Abstract
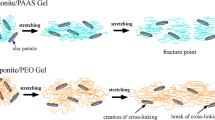
We investigated the structural, mechanical, and swelling properties of composite hydrogels consisting of clay, a dispersing agent (tetrasodium diphosphate), and sodium polyacrylate (PAAS) prepared by mixing. Regardless of the simple preparation method, the gel exhibits excellent properties such as mechanical toughness and high swelling ability. For production of the tough gels, it is important to disperse clay particles using the dispersing agent and to use high molecular weight PAAS for formation of bridge connecting different clay particles in a dispersed state. Synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering experiments reveal that PAAS was adsorbed on the positively charged edge of the clay particles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvert P (2009) Hydrogels for soft machines. Adv Mater 21:743–756
Can V, Abdurrahmanoglu S, Okay O (2007) Unusual swelling behavior of polymer-clay nanocomposite hydrogels. Polymer 48:5016–5023
Dijkstra M, Hansen JP, Madden PA (1995) Gelation of a clay colloid suspension. Phys Rev Lett 75:2236–2239
Feigin LA, Svergun DI, Taylor GW (1987) Structure analysis by small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering. Plenum Press, New York
Flory PJ (1953) Principles of polymer chemistry. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Glatter O, Kratky O (1982) Small angle X-ray scattering. Academic, London
Gong JP, Katsuyama Y, Kurokawa T, Osada Y (2003) Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv Mater 15:1155–1158
Haraguchi K, Farnworth R, Ohbayashi A, Takehisa T (2003) Compositional effects on mechanical properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 36:5732–5741
Haraguchi K, Li HJ, Matsuda K, Takehisa T, Elliott E (2005) Mechanism of forming organic/inorganic network structures during in-situ free-radical polymerization in PNIPA-clay nanocomposite hydrogels. Macromolecules 38:3482–3490
Haraguchi K, Takehisa T, Fan S (2002) Effects of clay content on the properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 35:10162–10171
Heppenstall-Butler M, Butler MF (2003) Nonequilibrium behavior in the three-component system stearic acid-sodium stearate-water. Langmuir 19:10061–10072
Kroon M, Vos WL, Wegdam GH (1998) Structure and formation of a gel of colloidal disks. Phys Rev E 57:1962–1970
Nie JJ, Du BY, Oppermann W (2005) Swelling, elasticity, and spatial inhomogeneity of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/clay nanocomposite hydrogels. Macromolecules 38:5729–5736
Okay O, Oppermann W (2007) Polyacrylamide-clay nanocomposite hydrogels: rheological and light scattering characterization. Macromolecules 40:3378–3387
Pignon F, Magnin A, Piau JM, Cabane B, Lindner P, Diat O (1997) Yield stress thixotropic clay suspension: investigation of structure by light, neutron, and X-ray scattering. Phys Rev E 56:3281–3289
Ren HY, Zhu M, Haraguchi K (2011) Characteristic swelling-deswelling of polymer/clay nanocomposite gels. Macromolecules 44:8516–8526
Schweins R, Hollmann J, Huber K (2003) Dilute solution behaviour of sodium polyacrylate chains in aqueous NaCl solutions. Polymer 44:7131–7141
Takeno H, Maehara A, Yamaguchi D, Koizumi S (2012) A structural study of an organogel investigated by small-angle neutron scattering and synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering. J Phys Chem B 116:7739–7745
Takeno H, Obuchi K, Maki Y, Kondo S, Dobashi T (2011) A structural study of polyelectrolyte gels in a unidirectionally swollen state. Polymer 52:2685–2692
Treloar LRG (1975) The physics of rubber elasticity, 3rd edn. Clarendon, Oxford
Wang Q, Mynar JL, Yoshida M, Lee E, Lee M, Okuro K, Kinbara K, Aida T (2010) High-water-content mouldable hydrogels by mixing clay and a dendritic molecular binder. Nature 463:339–343
Yin DW, Horkay F, de Douglas JF, Pablo JJ (2008) Molecular simulation of the swelling of polyelectrolyte gels by monovalent and divalent counterions. J Chem Phys 129:154902
Acknowledgments
The synchrotron SAXS measurements were conducted under the approval of Photon Factory Program Advisory Committee (Proposals 2010G699 and 2010G134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeno, H., Nakamura, W. Structural and mechanical properties of composite hydrogels composed of clay and a polyelectrolyte prepared by mixing. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 1393–1399 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2871-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2871-z