Abstract
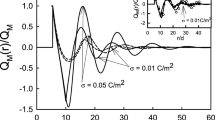
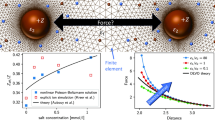
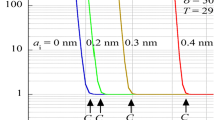
In this work, the role of ionic dispersion forces in specific ion effects is evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations in the primitive model. More specifically, we assess the effect of such forces on the diffuse potential, since this property is essential to understand the electrokinetic behavior of colloids. In this way, ion specificity arises naturally since ion dispersion forces depend on ionic polarizability, which differs for ions with the same valence. This property is included in the primitive model by means of the Lifshitz theory. The results for different ions are summarized with the help of a nondimensional parameter characterizing the relative weight of ionic van der Waals interactions. Our data reveal that for small ions with high polarizability the ionic dispersion forces can considerably contribute to the specificity of the diffuse potential. In any case, the specific ion effects due to ion polarizability are strongly influenced by ion size.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stern O (1924) The theory of the electrolytic double shift. Z Elektrochem 30:508–516
Biesheuvel PM, van Soestbergen M (2007) Counterion volume effects in mixed electrical double layers. J Colloid Interface Sci 316:490–499
Fawcett WR, Smagala TG (2006) New developments in the theory of the diffuse double layer. Langmuir 22:10635–10642
Vlachy V (1999) Ionic effects beyond Poisson–Boltzmann theory. Annu Rev Phys Chem 50:145–165
Quesada-Pérez M, González-Tovar E, Martín-Molina A, Lozada-Cassou M, Hidalgo-Álvarez R (2003) Overcharging in colloids: Beyond the Poisson–Boltzmann approach. ChemPhysChem 4:235–248
Collins KD, Washabaugh MW (1985) The Hofmeister effect and the behavior of water at interfaces. Q Rev Biophys 18:323–422
Collins KD (1997) Charge density-dependent strength of hydration and biological structure. Biophys J 72:65–76
Collins KD (2006) Ion hydration: Implications for cellular function, polyelectrolytes, and protein crystallization. Biophys Chem 119:271–281
Ninham BW, Yaminsky V (1997) Ion binding and ion specificity: The Hofmeister effect and Onsager and Lifshitz theories. Langmuir 13:2097–2108
Ottewill RH, Shaw JN (1968) An electrophoretic investigation of behavior of monodisperse polystyrene latices in solutions of lanthanum neodymium and thorium nitrates. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:110
Quesada-Pérez M, González-Tovar E, Martín-Molina A, Lozada-Cassou M, Hidalgo-Álvarez R (2005) Ion size correlations and charge reversal in real colloids. Colloid Surf A 267:24–30
Quesada-Pérez M, Martín-Molina A, Hidalgo-Álvarez R (2005) Simulation of electric double layers undergoing charge inversion: mixtures of mono- and multivalent ions. Langmuir 21:9231–9237
Grosberg AY, Nguyen TT, Shklovskii BI (2002) The physics of charge inversion in chemical and biological systems. Rev Mod Phys 74:329–345
Levin Y (2002) Elecrostatic correlations: from plasma to biology. Rep Prog Phys 65:1577
Bostrom M, Williams DRM, Ninham BW (2001) Specific ion effects: why DLVO theory fails for biology and colloid systems. Phys Rev Lett 87:168103
Bostrom M, Williams DRM, Ninham BW (2001) Surface tension of electrolytes: specific ion effects explained by dispersion forces. Langmuir 17:4475–4478
Bostrom M, Williams DRM, Ninham BW (2002) Ion specificity of micelles explained by ionic dispersion forces. Langmuir 18:6010–6014
Tavares FW, Brakto D, Blanch HW, Prausnitz JM (2004) Ion-specific effects in the colloid–colloid or protein–protein potential of mean force: Role of salt–macroion van der Waals interactions. J Phys Chem B 108:9228–9235
Boström M, Tavares FW, Ninham BW, Prausnitz JM (2006) Effect of salt identity on the phase diagram for a globular protein in aqueous electrolyte solution. J Phys Chem B 110:24757–24760
