Abstract
Purpose
Studies have shown that Alzheimer’s disease is associated with significant alterations in the gut microbiota. But the effect of probiotics and/or prebiotics on Alzheimer’s disease still remains to be explored. The aim of this study was to determine whether Bifidobacterium Lactis Probio-M8 could alleviate Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiologies in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model.
Methods
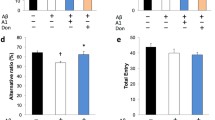
4-month old APP/PS1 mice were randomly put into two groups and fed with either Probio-M8 or saline water for 45 days. Fecal samples of mice were collected at the beginning and the end of the treatment period to determine the composition of the gut microbiota via 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing technology. The number and size of Aβ plaques in the brain were quantified. In addition, Y maze, novel object recognition and nest building were employed to access cognitive function in the 8-months old APP/PS1 mice at the end of the treatment period.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrated that Probio-M8 reduced Aβ plaque burden in the whole brain and protected against gut microbiota dysbiosis. Furthermore, Probio-M8 could alleviate cognitive impairment in the APP/PS1 mouse.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sampson T, Debelius J, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri G, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter C, Rocha S, Gradinaru V (2016) Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167(6):1469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
Vogt NM, Kerby RL, Dillmcfarland KA, Harding SJ, Merluzzi AP, Johnson SC, Carlsson CM, Asthana S, Zetterberg H, Blennow K (2017) Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):P563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13601-y
Long-Smith C, O’Riordan KJ, Clarke G, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2020) Microbiota-gut-brain axis: new therapeutic opportunities. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 60:477–502. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010919-023628
Cecarini V, Bonfili L, Gogoi O, Lawrence S, Venanzi FM, Azevedo V, Mancha-Agresti P, Drumond MM, Rossi G, Berardi S, Galosi L, Cuccioloni M, Angeletti M, Suchodolski JS, Pilla R, Lidbury JA, Eleuteri AM (2020) Neuroprotective effects of p62(SQSTM1)-engineered lactic acid bacteria in Alzheimer’s disease: a pre-clinical study. Aging (Albany NY) 12(16):15995–16020. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103900
Messaoudi M, Lalonde R, Violle N, Javelot H, Desor D, Nejdi A, Bisson JF, Rougeot C, Pichelin M, Cazaubiel M, Cazaubiel JM (2011) Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br J Nutr 105(5):755–764. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114510004319
Kowalski K, Mulak A (2019) Brain–gut–microbiota axis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(1):48–60. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm18087
Alonso C, Guilarte M, Vicario M, Ramos L, Rezzi S, Martinez C, Lobo B, Martin FP, Pigrau M, Gonzalez-Castro AM, Gallart M, Malagelada JR, Azpiroz F, Kochhar S, Santos J (2012) Acute experimental stress evokes a differential gender-determined increase in human intestinal macromolecular permeability. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24(8):740–746. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01928.x
Challis C, Hori A, Sampson TR, Yoo BB, Challis RC, Hamilton AM, Mazmanian SK, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Gradinaru V (2020) Gut-seeded alpha-synuclein fibrils promote gut dysfunction and brain pathology specifically in aged mice. Nat Neurosci 23(3):327–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-0589-7
Kim S, Kwon S-H, Kam T-I, Panicker N, Karuppagounder SS, Lee S, Lee JH, Kim WR, Kook M, Foss CA, Shen C, Lee H, Kulkarni S, Pasricha PJ, Lee G, Pomper MG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ko HS (2019) Transneuronal propagation of pathologic alpha-synuclein from the gut to the brain models Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 103(4):627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.035
Lai NY, Musser MA, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Baral P, Jacobson A, Ma P, Potts DE, Chen Z, Paik D, Soualhi S, Yan Y, Misra A, Goldstein K, Lagomarsino VN, Nordstrom A, Sivanathan KN, Wallrapp A, Kuchroo VK, Nowarski R, Starnbach MN, Shi H, Surana NK, An D, Wu C, Huh JR, Rao M, Chiu IM (2020) Gut-innervating nociceptor neurons regulate Peyer’s patch microfold cells and SFB levels to mediate salmonella host defense. Cell 180(1):33–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.014
Cattaneo A, Cattane N, Galluzzi S, Provasi S, Lopizzo N, Festari C, Ferrari C, Guerra UP, Paghera B, Muscio C, Bianchetti A, Volta GD, Turla M, Cotelli MS, Gennuso M, Prelle A, Zanetti O, Lussignoli G, Mirabile D, Bellandi D, Gentile S, Belotti G, Villani D, Harach T, Bolmont T, Padovani A, Boccardi M, Frisoni GB, Grp I-F (2017) Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol Aging 49:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.08.019
As A (2019) 2019 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 15(3):321–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2019.01.010
Seo D-o, Boros BD, Holtzman DM (2019) The microbiome: a target for Alzheimer disease? Cell Res 29(10):779–780. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0227-7
Zhuang ZQ, Shen LL, Li WW, Fu X, Zeng F, Gui L, Lü Y, Cai M, Zhu C, Tan YL (2018) Gut microbiome is altered in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis Jad 63(4):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180176
Brandscheid C, Schuck F, Reinhardt S, Schafer KH, Pietrzik CU, Grimm M, Hartmann T, Schwiertz A, Endres K (2017) Altered gut microbiome composition and tryptic activity of the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 56(2):775–788. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160926
