Abstract
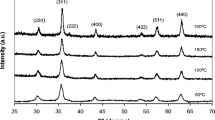
In the present work, iron oxide nanoparticles have been prepared by microwave-assisted synthesis with the influence of different glycols. The presence of different glycols in different experiments has an effect on the final phase and size of synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. Synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). XRD measurements show that the peaks of diffractogram are in agreement with the theoretical data of iron oxide nanoparticle phases, i.e. magnetite, hematite and maghemite. Crystallite size of the particles was found to be 35.5, 29.9 and 28.2 nm for Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3, respectively. FESEM studies further confirm the particle size measurement. EDX spectral analysis reveals the presence of carbon, oxygen, iron in the synthesized nanoparticles. The FTIR graphs indicated absorption bands due to O–H stretching, C–O bending, C–H stretching and Fe–O stretching vibrations. TGA curve represented weight loss percentage of synthesized nanoparticles due to the elimination of the water molecules and solvent evaporation; finally, the residual weight corresponds to 76, 93 and 94 % for Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu A-H, Salabas EL, Schuth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1222–1244
Shao M., Ning F., Zhao J., Wei M., Evans D. G. and Duan X., (2012) Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2@layered double hydroxide coreshell microspheres for magnetic separation of proteins. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134:1071–1077
Majeed MI, Lu Q, Yan W, et al. (2013) Highly water-soluble magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for drug delivery: enhanced in vitro therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin and MION conjugates. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 1(22):2874–2884
Bae KH, Park M, Do MJ, et al. (2012) Chitosan oligosaccharide stabilized ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes for magnetically modulated cancer hyperthermia. ACS Nano 6:5266–5273
Xiao L, Li J, Brougham DF, et al. (2011) Water-soluble superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles with biocompatible coating for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Nano 5:6315–6324
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 63:24–46
Laurent S, Dutz S, Hafeli UO, Mahmoudi M (2011) Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 166:8–23
de Montferrand C., Hu L., Milosevic I. et al., (2013) Iron oxide nanoparticles with sizes, shapes and compositions resulting in different magnetization signatures as potential labels for multiparametric detection. Acta Biomater, 9:6150–6157
Kievit FM, Zhang MQ (2011) Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acc Chem Res 44:853–862
Yang X, Jiang W, Liu L, et al. (2012) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of highly water-soluble secondary structural Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2249–2257
Wan J. Q., Cai W., Meng X. X. and. Liu E., (2007) Monodisperse water soluble magnetite nanoparticles prepared by polyol process for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Chem Commun 47:5004–5006
Yang X. C., Shang Y. L., Li Y. H., Zhai J., Foster N. R., Li Y. X., Zou D. and Pu Y, (2014) Synthesis of monodisperse iron oxide nanoparticles without surfactants. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Nanomaterials, Article ID 740856, 5 pages
Rosenzweig RE (1985) Ferrohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Berry CC, Curtis ASG, (2003) Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36(13):198–206
Thach CV, Hai NH, Chau N, (2008) Size controlled magnetite nanoparticles and their drug loading ability. J Korean Phys Soc 52:1332–1335
Leslie-Pelecky D. L., Labhasetwar V. and Kraus R. H., (2005) Jr Nanobiomagnetics. In: Advanced magnetic nanostructures. D. J. Sellmyer and R. S. Skomski (Eds.). Kluwer, New York
Zboril R, Petridis MMD (2002) Iron(III) oxides from thermal processes synthesis, structural and magnetic properties, Mössbauer spectroscopy characterization, and applications. Chem Mater 14(3):969–982
Cao X, Koltypin Y, Prozorov R, Kataby G, Gedanken A (1997) Preparation of amorphous Fe2O3 powder with different particle sizes. J Mater Chem 7:2447–2451
Mohapatra M, Anand S, (2010) Synthesis and applications of nano-structured iron oxides/hydroxides—a review. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2:127–146
Cheng Z., Tan A. L. K., Tao Y., Shan D., Ting K. E. and Yin X. J., (2012) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles and applications in the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. International Journal of Photoenergy, Volume 2012, Article ID 608298, 5 pages
Hasany SF, Ahmed I, Rajan J, Rehman A (2012) Systematic review of the preparation techniques of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Nanosci Nanotechnol 2:148–158
Benyettou F., Milosevic I., Olsen J. C., Motte L. and Trabolsi A., (2012) Ultra-small super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles made to order. J Bioanal Biomed, S5 ISSN:1948-593X JBABM.
Nidhin M, Indumathy R, Sreeram KJ, NAIR BU, (2008) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles of narrow size distribution of polysaccharide template. Bull Mater Sci 31:93–96
Colvin VL, Schlamp MC, Alivisatos AP, (1994) Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature 370:354–357
Luo C, Zhang Y, Zeng X, Zeng Y, Wang Y, (2005) The role of poly (ethylene glycol) in the formation of silver nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 288:444–448
Shimmin RG, Schoch AB, Braun PV, (2004) Polymer size and concentration effects on the size of gold nanoparticles capped by polymeric thiols. Langmuir 20:5613–5620
Deng YH, Wang CC, Hu JH, Yang WL, Fu SK (2005) Investigation of formation of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles via sol-gel approach. Colloids Surf A 262:87–93
Mahdavi M., Ahmad M. B., Haron M. J., Namvar F., Nadi B., Rahman M. Z. A. and Amin J., (2013) Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 18:7533–7548.
Powder diffraction file, alphabetical index inorganic phases, (1984) Published by JCPDS International Centre for Diffraction Data 1601, Park Lane Swarthmore, Pennsylvania, 19081 USA
Peng Q, Dong YJ, Li YD (2003) ZnSe semiconductor hollow microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:3027–3030
Peng Q, Xu S, Zhuang ZB, Wang X, Li YD (2005) A general chemical conversion method to various semiconductor hollow structures. Small 1:216–221
Sun XM, Li YD, (2004) Ga2O3 and GaN semiconductor hollow spheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:3827–3831
Sun XM, Li YD (2004) Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:597–601
Wang J. W., Wang X., Peng Q. and Li Y. D., (2004) Synthesis and characterization of bismuth single-crystalline nanowires and nanospheres. Inorg Chem 43:7552–7556.
Zhang Y, Li YD (2004) Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse doped ZnS nanospheres with enhanced thermal stability. J Phys Chem B 108:17805–17811
Phu ND, Ngo DT, Hoang LH, Luong NH, Hai NH (2011) Crystallization process and magnetic properties of amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys D Appl Phys 44:345002. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/44/34/345002
Stuart BH, (2004) Infrared spectroscopy: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, England
Battisha JK, Afify HH, Ibrahim M, (2006) Synthesis of Fe2O3 concentrations and sintering temperature on FTIR and magnetic susceptibility measured from 4 to 300 K of monolith silica gel prepared by sol-gel technique. J Magn Magn Mater 306:211–217. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.251
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Director CSIR-AMPRI Bhopal for providing the necessary institutional facilities and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guru, S., Mishra, D., Amritphale, S.S. et al. Influence of glycols in microwave assisted synthesis of ironoxide nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 294, 207–213 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3755-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3755-9