1463–1473. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260191005
Gemeiner P, Benes MJ, Stamberg J (1989) Bead cellulose and its use in biochemistry and Biotechnology. Chem Pap 43:805
Navarro RR, Sumi K, Fujii N, Matsumura M (1996) Mercury removal from wastewater using porous cellulose carrier modified with polyethyleneimine. Water Res 30:2488–2494. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(96)00143-1
Gonte RR, Balasubramanian K, Mumbrekar JD (2013) Porous and cross-linked cellulose beads for toxic metal ion removal: hg(II) ions. J Polym 2013:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/309136
Voon LK, Pang SC, Chin SF (2015) Highly porous cellulose beads of controllable sizes derived from regenerated cellulose of printed paper wastes. Mater Lett 164:264–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.161
Chen KI, Yao Y, Chen HJ, Lo YC, Yu RC, Cheng KC (2016) Hydrolysis of isoflavone in black soy milk using cellulose bead as enzyme immobilizer. J Food Drug Anal 24:788–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.03.007
Liu D-M (2000) Particle packing and rheological property of highly-concentrated ceramic suspensions: φm determination and viscosity prediction. J Mater Sci 35:5503–5507. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004885432221
Kalman DP, Schein JB, Houghton JM et al (2007) Polymer dispersion based shear thickening fluid-fabrics for protective applications. Proc SAMPE 1:3–7
Wetzel ED (2004) The effect of rheological parameters on the ballistic properties of shear thickening fluid (STF)-Kevlar composites. AIP Conf Proc 712:288–293. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1766538
Chen Q, Xuan S, Jiang W, Cao S, Gong X (2016) Shear time dependent viscosity of polystyrene-ethylacrylate based shear thickening fluid. Smart Mater Struct 25:45005. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/25/4/045005
Moriana AD, Tian T, Sencadas V, Li W (2016) Comparison of rheological behaviors with fumed silica-based shear thickening fluids. Korea Aust Rheol J 28:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0020-9
Huang W, Wu Y, Qiu L, Dong C, Ding J, Li D (2015) Tuning rheological performance of silica concentrated shear thickening fluid by using graphene oxide. Adv Condens Matter Phys 2015:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/734250
Xu Y, Gong X, Peng C, Sun YQ, Jiang WQ, Zhang Z (2010) Shear thickening fluids based on additives with different concentrations and molecular chain lengths. Chin J Chem Phys 23:342–346. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-0068/23/03/342-346
Lootens D, Hébraud P, Lécolier E, Van Damme H (2004) Gelation, shear-thinning and shear-thickening in cement slurries solid/liquid dispersions in drilling and production fluides chargés en forage et production pétrolière. Oil Gas Sci Technol – Rev IFP 59:31–40
Fall A, Bertrand F, Ovarlez G, Bonn D (2012) Shear thickening of cornstarch suspensions. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 56:575–591. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.3696875
Boersma WH, Laven J, Stein HN (1992) Viscoelastic properties of concentrated shear-thickening dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 149:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(92)90385-Y
Mewis J, Biebaut G (2001) Shear thickening in steady and superposition flows effect of particle interaction forces. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 45:799–813. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.1359761
Gürgen S, Li W, Kushan MC (2016) The rheology of shear thickening fluids with various ceramic particle additives. Mater Des 104:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.055
Russel WB, Saville DA, Schowalter WR (1989) Colloidal dispersions
Macosko CW (1994) Rheology: principles, measurements, and applications. VCH
Raghavan S, Khan S (1997) Shear-thickening response of Fumed silica suspensions under steady and oscillatory shear. J Colloid Interface Sci 185:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1996.4581
Wagner NJ, Brady JF (2009) Shear thickening in colloidal dispersions. Phys Today 62:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3248476
Liang X-H, Guo Y-Q, Gu L-Z, Ding E-Y (1995) Crystalline-amorphous phase transition of poly(ethylene glycol)/cellulose blend. Macromolecules 28:6551–6555. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00123a023
Turhan KN, Sahbaz F, Güner A (2001) A spectrophotometric study of hydrogen bonding in methylcellulose-based edible films plasticized by polyethylene glycol. J Food Sci 66:59–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.tb15581.x
Kondo T, Sawatari C, Manley RSJ, Gray DG (1994) Characterization of hydrogen bonding in cellulose-synthetic polymer blend systems with regioselectively substituted methylcellulose. Macromolecules 27:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00079a031
Yang G, Zhang L, Feng H (1999) Role of polyethylene glycol in formation and structure of regenerated cellulose microporous membrane. J Membr Sci 161:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00095-2
Zhang GD, Wu JR, Tang LC, Li JY, Lai GQ, Zhong MQ (2014) Rheological behaviors of fumed silica/low molecular weight hydroxyl silicone oil. J Appl Polym Sci 131:8846–8850. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40722
Ye F, Zhu W, Jiang W, Wang Z, Chen Q, Gong X, Xuan S (2013) Influence of surfactants on shear-thickening behavior in concentrated polymer dispersions. J Nanopart Res 15:2122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2122-3
Acknowledgments
Our grateful acknowledgments are due to the Director (TBRL Chandigarh) for his kind support and encouragement. We would also like to record our gratitude to Ms. Vandana P. Arya and Ms. Gurvinder Kaur of TBRL at Chandigarh, to the Centre for Polymer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi and to Dr. Rajeev Mehta of Thapar University, Patiala for allowing us to use their facilities for the experimentations on the synthesis and characterization of STF.
Funding
This research work was wholly funded and supported by Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory, Chandigarh which is a part of D.R.D.O., under Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 70 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, E., Kaur, G., Bhattacharjee, D. et al. Effect of cellulose beads on shear-thickening behavior in concentrated polymer dispersions. Colloid Polym Sci 296, 883–893 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4299-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4299-6