Zhang L, Wang Y, Xiayu X, Shi C, Chen W, Song N, Fu X, Zhou R, Xu YF, Huang L, Zhu H, Han Y, Qin C (2017) Altered gut microbiota in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 60(4):1241–1257. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170020
Harach T, Marungruang N, Duthilleul N, Cheatham V, Mc Coy KD, Frisoni G, Neher JJ, Fak F, Jucker M, Lasser T, Bolmont T (2017) Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci Rep 7:41802. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41802
Kim M-S, Kim Y, Choi H, Kim W, Park S, Lee D, Kim DK, Kim HJ, Choi H, Hyun D-W, Lee J-Y, Choi EY, Lee D-S, Bae J-W, Mook-Jung I (2019) Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317431
Kim CS, Cha L, Sim M, Jung S, Chun WY, Baik HW, Shin DM (2020) Probiotic supplementation improves cognitive function and mood with changes in gut microbiota in community-dwelling elderly: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glaa090
Wang X, Sun G, Feng T, Zhang J, Huang X, Wang T, Xie Z, Chu X, Yang J, Wang H, Chang S, Gong Y, Ruan L, Zhang G, Yan S, Lian W, Du C, Yang D, Zhang Q, Lin F, Liu J, Zhang H, Ge C, Xiao S, Ding J, Geng M (2019) Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression. Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0216-x
Wang Y, Li N, Yang J-J, Zhao D-M, Chen B, Zhang G-Q, Chen S, Cao R-F, Yu H, Zhao C-Y, Zhao L, Ge Y-S, Liu Y, Zhang L-H, Hu W, Zhang L, Gai Z-T (2020) Probiotics and fructo-oligosaccharide intervention modulate the microbiota-gut brain axis to improve autism spectrum reducing also the hyper-serotonergic state and the dopamine metabolism disorder. Pharmacol Res 157:104784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104784
Liu W, Chen M, Duo L, Wang J, Guo S, Sun H, Menghe B, Zhang H (2020) Characterization of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from human colostrum. J Dairy Sci 103(5):4013–4025. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-17602
Zhang W, Wang Y, Li K, Kwok L-Y, Liu W, Zhang H (2020) Short communication: modulation of fatty acid metabolism improves oxygen tolerance of Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis Probio-M8. J Dairy Sci 103(10):8791–8795. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-18049
Jankowsky JL, Slunt HH, Ratovitski T, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Borchelt DR (2001) Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS a comparison of strategies. Biomol Eng 17(6):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-0344(01)00067-3
Jankowsky JL, Fadale DJ, Anderson J, Xu GM, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Lee MK, Younkin LH, Wagner SL, Younkin SG, Borchelt DR (2003) Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of the 42 residue β-amyloid peptide in vivo: evidence for augmentation of a 42-specific γ secretase. Hum Mol Genet 13(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh019
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodríguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu Y-X, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, Yutani H (2019) Welcome to the Tidyverse. J Open Source Softw 4(43):1686. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01686
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2013) phyloseq: an R Package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061217
Yu G, Smith DK, Zhu H, Guan Y, Lam TT-Y (2017) ggtree: an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol Evol 8(1):28–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210x.12628
Gloor GB, Macklaim JM, Fernandes AD (2016) Displaying variation in large datasets: plotting a visual summary of effect sizes. J Comput Graph Stat 25(3):971–979. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2015.1131161
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Enis A, Dannon B, Bérénice B, van den Marius B, Dave B, Martin Č, John C, Dave C, Nate C, GB A (2018) The galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res W1:W1. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky379
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R, Beiko RG, Huttenhower C (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676
Jung JS, Yan JJ, Li HM, Sultan MT, Yu J, Lee HS, Shin KJ, Song DK (2016) Protective effects of a dimeric derivative of ferulic acid in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 782:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.04.047
Kraeuter AK, Guest PC, Sarnyai Z (2019) The Y-maze for assessment of spatial working and reference memory in mice. Methods Mol Biol 1916:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8994-2_10
Shehu A, Magaji MG, Yau J, Ahmed A (2019) Methanol stem bark extract of Adansonia digitata ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior: Involvement of the HPA axis, BDNF, and stress biomarkers pathways. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2018-0153
Antunes M, Biala G (2012) The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn Process 13(2):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-011-0430-z
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O’Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS, Fenton AA, Dranovsky A, Hen R (2011) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 472(7344):466-U539. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09817
Paumier KL, Sukoff Rizzo SJ, Berger Z, Chen Y, Gonzales C, Kaftan E, Li L, Lotarski S, Monaghan M, Shen W, Stolyar P, Vasilyev D, Zaleska M, W DH, Dunlop J, (2013) Behavioral characterization of A53T mice reveals early and late stage deficits related to Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 8(8):e70274. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070274
Ann-Katrin K, Paul G, Zoltán S (2019) The nest building test in mice for assessment of general well-being. Methods Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8994-2_7
Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, Rowe CC, Sperling RA, Cummings JL (2015) Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15056. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.56
Selkoe DJ, Hardy J (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 8(6):595–608. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606210
