Abstract
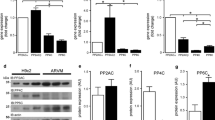
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is a key regulator of important cardiac signaling pathways. Dysregulation of PP1 has been heavily implicated in cardiac dysfunctions. Accordingly, pharmacological targeting of PP1 activity is considered for therapeutic intervention in human cardiomyopathies. Recent evidence from animal models implicated previously unrecognized, isoform-specific activities of PP1 in the healthy and diseased heart. Therefore, this study examined the expression of the distinct PP1 isoforms PP1α, β, and γ in human heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) and addressed the consequences of β-adrenoceptor blocker (beta-blocker) therapy for HF patients with reduced ejection fraction on PP1 isoform expression. Using western blot analysis, we found greater abundance of PP1 isoforms α and γ but unaltered PP1β levels in left ventricular myocardial tissues from HF patients as compared to non-failing controls. However, expression of all three PP1 isoforms was higher in atrial appendages from patients with AF compared to patients with sinus rhythm. Moreover, we found that in human failing ventricles, beta-blocker therapy was associated with lower PP1α abundance and activity, as indicated by higher phosphorylation of the PP1α-specific substrate eIF2α. Greater eIF2α phosphorylation is a known repressor of protein translation, and accordingly, we found lower levels of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress marker Grp78 in the very same samples. We propose that isoform-specific targeting of PP1α activity may be a novel and innovative therapeutic strategy for the treatment of human cardiac diseases by reducing ER stress conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 July 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Aoyama H, Ikeda Y, Miyazaki Y, Yoshimura K, Nishino S, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Inui M, Aoki H, Matsuzaki M (2011) Isoform-specific roles of protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunits in sarcoplasmic reticulum-mediated Ca(2+) cycling. Cardiovasc Res 89:79–88. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq252
Brush MH, Weiser DC, Shenolikar S (2003) Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biol 23:1292–1303. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.4.1292-1303.2003
Carr AN, Schmidt AG, Suzuki Y, del Monte F, Sato Y, Lanner C, Breeden K, Jing SL, Allen PB, Greengard P, Yatani A, Hoit BD, Grupp IL, Hajjar RJ, DePaoli-Roach AA, Kranias EG (2002) Type 1 phosphatase, a negative regulator of cardiac function. Mol Cell Biol 22:4124–4135. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.12.4124-4135.2002
Chiang DY, Li N, Wang Q, Alsina KM, Quick AP, Reynolds JO, Wang G, Skapura D, Voigt N, Dobrev D, Wehrens XH (2014) Impaired local regulation of ryanodine receptor type 2 by protein phosphatase 1 promotes atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 103:178–187. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvu123
Christ T, Boknik P, Wohrl S, Wettwer E, Graf EM, Bosch RF, Knaut M, Schmitz W, Ravens U, Dobrev D (2004) L-type Ca2+ current downregulation in chronic human atrial fibrillation is associated with increased activity of protein phosphatases. Circulation 110:2651–2657. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000145659.80212.6A
El-Armouche A, Boknik P, Eschenhagen T, Carrier L, Knaut M, Ravens U, Dobrev D (2006) Molecular determinants of altered Ca2+ handling in human chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation 114:670–680. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.636845
Eleftheriadou O, Boguslavskyi A, Longman MR, Cowan J, Francois A, Heads RJ, Wadzinski BE, Ryan A, Shattock MJ, Snabaitis AK (2017) Expression and regulation of type 2A protein phosphatases and alpha4 signalling in cardiac health and hypertrophy. Basic Res Cardiol 112:37. doi:10.1007/s00395-017-0625-2
Fan J, Zou L, Cui K, Woo K, Du H, Chen S, Ling Z, Zhang Q, Zhang B, Lan X, Su L, Zrenner B, Yin Y (2015) Atrial overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 improves the canine rapid atrial pacing-induced structural and electrical remodeling. Fan, ACE2 improves atrial substrate remodeling. Basic Res Cardiol 110:45. doi:10.1007/s00395-015-0499-0
George I, Sabbah HN, Xu K, Wang N, Wang J (2011) Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and normalizes calcium handling in a coronary embolization model of heart failure in canines. Cardiovasc Res 91:447–455. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr106
Heijman J, Dewenter M, El-Armouche A, Dobrev D (2013) Function and regulation of serine/threonine phosphatases in the healthy and diseased heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 64:90–98. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.09.006
Heijman J, Ghezelbash S, Wehrens XH, Dobrev D (2017) Serine/threonine phosphatases in atrial fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 103:110–120. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.009
Janes KA (2015) An analysis of critical factors for quantitative immunoblotting. Sci Signal 8:rs2. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2005966
Korrodi-Gregorio L, Esteves SL, Fardilha M (2014) Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic isoforms: specificity toward interacting proteins. Transl Res 164:366–391. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2014.07.001
