Abstract
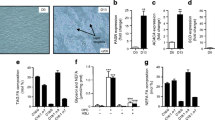
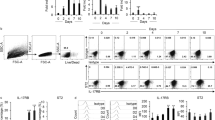
Human monocytes/macrophages express the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) but nothing is known about its role under physiological conditions. As adipose tissue contains resident macrophages that have been implicated in the generation of insulin resistance in expanding fat mass, we determined whether adipocytes release factors that affect ACE expression and function in monocytes. Incubation of human monocyte-derived macrophages with conditioned medium from freshly isolated human adipocytes (BMI = 25.4 ± 0.96) resulted in a 4-fold increase in ACE expression. The effect was insensitive to denaturation and different proteases but abolished after lipid extraction. mRNA levels of the major histocompatibility complex class II protein increased in parallel with ACE, whereas the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interleukin (IL)-6, and cyclooxygenase-2 decreased. As a consequence of the reduction in MCP-1, monocyte recruitment was also attenuated. Moreover, adipocyte-conditioned medium prevented the interferon (IFN)-γ induced formation of TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1, all markers of classically-activated (M1 type) macrophages. The decrease in cytokine expression in adipocyte-conditioned medium-treated macrophages was sensitive to ACE silencing by small interfering RNA (siRNA). Accordingly, ACE overexpression in THP-1 cells mimicked the effect of adipocyte-conditioned medium. In both cell types, ACE inhibition failed to affect the changes induced by adipocyte conditioned-medium treatment and ACE overexpression. Thus, the modulation of macrophage polarization by ACE appears to be mediated independently of enzyme activity, probably via intracellular signaling. Interestingly, human macrophage ACE expression was also upregulated by IL-4 and IL-13, which promote the “alternative” activation of macrophages and decreased by LPS and IFN-γ. Mechanistically, adipocyte-conditioned medium stimulated the phosphorylation of the AMP-activated protein kinase and AMPK inhibition prevented the increase in ACE expression. Moreover, ACE expression was reduced in spleen derived-monocytes from AMPKα1−/− mice versus their wild-type littermates. These data indicate that mature adipocytes modulate the expression profile of macrophages by releasing lipid mediators that increase ACE expression via AMPK. This prevents the pro-inflammatory cytokine production by macrophages.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference list
Balyasnikova IV, Sun ZL, Metzger R, Taylor PR, Vicini E, Muciaccia B, Visintine DJ, Berestetskaya YV, McDonald TD, Danilov SM (2006) Monoclonal antibodies to native mouse angiotensin-converting enzyme (CD143): ACE expression quantification, lung endothelial cell targeting and gene delivery. Tissue Antigens 67:10–29. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2005.00516.x
Benharouga M, Haardt M, Kartner N, Lukacs GL (2001) COOH-terminal truncations promote proteasome-dependent degradation of mature cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator from post-Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 153:957–970. doi:10.1083/jcb.153.5.957
Boettger T, Beetz N, Kostin S, Schneider J, Kruger M, Hein L, Braun T (2009) Acquisition of the contractile phenotype by murine arterial smooth muscle cells depends on the Mir143/145 gene cluster. J Clin Invest 119:2634–2647. doi:10.1172/JCI38864
Bose D, Leineweber K, Konorza T, Zahn A, Brocker-Preuss M, Mann K, Haude M, Erbel R, Heusch G (2007) Release of TNF-alpha during stent implantation into saphenous vein aortocoronary bypass grafts and its relation to plaque extrusion and restenosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H2295–H2299. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01116.2006
Bourlier V, Zakaroff-Girard A, Miranville A, De BS, Maumus M, Sengenes C, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, Karpe F, Frayn KN, Bouloumie A (2008) Remodeling phenotype of human subcutaneous adipose tissue macrophages. Circulation 117:806–815. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.724096
Cao H, Gerhold K, Mayers JR, Wiest MM, Watkins SM, Hotamisligil GS (2008) Identification of a lipokine, a lipid hormone linking adipose tissue to systemic metabolism. Cell 134:933–944. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.048
Chen Y, Wang J, Nie R, Zhou S (2008) Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: the new hope of atherosclerotic diseases. Med Hypotheses 71:237–240. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2008.03.026
Curat CA, Miranville A, Sengenes C, Diehl M, Tonus C, Busse R, Bouloumie A (2004) From blood monocytes to adipose tissue-resident macrophages: induction of diapedesis by human mature adipocytes. Diabetes 53:1285–1292. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1285