Bloom GS (2014) Amyloid-beta and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol 71(4):505–508. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847
Lee D, Lee G, Yoon DS (2018) Anti-Abeta drug candidates in clinical trials and plasmonic nanoparticle-based drug-screen for Alzheimer’s disease. Analyst 143(10):2204–2212. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an02013a
Fang X, Zhou X, Miao Y, Han Y, Wei J, Chen T (2020) Therapeutic effect of GLP-1 engineered strain on mice model of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. AMB Express 10(1):80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01014-6
Téglás T, Ábrahám D, Jókai M, Kondo S, Mohammadi R, Fehér J, Szabó D, Wilhelm M, Radák Z (2020) Exercise combined with a probiotics treatment alters the microbiome, but moderately affects signalling pathways in the liver of male APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Biogerontology 21(6):807–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-020-09895-7
Patel C, Pande S, Acharya S (2020) Potentiation of anti-Alzheimer activity of curcumin by probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393(10):1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01904-3
Kaur H, Nagamoto-Combs K, Golovko S, Golovko MY, Klug MG, Combs CK (2020) Probiotics ameliorate intestinal pathophysiology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 92:114–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.04.009
Dziarski R, Park SY, Kashyap DR, Dowd SE, Gupta D (2016) Pglyrp-regulated gut microflora Prevotella falsenii, Parabacteroides distasonis and Bacteroides eggerthii enhance and Alistipes finegoldii attenuates colitis in mice. PLoS ONE 11(1):e0146162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146162
Fang Z, Li L, Zhao J, Zhang H, Lee YK, Lu W, Chen W (2019) Bifidobacteria adolescentis regulated immune responses and gut microbial composition to alleviate DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02145-8
Kong C, Gao R, Yan X, Huang L, Qin H (2019) Probiotics improve gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese mice fed a high-fat or high-sucrose diet. Nutrition 60:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.10.002
Gordon MN, Holcomb LA, Jantzen PT, DiCarlo G, Wilcock D, Boyett KW, Connor K, Melachrino J, O’Callaghan JP, Morgan D (2002) Time course of the development of Alzheimer-like pathology in the doubly transgenic PS1+APP mouse. Exp Neurol 173(2):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.2001.7754
Colpitts SL, Kasper EJ, Keever A, Liljenberg C, Kirby T, Magori K, Kasper LH, Ochoa-Reparaz J (2017) A bidirectional association between the gut microbiota and CNS disease in a biphasic murine model of multiple sclerosis. Gut Microbes 8(6):561–573. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2017.1353843
Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2012) Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(10):701–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3346
Aalten P, de Vugt ME, Lousberg R, Korten E, Jaspers N, Senden B, Jolles J, Verhey FR (2003) Behavioral problems in dementia: a factor analysis of the neuropsychiatric inventory. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 15(2):99–105. https://doi.org/10.1159/000067972
Filali M, Lalonde R (2009) Age-related cognitive decline and nesting behavior in an APPswe/PS1 bigenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1292:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.066
Ho L, Ono K, Tsuji M, Mazzola P, Singh R, Pasinetti GM (2018) Protective roles of intestinal microbiota derived short chain fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease-type beta-amyloid neuropathological mechanisms. Expert Rev Neurother 18(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1400909
Unger MM, Spiegel J, Dillmann KU, Grundmann D, Philippeit H, Burmann J, Fassbender K, Schwiertz A, Schafer KH (2016) Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 32:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.08.019
Sun J, Xu J, Ling Y, Wang F, Gong T, Yang C, Ye S, Ye K, Wei D, Song Z, Chen D, Liu J (2019) Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl Psychiat. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0525-3
Kobayashi Y, Sugahara H, Shimada K, Mitsuyama E, Kuhara T, Yasuoka A, Kondo T, Abe K, Xiao J-z (2017) Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):13510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13368-2
Morrison DJ, Preston T (2016) Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 7(3):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2016) Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16(6):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.42
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Heping Zhang, Zhihong Sun and all the staff of the Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology and Engineering for critical comments. We thank the Beijing Scitop Bio-tech Co Ltd for providing Probio-M8 strain. We also thank Maojin Yao for his insightful suggestions. We thank Wenliang Lei for his support with experimental apparatus.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0901101); General Program of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (2019A1515012230); Key Research and Development Project of Guangdong Province of China (2019B020210002); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019KZ01); National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671804).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC: investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. WKA: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. CQ: methodology, investigation, visualization. XL: investigation, resources. jm: resources, methodology. JR: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Amakye, W.K., Qi, C. et al. Bifidobacterium Lactis Probio-M8 regulates gut microbiota to alleviate Alzheimer’s disease in the APP/PS1 mouse model. Eur J Nutr 60, 3757–3769 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02543-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02543-x