Li CY, Zhou Q, Yang LC, Chen YH, Hou JW, Guo K, Wang YP, Li YG (2016) Dual-specificity phosphatase 14 protects the heart from aortic banding-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction through inactivation of TAK1-P38MAPK/-JNK1/2 signaling pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 111:19. doi:10.1007/s00395-016-0536-7
Liu M, Dudley SC Jr (2015) Role for the unfolded protein response in heart disease and cardiac arrhythmias. Int J Mol Sci 17:52. doi:10.3390/ijms17010052
Liu MQ, Chen Z, Chen LX (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel mechanism and therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:425–443. doi:10.1038/aps.2015.145
Liu R, Correll RN, Davis J, Vagnozzi RJ, York AJ, Sargent MA, Nairn AC, Molkentin JD (2015) Cardiac-specific deletion of protein phosphatase 1beta promotes increased myofilament protein phosphorylation and contractile alterations. J Mol Cell Cardiol 87:204–213. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.08.018
Lu Z, Xu X, Fassett J, Kwak D, Liu X, Hu X, Wang H, Guo H, Xu D, Yan S, McFalls EO, Lu F, Bache RJ, Chen Y (2014) Loss of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase general control nonderepressible 2 protects mice from pressure overload-induced congestive heart failure without affecting ventricular hypertrophy. Hypertension 63:128–135. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02313
Ma L, Bayram Y, McLaughlin HM, Cho MT, Krokosky A, Turner CE, Lindstrom K, Bupp CP, Mayberry K, Mu W, Bodurtha J, Weinstein V, Zadeh N, Alcaraz W, Powis Z, Shao Y, Scott DA, Lewis AM, White JJ, Jhangiani SN, Gulec EY, Lalani SR, Lupski JR, Retterer K, Schnur RE, Wentzensen IM, Bale S, Chung WK (2016) De novo missense variants in PPP1CB are associated with intellectual disability and congenital heart disease. Hum Genet 135:1399–1409. doi:10.1007/s00439-016-1731-1
MacDougall LK, Jones LR, Cohen P (1991) Identification of the major protein phosphatases in mammalian cardiac muscle which dephosphorylate phospholamban. Eur J Biochem 196:725–734. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15871.x
Mishra S, Gupta RC, Tiwari N, Sharov VG, Sabbah HN (2002) Molecular mechanisms of reduced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) uptake in human failing left ventricular myocardium. J Heart Lung Transplant 21:366–373. doi:10.1016/S1053-2498(01)00390-4
Moorhead G, Johnson D, Morrice N, Cohen P (1998) The major myosin phosphatase in skeletal muscle is a complex between the beta-isoform of protein phosphatase 1 and the MYPT2 gene product. FEBS Lett 438:141–144. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01276-9
Neumann J (2002) Altered phosphatase activity in heart failure, influence on Ca2+ movement. Basic Res Cardiol 97(Suppl 1):I91–I95. doi:10.1007/s003950200036
Neumann J, Eschenhagen T, Jones LR, Linck B, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Zimmermann N (1997) Increased expression of cardiac phosphatases in patients with end-stage heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:265–272. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1996.0271
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GM, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, Authors/Task Force Members (2016) 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 37:2129–2200. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128
Santos CX, Hafstad AD, Beretta M, Zhang M, Molenaar C, Kopec J, Fotinou D, Murray TV, Cobb AM, Martin D, Zeh Silva M, Anilkumar N, Schroder K, Shanahan CM, Brewer AC, Brandes RP, Blanc E, Parsons M, Belousov V, Cammack R, Hider RC, Steiner RA, Shah AM (2016) Targeted redox inhibition of protein phosphatase 1 by Nox4 regulates eIF2alpha-mediated stress signaling. EMBO J 35:319–334. doi:10.15252/embj.201592394
Terry-Lorenzo RT, Carmody LC, Voltz JW, Connor JH, Li S, Smith FD, Milgram SL, Colbran RJ, Shenolikar S (2002) The neuronal actin-binding proteins, neurabin I and neurabin II, recruit specific isoforms of protein phosphatase-1 catalytic subunits. J Biol Chem 277:27716–27724. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203365200
Tsaytler P, Harding HP, Ron D, Bertolotti A (2011) Selective inhibition of a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1 restores proteostasis. Science 332:91–94. doi:10.1126/science.1201396
Wang H, Xu X, Fassett J, Kwak D, Liu X, Hu X, Falls TJ, Bell JC, Li H, Bitterman P, Bache RJ, Chen Y (2014) Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase deficiency protects the heart from systolic overload-induced congestive heart failure. Circulation 129:1397–1406. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002209
Weber S, Meyer-Roxlau S, Wagner M, Dobrev D, El-Armouche A (2015) Counteracting protein kinase activity in the heart: the multiple roles of protein phosphatases. Front Pharmacol 6:270. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by DFG Grant EL270/7-1, DZHK (Grant-Nr.: 81X2800134) (to A. E.-A.), the National Institutes of Health (HL131517 to D.D.) and research stipend of the German Society of Cardiology (to S.W.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The spelling of the author name Samuel Sossalla was incorrect.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0638-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer-Roxlau, S., Lämmle, S., Opitz, A. et al. Differential regulation of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) isoforms in human heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol 112, 43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0635-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0635-0