Danilov SM, Sadovnikova E, Scharenborg N, Balyasnikova IV, Svinareva DA, Semikina EL, Parovichnikova EN, Savchenko VG, Adema GJ (2003) Angiotensin-converting enzyme (CD143) is abundantly expressed by dendritic cells and discriminates human monocyte-derived dendritic cells from acute myeloid leukemia-derived dendritic cells. Exp Hematol 31:1301–1309. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2003.08.018
Das UN (2005) Is angiotensin-II an endogenous pro-inflammatory molecule? Med Sci Monit 11:RA155–RA162
Engeli S, Bohnke J, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Schling P, Bader M, Luft FC, Sharma AM (2005) Weight loss and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Hypertension 45:356–362. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000154361.47683.d3
Fisslthaler B, Fleming I (2009) Activation and signaling by the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells. Circ Res 105:114–127. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.201590
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL (2002) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 288:1723–1727. doi:10.1001/jama.288.14.1723
Fleming I (2006) Signaling by the angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circ Res 98:887–896. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000217340.40936.53
Fleming I, Kohlstedt K, Busse R (2005) New fACEs to the renin-angiotensin system. Physiology (Bethesda) 20:91–95. doi:10.1152/physiol.00003.2005
Fukuhara M, Geary RL, Diz DI, Gallagher PE, Wilson JA, Glazier SS, Dean RH, Ferrario CM (2000) Angiotensin-converting enzyme expression in human carotid artery atherosclerosis. Hypertension 35:353–359
Hong C, Tontonoz P (2008) Coordination of inflammation and metabolism by PPAR and LXR nuclear receptors. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18:461–467. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2008.07.016
Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Tikellis C, Reid CM, Johnston CI, Cooper ME (2005) Why blockade of the renin-angiotensin system reduces the incidence of new-onset diabetes. J Hypertens 23:463–473
Jayasooriya AP, Mathai ML, Walker LL, Begg DP, Denton DA, Cameron-Smith D, Egan GF, McKinley MJ, Rodger PD, Sinclair AJ, Wark JD, Weisinger HS, Jois M, Weisinger RS (2008) Mice lacking angiotensin-converting enzyme have increased energy expenditure, with reduced fat mass and improved glucose clearance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6531–6536. doi:10.1073/pnas.0802690105
Jeong HW, Hsu KC, Lee JW, Ham M, Huh JY, Shin HJ, Kim WS, Kim JB (2009) Berberine suppresses proinflammatory responses through AMPK activation in macrophages. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E955–E964. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90599.2008
Jorgensen SB, Viollet B, Andreelli F, Frosig C, Birk JB, Schjerling P, Vaulont S, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF (2004) Knockout of the alpha2 but not alpha1 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase isoform abolishes 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranosidebut not contraction-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 279:1070–1079. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306205200
Juan CC, Chien Y, Wu LY, Yang WM, Chang CL, Lai YH, Ho PH, Kwok CF, Ho LT (2005) Angiotensin II enhances insulin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology 146:2246–2254. doi:10.1210/en.2004-1136
Kadl A, Meher AK, Sharma PR, Lee MY, Doran AC, Johnstone SR, Elliott MR, Gruber F, Han J, Chen W, Kensler T, Ravichandran KS, Isakson BE, Wamhoff BR, Leitinger N (2010) Identification of a novel macrophage phenotype that develops in response to atherogenic phospholipids via Nrf2. Circ Res 107:737–746. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.215715
Kleinbongard P, Heusch G, Schulz R (2010) TNFα in atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther 127:295–314. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.05.002
Ko HJ, Zhang Z, Jung DY, Jun JY, Ma Z, Jones KE, Chan SY, Kim JK (2009) Nutrient stress activates inflammation and reduces glucose metabolism by suppressing AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart. Diabetes 58:2536–2546. doi:10.2337/db08-1361
Kohan AB, Talukdar I, Walsh CM, Salati LM (2009) A role for AMPK in the inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:117–121. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.130
Kohlstedt K, Brandes RP, Muller-Esterl W, Busse R, Fleming I (2004) Angiotensin-converting enzyme is involved in outside-in signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 94:60–67. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000107195.13573.E4
Kohlstedt K, Shoghi F, Muller-Esterl W, Busse R, Fleming I (2002) CK2 phosphorylates the angiotensin-converting enzyme and regulates its retention in the endothelial cell plasma membrane. Circ Res 91:749–756. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000038114.17939.C8
Lee WJ, Lee IK, Kim HS, Kim YM, Koh EH, Won JC, Han SM, Kim MS, Jo I, Oh GT, Park IS, Youn JH, Park SW, Lee KU, Park JY (2005) Alpha-lipoic acid prevents endothelial dysfunction in obese rats via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2488–2494. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000190667.33224.4c
