Abstract
Purpose
Chronic gastritis is observed in almost half world population. Traditional medications against chronic gastritis might produce adverse effects, so alternative nutritional strategies are needed to prevent the aggravation of gastric mucosal damage. The aim of this study is to evaluate the protective effect of the combination of wheat peptides and fucoidan (WPF) on adults diagnosed with chronic superficial gastritis in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Methods
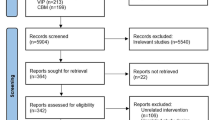
Participants were randomized to receive WPF (N = 53) or placebo (N = 53) once daily for 45 days. Pathological grading of gastric mucosal damage was scored using gastroscopy. Fecal samples were collected for the determination of calprotectin, short chain fatty acids (SCFA) levels and metagenomics analysis. Questionnaires for self-reported gastrointestinal discomforts, life quality and food frequency were collected throughout the study.
Results
WPF intervention reduced gastric mucosal damage in 70% subjects (P < 0.001). Significantly less stomach pain (P < 0.001), belching (P = 0.028), bloating (P < 0.001), acid reflux (P < 0.001), loss of appetite (P = 0.021), increased food intake (P = 0.020), and promoted life quality (P = 0.014) were reported in the WPF group. WPF intervention significantly decreased fecal calprotectin level (P = 0.003) while slightly increased fecal SCFAs level (P = 0.092). In addition, we found altered microbiota composition post-intervention with increased Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum (P = 0.032), Eubacterium siraeum (P = 0.036), Bacteroides intestinalis (P = 0.024) and decreased Prevotella copri (P = 0.055).
Conclusions
WPF intervention could be utilized as a nutritional alternative to mitigate the progression of chronic gastritis. Furthermore, WPF played an important role in altering gut microbial profile and SCFA production, which might benefit the lower gastrointestinal tract.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 14C-UBT:
-
Carbon-14 urea breath test
- CD:
-
Crohn’s disease
- HP:
-
Helicobacter pylori
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- QOL:
-
Quality of life
- SCFA:
-
Short chain fatty acids
- UC:
-
Ulcerative colitis
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
- WPF:
-
Combination of wheat peptides and fucoidan
References
Du Y, Bai Y, Xie P, Fang J, Wang X, Hou X, Tian D, Wang C, Liu Y, Sha W, Wang B, Li Y, Zhang G, Li Y, Shi R, Xu J, Li Y, Huang M, Han S, Liu J, Ren X, Xie P, Wang Z, Cui L, Sheng J, Luo H, Wang Z, Zhao X, Dai N, Nie Y, Zou Y, Xia B, Fan Z, Chen Z, Lin S, Li ZS (2014) Chronic gastritis in China: a national multi-center survey. BMC Gastroenterol 14:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230x-14-21
Sipponen P, Maaroos HI (2015) Chronic gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol 50(6):657–667. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2015.1019918
Ddine LC, Ddine CC, Rodrigues CC, Kirsten VR, Colpo E (2012) Factors associated with chronic gastritis in patients with presence and absence of Helicobacter pylori. Arq Bras Cir Dig 25(2):96–100
Correa P, Yardley JH (1992) Grading and classification of chronic gastritis: one American response to the Sydney system. Gastroenterology 102(1):355–359
Siurala M, Sipponen P, Kekki M (1985) Chronic gastritis: dynamic and clinical aspects. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 109:69–76
Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V (2009) Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol 472:467–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-492-0_23
Sipponen P, Price AB (2011) The Sydney System for classification of gastritis 20 years ago. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(Suppl 1):31–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06536.x
Helicobacter A (2001) Gastric cancer and Helicobacter pylori: a combined analysis of 12 case control studies nested within prospective cohorts. Gut 49(3):347–353
Vorobjova T, Faller G, Maaroos HI, Sipponen P, Villako K, Uibo R, Kirchner T (2000) Significant increase in antigastric autoantibodies in a long-term follow-up study of H. pylori gastritis. Virchows Arch 437(1):37–45
Kan J, Hood M, Burns C, Scholten J, Chuang J, Tian F, Pan X, Du J, Gui M (2017) A novel combination of wheat peptides and fucoidan attenuates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage through anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and pro-survival mechanisms. Nutrients 9(9):E978. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090978
Kamada N, Seo SU, Chen GY, Núñez G (2013) Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 13(5):321–335
