Abstract
Purpose
Despite previous investigations on the effects of zinc supplementation on blood pressure, inconsistent findings are available in this regard. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials on the effects of zinc supplementation on blood pressure (BP) in adults.
Methods
Relevant studies published up to September 2019 were searched through PubMed/Medline, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and Google Scholar using suitable keywords. All randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that examined the effect of oral zinc supplementation on systolic blood pressure (SBP) or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in adults were included.
Results
Overall, nine trials were included in our study. Zinc supplementation significantly reduced SBP compared to the control [weighted mean differences (WMD) − 1.49 mmHg; 95% CI − 2.85 to − 0.13; P = 0.03]. However, zinc supplementation had no significant effects on DBP (WMD − 0.88 mmHg; 95% CI − 2.04 to 0.29; P = 0.14). Nonlinear analysis failed to indicate a significant influence of supplementation dosage or duration on both SBP and DBP. Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had a significant impact on our final results. In addition, we found no evidence for the presence of small-study effects among studies for both SBP and DBP.
Conclusion
We found a significant reduction in SBP following zinc supplementation. However, zinc supplementation had no significant effect on DBP. In addition, no nonlinear association was found between supplementation dosage and duration with changes in both SBP and DBP. Further RCTs using different dosages of zinc in various durations are required to confirm our conclusion.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 March 2020
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake. The family name of “Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento” was incorrect.
References
Pagidipati NJ, Gaziano TA (2013) Estimating deaths from cardiovascular disease: a review of global methodologies of mortality measurement. Circulation 127(6):749–756
Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, Ng M, Biryukov S, Marczak L, Alexander L, Estep K, Abate KH, Akinyemiju TF (2017) Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA 317(2):165–182
Chan M (2013) A global brief on hypertension. World Health Organization, Geneva
Lawes CM, Hoorn SV, Rodgers A (2008) Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 371(9623):1513–1518
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, De Ferranti S, Després J-P, Fullerton HJ (2016) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 133(4):447–454
Townsend N, Wickramasinghe K, Bhatnagar P, Smolina K, Nichols M, Leal J, Luengo-Fernandez R, Rayner M (2012) Coronary heart disease statistics. A conpendium of health statistics. University of Oxford, Oxford
Savica V, Bellinghieri G, Kopple JD (2010) The effect of nutrition on blood pressure. Annu Rev Nutr 30:365–401
Appel LJ (2017) The effects of dietary factors on blood pressure. Cardiol Clin 35(2):197–212
Mousavi SM, Karimi E, Hajishafiee M, Milajerdi A, Amini MR, Esmaillzadeh A (2019) Anti-hypertensive effects of cinnamon supplementation in adults: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1678012
Vallee BL, Auld DS (1990) Zinc coordination, function, and structure of zinc enzymes and other proteins. Biochemistry 29(24):5647–5659
Chasapis CT, Loutsidou AC, Spiliopoulou CA, Stefanidou ME (2012) Zinc and human health: an update. Arch Toxicol 86(4):521–534
Wang X, Wu W, Zheng W, Fang X, Chen L, Rink L, Min J, Wang F (2019) Zinc supplementation improves glycemic control for diabetes prevention and management: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqz041
Mousavi SM, Djafarian K, Mojtahed A, Varkaneh HK, Shab-Bidar S (2018) The effect of zinc supplementation on plasma C-reactive protein concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Pharmacol 834:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.019
Ranasinghe P, Wathurapatha WS, Ishara MH, Jayawardana R, Galappatthy P, Katulanda P, Constantine GR (2015) Effects of zinc supplementation on serum lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab 12:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-015-0023-4
Cortese-Krott MM, Kulakov L, Opländer C, Kolb-Bachofen V, Kröncke K-D, Suschek CV (2014) Zinc regulates iNOS-derived nitric oxide formation in endothelial cells. Redox Biol 2:945–954
Nevarez-Lopez SC, Simental-Mendia LE, Guerrero-Romero F, Burciaga-Nava JA (2019) Zinc deficiency is an independent risk factor for prehypertension in healthy subjects. Int J Vitam Nutr Res Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1024/0300-9831/a000593
Cozzolino M, Delcanale P, Montali C, Tognolini M, Giorgio C, Corrado M, Cavanna L, Bianchini P, Diaspro A, Abbruzzetti S, Viappiani C (2019) Enhanced photosensitizing properties of protein bound curcumin. Life Sci 233:116710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116710
Kim J (2013) Dietary zinc intake is inversely associated with systolic blood pressure in young obese women. Nutr Res Pract 7(5):380–384
Feyh A, Bracero L, Lakhani HV, Santhanam P, Shapiro JI, Khitan Z, Sodhi K (2016) Role of dietary components in modulating hypertension. J Clin Exp Cardiol 7(4):1–15
Ranasinghe P, Wathurapatha WS, Galappatthy P, Katulanda P, Jayawardena R, Constantine GR (2018) Zinc supplementation in prediabetes: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Diabetes 10(5):386–397
Naghizadeh S, Kheirouri S, Ojaghi H, Kaffash AJ (2018) Zinc supplementation attenuate diabetic indices in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Prog Nutr 20(2-S):263–269
Seet RC, Lee C-YJ, Lim EC, Quek AM, Huang H, Huang SH, Looi WF, Long LH, Halliwell B (2011) Oral zinc supplementation does not improve oxidative stress or vascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes with normal zinc levels. Atherosclerosis 219(1):231–239
Kim J, Lee S (2012) Effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors in obese Korean women. Nutr Res Pract 6(3):221–225
Suliburska J, Skrypnik K, Szulińska M, Kupsz J, Bogdański P (2018) Effect of hypotensive therapy combined with modified diet or zinc supplementation on biochemical parameters and mineral status in hypertensive patients. J Trace Elem Med Biol 47:140–148
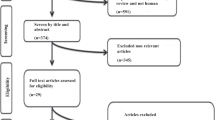
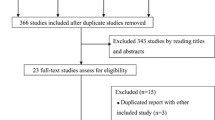
