Abstract
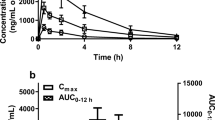
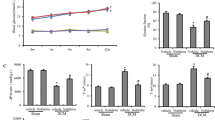
To investigate the effect of anti-cytokine-based therapy in the course of diabetic cardiomyopathy, we performed a study using an anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody treatment (mab) in Sprague male Dawley (SD) rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. Five days after streptozotocin injection, rats were treated with the anti-TNF-α mAb C432A for 6 weeks.At the end of the study, left ventricular (LV) function was determined by a pressure-catheter. Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, vascular adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, β2-lymphocyte-integrins+ (CD18+, CD11a+, CD11b+), ED1/CD68+ and cytokine (TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1β)- expressing infiltrates, total collagen content and stainings of collagen I and III were quantified by digital image analysis. LV phosphorylated and total ERK protein levels were determined by Western Blot. TNFα-antagonism reduced ICAM-1- and VCAM-1 expression and leukocyte infiltration to levels of non-diabetics and decreased macrophage residence by 3.3-fold compared with untreated diabetics. In addition, anti-TNF-α mAb-treatment decreased diabetes-induced cardiac TNF-α and IL-1β expression by 2.0-fold and 1.8- fold, respectively, and reduced the ratio of phosphorylated to total ERK by 2.7-fold. The reduction in intramyocardial inflammation was associated with a 5.4-fold and 3.6-fold reduction in cardiac collagen I and III content, respectively. This was reflected by a normalization of cardiac total collagen content to levels of non-diabetics and associated with an improved LV function. TNFα-antagonism attenuates the development of experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy associated with a reduction of intramyocardial inflammation and cardiac fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asbun J, Villarreal FJ (2006) The pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in the setting of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:693–700
Behrends M, Schulz R, Post H, Alexandrov A, Belosjorow S, Michel MC, Heusch G (2000) Inconsistent relation of MAPK activation to infarct size reduction by ischemic preconditioning in pigs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279:H1111–H1119
Blam ME, Stein RB, Lichtenstein GR (2001) Integrating anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: current and future perspectives. Am J Gastroenterol 96:1977–1997
Bristow MR (1998) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cardiomyopathy. Circulation 97:1340–1341
Bryant D, Becker L, Richardson J, Shelton J, Franco F, Peshock R, Thompson M, Giroir B (1998) Cardiac failure in transgenic mice with myocardial expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circulation 97:1375–1381
Cain BS, Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, Meng X, Joo KS, Banerjee A, Harken AH (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Crit Care Med 27:1309–1318
Chung ES, Packer M, Lo KH, Fasanmade AA, Willerson JT (2003) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor- alpha, in patients with moderateto- severe heart failure: results of the anti-TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) trial. Circulation 107:3133–3140
Clerk A, Harrison JG, Long CS, Sugden PH (1999) Pro-inflammatory cytokines stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase subfamilies, increase phosphorylation of c-Jun and ATF2 and upregulate c-Jun protein in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:2087–2099
Dorge H, Schulz R, Belosjorow S, Post H, van de Sand A, Konietzka I, Frede S, Hartung T, Vinten-Johansen J, Youker KA, Entman ML, Erbel R, Heusch G (2002) Coronary microembolization: the role of TNF-alpha in contractile dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:51–62
Dumitru CD, Ceci JD, Tsatsanis C, Kontoyiannis D, Stamatakis K, Lin JH, Patriotis C, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Kollias G, Tsichlis PN (2000) TNF-alpha induction by LPS is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent pathway. Cell 103:1071–1083