Israelachvili JN (1992) Intermolecular and surface forces. Academic Press, London
Quesada-Pérez M, Martín-Molina A, Hidalgo-Álvarez R (2004) Simulation of electric double layers with multivalent counterions: ion size effect. J Chem Phys 121:8618–8626
Ravindran S, Wu J (2005) Ion size effect on colloidal forces within the primitive model. Condens Matter Phys 8:377–388
Martín-Molina A, Ibarra-Armenta JG, Quesada-Pérez M (2009) Effect of ion dispersion forces on the electric double layer of colloids: a Monte Carlo simulation study. J Phys Chem B 113:2414–2421
Torrie GM, Valleau JP (1980) Electrical double layers 1. Monte-Carlo study of a uniformly charged surface. J Chem Phys 73:5807–5816
Gulbrand L, Jönsson B, Wennerström H, Linse P (1984) Electric double layer forces. A Monte Carlo study. J Chem Phys 80:2221–2228
Dobrynin AV (2008) Theory and simulations of charged polymers: from solution properties to polymeric nanomaterials. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 13:376–388
Linse P (2005) Simulation of charged colloids in solution. Adv Polym Sci 185:111–162
Dijkstra M (2001) Computer simulations of charge and steric stabilised colloidal suspensions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 6:372–382
Boda D, Chan KY, Henderson D (1998) Monte Carlo simulation of an ion–dipole mixture as a model of an electrical double layer. J Chem Phys 109:7362–7371
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science. Principles and applications. Academic Press, London
Lyklema J (1987) Solid/liquid dispersions. Academic Press, London
Grahame DC (1947) The electrical double layer and the theory of electrocapillarity. Chem Rev 41:441–501
López-León T, Jódar-Reyes AB, Bastos-González D, Ortega-Vinuesa JL (2003) Hofmeister Effects in the stability and electrophoretic mobility of polystyrene latex particles. J Phys Chem B 107:5696–5708
Martín-Molina A, Quesada-Pérez M, Galisteo-González F, Hidalgo-Álvarez R (2003) Looking into overcharging in model colloids through electrophoresis: asymmetric electrolytes. J Chem Phys 118:4183–4189
Roldán-Vargas S, Barnadas-Rodríguez R, Quesada-Pérez M, Estelrich J, Callejas-Fernández J (2009) Surface fractal in liposome aggregation. Phys Rev E 79:011905
Roldán-Vargas S, Martín-Molina A, Quesada-Pérez M, Barnadas-Rodríguez R, Estelrich J, Callejas-Fernández J (2007) Aggregation of liposomes induced by calcium: a structural and kinetic study. Phys Rev E 75:021912
Faraudo J, Travesset A (2007) Phosphatidic acid domains in membranes: effect of divalent counterions. Biophys J 92:2806–2818
Faraudo J, Travesset A (2007) Electrostatics of phosphatidic acid monolayers: insights from computer simulations. Colloid Surf A 300:287–292
Lima ERA, Horinek D, Netz RR, Biscaia EC, Tavares FW, Kunz W, Boström M (2008) Specific ion adsorption and surface forces in colloid science. J Phys Chem B 112:1580–1585
Netz RR (2004) Water and ions at interfaces. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 9:192–197
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to “Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, Plan Nacional de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación Tecnológica (I + D + i),” project MAT2009-13155-C04-04, “Consejería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa de la Junta de Andalucía” projects P07-FQM-02496, P07-FQM-02517, and FQM-4698, as well as the European Regional Development Fund for financial support. A.M.-M. also thanks the “Programa Ramón y Cajal, 2005, Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia–Fondo Social Europeo (RYC-2005-000829).”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quesada-Pérez, M., Hidalgo-Álvarez, R. & Martín-Molina, A. Effect of ionic van der Waals forces on the diffuse potential of model colloids. Colloid Polym Sci 288, 151–158 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-009-2139-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-009-2139-4