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 117:175–184. doi:10.1172/JCI29881
Maxeiner H, Husemann J, Thomas CA, Loike JD, El KJ, Silverstein SC (1998) Complementary roles for scavenger receptor A and CD36 of human monocyte-derived macrophages in adhesion to surfaces coated with oxidized low-density lipoproteins and in secretion of H2O2. J Exp Med 188:2257–2265. doi:10.1084/jem.188.12.2257
Mokdad AH, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, Bowman BA, Marks JS, Koplan JP (1999) The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991–1998. JAMA 282:1519–1522. doi:10.1001/jama.282.16.1519
Neels JG, Olefsky JM (2006) Inflamed fat: what starts the fire? J Clin Invest 116:33–35. doi:10.1172/JCI27280
Nguyen MT, Favelyukis S, Nguyen AK, Reichart D, Scott PA, Jenn A, Liu-Bryan R, Glass CK, Neels JG, Olefsky JM (2007) A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 282:35279–35292. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706762200
Prieur X, Roszer T, Ricote M (2010) Lipotoxicity in macrophages: evidence from diseases associated with the metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:327–337. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.09.017
Sag D, Carling D, Stout RD, Suttles J (2008) Adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional phenotype. J Immunol 181:8633–8641
Santos EL, de Picoli SK, da Silva ED, Batista EC, Martins PJ, D’Almeida V, Pesquero JB (2009) Long term treatment with ACE inhibitor enalapril decreases body weight gain and increases life span in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 78:951–958. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.018
Sarzani R, Salvi F, Dessi-Fulgheri P, Rappelli A (2008) Renin-angiotensin system, natriuretic peptides, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension: an integrated view in humans. J Hypertens 26:831–843. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f624a0
Schaper W (2009) Collateral circulation: past and present. Basic Res Cardiol 104:5–21. doi:10.1007/s00395-008-0760-x
Sengenes C, Lolmede K, Zakaroff-Girard A, Busse R, Bouloumie A (2005) Preadipocytes in the human subcutaneous adipose tissue display distinct features from the adult mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells. J Cell Physiol 205:114–122. doi:10.1002/jcp.20381
Shen XZ, Li P, Weiss D, Fuchs S, Xiao HD, Adams JA, Williams IR, Capecchi MR, Taylor WR, Bernstein KE (2007) Mice with enhanced macrophage angiotensin-converting enzyme are resistant to melanoma. Am J Pathol 170:2122–2134. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.061205
Shen XZ, Lukacher AE, Billet S, Williams IR, Bernstein KE (2008) Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme changes major histocompatibility complex class I peptide presentation by modifying C termini of peptide precursors. J Biol Chem 283:9957–9965. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709574200
Viinikainen A, Nyman T, Fyhrquist F, Saijonmaa O (2002) Downregulation of angiotensin converting enzyme by TNF-α in differentiating human macrophages. Cytokine 18:304–310. doi:10.1006/cyto.2002.1047
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808. doi:10.1172/JCI19246
Weisinger RS, Stanley TK, Begg DP, Weisinger HS, Spark KJ, Jois M (2009) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition lowers body weight and improves glucose tolerance in C57BL/6 J mice maintained on a high fat diet. Physiol Behav 98:192–197. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.05.009
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112:1821–1830. doi:10.1172/JCI19451
Yvan-Charvet L, Even P, Lamande N, Ferre P, Quignard-Boulange A (2006) Prevention of adipose tissue depletion during food deprivation in angiotensin type 2 receptor-deficient mice. Endocrinology 147:5078–5086. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0754
Zhang C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 103:398–406. doi:10.1007/s00395-008-0733-0
Zhang C, Wu J, Xu X, Potter BJ, Gao X (2010) Direct relationship between levels of TNF-α expression and endothelial dysfunction in reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 105:453–464. doi:10.1007/s00395-010-0083-6
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Marie von Reutern and Isabel Winter for expert technical assistance. The experimental work described in this manuscript was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FL 364/2-2, SFB 834/A5 and Exzellenzcluster 147 “Cardio-Pulmonary Systems”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlstedt, K., Trouvain, C., Namgaladze, D. et al. Adipocyte-derived lipids increase angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) expression and modulate macrophage phenotype. Basic Res Cardiol 106, 205–215 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0137-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0137-9