Fischer P, Hilfiker-Kleiner D (2007) Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: The gp130-STAT3 axis. Basic Res Cardiol 102:279–297
Gullestad L, Aukrust P (2005) Review of trials in chronic heart failure showing broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory approaches. Am J Cardiol 95:17C–23C; discussion 38C–40C
Gurevitch J, Frolkis I, Yuhas Y, Lifschitz- Mercer B, Berger E, Paz Y, Matsa M, Kramer A, Mohr R (1997) Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha improves myocardial recovery after ischemia and reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1554–1561
Kadokami T, Frye C, Lemster B, Wagner CL, Feldman AM, McTiernan CF (2001) Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody limits heart failure in a transgenic model. Circulation 104:1094–1097
Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP (1974) Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol 34:29–34
Karkar AM, Tam FW, Steinkasserer A, Kurrle R, Langner K, Scallon BJ, Meager A, Rees AJ (1995) Modulation of antibody- mediated glomerular injury in vivo by IL-1ra, soluble IL-1 receptor, and soluble TNF receptor. Kidney Int 48:1738–1746
Kelly RA, Smith TW (1997) Cytokines and cardiac contractile function.Circulation 95:778–781
Kubota T, McTiernan CF, Frye CS, Slawson SE, Lemster BH, Koretsky AP, Demetris AJ, Feldman AM (1997) Dilated cardiomyopathy in transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ Res 81:627–635
Labruto F, Yang J, Vaage J, Valen G (2005) Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha and its receptor I in preconditioning by hyperoxia. Basic Res Cardiol 100:198–207
Li M, Georgakopoulos D, Lu G, Hester L, Kass DA, Hasday J, Wang Y (2005) p38 MAP kinase mediates inflammatory cytokine induction in cardiomyocytes and extracellular matrix remodeling in heart. Circulation 111:2494–2502
Libby P, Ross R (1996) Cytokines and growth regulatory molecules. In: Fuster V, Ross R, Topol EJ (eds) Lippincott- Raven, Philadelphia, p 585–594
Liu X, Sun SQ, Hassid A, Ostrom RS (2006) cAMP Inhibits Transforming Growth Factor-beta-Stimulated Collagen Synthesis via Inhibition of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 and Smad Signaling in Cardiac Fibroblasts. Mol Pharmacol 70:1992–2003
Lorenz HM, Kalden JR (2002) Perspectives for TNF-alpha-targeting therapies. Arthritis Res 4(Suppl 3):S17–24
Mann DL (2003) Stress-activated cytokines and the heart: from adaptation to maladaptation. Annu Rev Physiol 65:81–101
Mann DL, McMurray JJ, Packer M, Swedberg K, Borer JS, Colucci WS, Djian J, Drexler H, Feldman A, Kober L, Krum H, Liu P, Nieminen M, Tavazzi L, van Veldhuisen DJ, Waldenstrom A, Warren M, Westheim A, Zannad F, Fleming T (2004) Targeted anticytokine therapy in patients with chronic heart failure: results of the Randomized Etanercept Worldwide Evaluation (RENEWAL). Circulation 109:1594–1602
Matsumori A, Yamada T, Suzuki H, Matoba Y, Sasayama S (1994) Increased circulating cytokines in patients with myocarditis and cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J 72:561–566
Maury CP, Teppo AM (1989) Circulating tumour necrosis factor-alpha (cachectin) in myocardial infarction. J Intern Med 225:333–336
Miki T, Miura T, Tanno M, Nishihara M, Naitoh K, Sato T, Takahashi A, Shimamoto K (2007) Impairment of cardioprotective PI3K-Akt signaling by post-infarct ventricular remodeling is compensated by an ERK-mediated pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 102:163–170
Millan J, Hewlett L, Glyn M, Toomre D, Clark P, Ridley AJ (2006) Lymphocyte transcellular migration occurs through recruitment of endothelial ICAM-1 to caveola- and F-actin-rich domains. Nat Cell Biol 8(2):113–123
Noutsias M, Pauschinger M, Ostermann K, Escher F, Blohm JH, Schultheiss H, Kuhl U (2002) Digital image analysis system for the quantification of infiltrates and cell adhesion molecules in inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Med Sci Monit 8:MT59–MT71
Pauschinger M, Knopf D, Petschauer S, Doerner A, Poller W, Schwimmbeck PL, Kuhl U, Schultheiss HP (1999) Dilated cardiomyopathy is associated with significant changes in collagen type I/III ratio. Circulation 99:2750–2756