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savović J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR (2011) Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley, Hoboken
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5(1):13
Furuya-Kanamori L, Barendregt JJ, Doi SA (2018) A new improved graphical and quantitative method for detecting bias in meta-analysis. Int J Evid Based Healthc 16(4):195–203
Afkhami-Ardekani M, Karimi M, Mohammadi SM, Nourani F (2008) Effect of zinc sulfate supplementation on lipid and glucose in type 2 diabetic patients. Pak J Nutr 7(4):550–553
Parham M, Amini M, Aminorroaya A, Heidarian E (2008) Effect of zinc supplementation on microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes: a double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Rev Diabetic Stud 5(2):102
Sadeghi SM, Sadeghi F, Akhlaghi M (2019) Effect of zinc supplementation on weight and food intake in patients under hemodialysis. Int J Nutr Sci 4(2):72
Tabrizi FPF, Alipoor B, Ostadrahimi A, Sadagiani MM (2011) Effect of zinc supplementation on inflammatory markers in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Shiraz E Med J 12(1):30–38
Carpenter WE, Lam D, Toney GM, Weintraub NL, Qin Z (2013) Zinc, copper, and blood pressure: human population studies. Med Sci Monit 19:1–8. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.883708
Roohani N, Hurrell R, Kelishadi R, Schulin R (2013) Zinc and its importance for human health: an integrative review. J Res Med Sci 18(2):144–157
Canatan H, Bakan I, Akbulut M, Halifeoglu I, Cikim G, Baydas G, Kilic N (2004) Relationship among levels of leptin and zinc, copper, and zinc/copper ratio in plasma of patients with essential hypertension and healthy normotensive subjects. Biol Trace Elem Res 100(2):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:100:2:117
Bergomi M, Rovesti S, Vinceti M, Vivoli R, Caselgrandi E, Vivoli G (1997) Zinc and copper status and blood pressure. J Trace Elem Med Biol 11(3):166–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0946-672X(97)80047-8
Sato M, Yanagisawa H, Nojima Y, Tamura J, Wada O (2002) Zn deficiency aggravates hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats: possible role of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. Clin Exp Hypertens 24(5):355–370
Sato M, Kurihara N, Moridaira K, Sakamoto H, Ji T, Wada O, Yanagisawa H (2003) Dietary Zn deficiency does not influence systemic blood pressure and vascular nitric oxide signaling in normotensive rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 91(2):157–171
Kunutsor SK, Laukkanen JA (2016) Serum zinc concentrations and incident hypertension: new findings from a population-based cohort study. J Hypertens 34(6):1055–1061
Forstermann U, Sessa WC (2012) Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J 33(7):829–837. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
Hermann M, Flammer A, Luscher TF (2006) Nitric oxide in hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 8(12 Suppl 4):17–29
Yang WW, Krukoff TL (2000) Nitric oxide regulates body temperature, neuronal activation and interleukin-1 beta gene expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in response to immune stress. Neuropharmacology 39(11):2075–2089. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0028-3908(00)00054-x
Riordan JF (2003) Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and its relatives. Genome Biol 4(8):225. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2003-4-8-225
Tanonaka K, Marunouchi T (2016) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Nihon yakurigaku zasshi Folia pharmacologica Japonica 147(2):120–121. https://doi.org/10.1254/fpj.147.120
Dobzhansky T, Epling C (1948) The suppression of crossing over in inversion heterozygotes of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 34(4):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.34.4.137
Miloradovic Z, Ivanov M, Mihailovic-Stanojevic N, Grujic Milanovic J, Jovovic D, Vajic UJ, Markovic-Lipkovski J (2014) Acute superoxide radical scavenging reduces blood pressure but does not influence kidney function in hypertensive rats with postischemic kidney injury. Biomed Res Int 2014:512619. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/512619
Feng D, Ma B, Nazary-Vannani A, Kord-Varkaneh H, Fatahie S, Papageorgiou M, Poursoleiman F, Bd IJ, Li H, Ham D, Wang D (2019) The effects of green coffee been extract supplementation on lipid profile in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2019.10.002
Filippini T, Violi F, D'Amico R, Vinceti M (2017) The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol 230:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.048
Chopra S, Baby C, Jacob JJ (2011) Neuro-endocrine regulation of blood pressure. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 15(Suppl 4):S281–288. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.86860
National Institute of Health (2019) Zinc. National Institute of Health, Bethesda
Yanagisawa H (2008) Zinc deficiency and clinical practice—validity of zinc preparations. Yakugaku Zasshi 128(3):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.128.333
Penttila O, Hurme H, Neuvonen PJ (1975) Effect of zinc sulphate on the absorption of tetracycline and doxycycline in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9(2–3):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00614009
Lomaestro BM, Bailie GR (1995) Absorption interactions with fluoroquinolones. 1995 Update. Drug Saf 12(5):314–333. https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199512050-00004
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMM and AE conceived the study. TM and AM carried out the literature search and screening articles. MDM and HKV performed data extraction and quality assessment, independently. SMM, JR, and TM analyzed and interpreted data and wrote the manuscript. AE supervised the study. The final version of manuscript has been read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The family name of “Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento” was incorrect.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, S.M., Mofrad, M.D., do Nascimento, I.J.B. et al. The effect of zinc supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Eur J Nutr 59, 1815–1827 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02204-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02204-5