Poornima IG, Parikh P, Shannon RP (2006) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: the search for a unifying hypothesis. Circ Res 98:596–605
Ruusalepp A, Czibik G, Flatebo T, Vaage J, Valen G (2007) Myocardial protection evoked by hyperoxic exposure involves signaling through nitric oxide and mitogen activated protein kinases. Basic Res Cardiol 102:318–326
Schulz R, Aker S, Belosjorow S, Heusch G (2004) TNFalpha in ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 99:8–11
Skyschally A, Gres P, Hoffmann S, Haude M, Erbel R, Schulz R, Heusch G (2007) Bidirectional role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in coronary microembolization: progressive contractile dysfunction versus delayed protection against infarction. Circ Res 100:140–146
Takami S, Yamashita S, Kihara S, Kameda-Takemura K, Matsuzawa Y (1998) High concentration of glucose induces the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 138:35–41
Thielmann M, Dorge H, Martin C, Belosjorow S, Schwanke U, van De Sand A, Konietzka I, Buchert A, Kruger A, Schulz R, Heusch G (2002) Myocardial dysfunction with coronary microembolization: signal transduction through a sequence of nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and sphingosine. Circ Res 90:807–913
Torre-Amione G, Kapadia S, Lee J, Durand JB, Bies RD, Young JB, Mann DL (1996) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor necrosis factor receptors in the failing human heart. Circulation 93:704–711
Tschope C, Walther T, Koniger J, Spillmann F, Westermann D, Escher F, Pauschinger M, Pesquero JB, Bader M, Schultheiss HP, Noutsias M (2004) Prevention of cardiac fibrosis and left ventricular dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by transgenic expression of the human tissue kallikrein gene. Faseb J 18:828–835
Tschope C, Walther T, Escher F, Spillmann F, Du J, Altmann C, Schimke I, Bader M, Sanchez-Ferrer CF, Schultheiss HP, Noutsias M (2005) Transgenic activation of the kallikreinkinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Faseb J 19:2057–2059
Tschope C, Walther T, Escher F, Spillmann F, Du J, Altmann C, Schimke I, Bader M, Sanchez-Ferrer CF, Schultheiss HP, Noutsias M (2005) Transgenic activation of the kallikreinkinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Faseb J 19:2057–2059
Valen G (2004) Signal transduction through nuclear factor kappa B in ischemia-reperfusion and heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 99:1–7
Westermann D, Rutschow S, Van Linthout S, Linderer A, Bucker-Gartner C, Sobirey M, Riad A, Pauschinger M, Schultheiss HP, Tschope C (2006) Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase attenuates left ventricular dysfunction by mediating pro-inflammatory cardiac cytokine levels in a mouse model of diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 49:2507–2513
Westermann D, Rutschow S, Jager S, Linderer A, Anker S, Riad A, Unger T, Schultheiss HP, Pauschinger M, Tschope C (2007) Contributions of inflammation and cardiac matrix metalloproteinase activity to cardiac failure in diabetic cardiomyopathy: the role of angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonism. Diabetes 56:641–646
Westermann D, Van Linthout S, Dhayat S, Dhayat N, Escher F, Bucker-Gartner C, Spillmann F, Noutsias M, Riad A, Schultheiss H-P, Tschope C (2007) Cardioprotective and anti inflammatory effects of interleukin converting enzyme inhibition in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. In, p db06–1662
Yokoyama T, Vaca L, Rossen RD, Durante W, Hazarika P, Mann DL (1993) Cellular basis for the negative inotropic effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the adult mammalian heart. J Clin Invest 92:2303–2312
Zhang M, Tracey KJ (1998) Tumor necrosis factor. In: AW T (ed) The Cytokine handbook. Academic Press, San Diego, Californie, p 517–548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westermann, D., Van Linthout, S., Dhayat, S. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonism protects from myocardial inflammation and fibrosis in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 102, 500–507 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0673-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0673-0