Kostic AD, Xavier RJ, Gevers D (2014) The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology 146(6):1489–1499
Le Poul E, Loison C, Struyf S, Springael JY, Lannoy V, Decobecq ME, Brezillon S, Dupriez V, Vassart G, Van Damme J, Parmentier M, Detheux M (2003) Functional characterization of human receptors for short chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J Biol Chem 278(28):25481–25489. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301403200
Chambers ES, Preston T, Frost G, Morrison DJ (2018) Role of Gut microbiota-generated short-chain fatty acids in metabolic and cardiovascular health. Curr Nutr Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-018-0248-8
Anand S, Mande SS (2018) Diet, microbiota and gut-lung connection. Front Microbiol 9:2147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02147
Sircana A, Framarin L, Leone N, Berrutti M, Castellino F, Parente R, De Michieli F, Paschetta E, Musso G (2018) Altered gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes: just a coincidence? Curr Diabetes Rep 18(10):98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-018-1057-6
Valle J, Seppala K, Sipponen P, Kosunen T (1991) Disappearance of gastritis after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. A morphometric study. Scand J Gastroenterol 26(10):1057–1065
Arkkila PE, Seppala K, Farkkila MA, Veijola L, Sipponen P (2006) Helicobacter pylori eradication in the healing of atrophic gastritis: a one-year prospective study. Scand J Gastroenterol 41(7):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520500463175
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444(7122):1022–1023. https://doi.org/10.1038/4441022a
Couzin-Frankel J (2010) Bacteria and asthma: untangling the links. Science 330(6008):1168–1169. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.330.6008.1168
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LC, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 90(3):859–904. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
Yin H, Pan X, Song Z, Wang S, Yang L, Sun G (2014) Protective effect of wheat peptides against indomethacin-induced oxidative stress in IEC-6 cells. Nutrients 6(2):564–574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020564
Zhang QX, Ling YF, Sun Z, Zhang L, Yu HX, Kamau SM, Lu RR (2012) Protective effect of whey protein hydrolysates against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress on PC12 cells. Biotechnol Lett 34(11):2001–2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1017-1
Yang X, Wang Y, Wang F, Xia H, Pan X, Zhu H, Ruizeng GU, Yongqing MA, Tang H, Wang S (2016) Effect of hydrolyzed wheat protein peptide on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal damage in rats. Food Sci 37:178–182
Hong Y, Pan XC, Wang SK, Yang LG, Sun GJ (2014) Protective effect of wheat peptides against small intestinal damage induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in rats. J Integr Agr 13(9):2019–2027
Wijesinghe WAJP, Jeon YJ (2012) Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: a review. Carbohydr Polym 88:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.029
Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, D’Incecco A, Piccoli A, Totani L, Tinari N, Morozevich GE, Berman AE, Bilan MI, Usov AI, Ustyuzhanina NE, Grachev AA, Sanderson CJ, Kelly M, Rabinovich GA, Iacobelli S, Nifantiev NE (2007) A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 17(5):541–552. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwm014
Yang C, Chung D, Shin IS, Lee H, Kim J, Lee Y, You S (2008) Effects of molecular weight and hydrolysis conditions on anticancer activity of fucoidans from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. Int J Biol Macromol 43(5):433–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2008.08.006
Drossman DA (2006) The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology 130(5):1377–1390
Price AB (1991) The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(3):209–222
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P (1996) Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol 20(10):1161–1181
Yu Z (2004) Endoscopic classification and trial standards on treatment of chronic gastritis. Chin J Dig Endosc 21(2):77–78
CFDA (2003) Method for the assessment of protection of gastric mucosa function. Technical Standards for Testing and Assessment for Health Food, pp 163–166
Group TW (1995) The World Health Organization Quality of Life assessment (WHOQOL): position paper from the World Health Organization. Soc Sci Med 41(10):1403–1409
Waller PA, Gopal PK, Leyer GJ, Ouwehand AC, Reifer C, Stewart ME, Miller LE (2011) Dose-response effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on whole gut transit time and functional gastrointestinal symptoms in adults. Scand J Gastroenterol 46(9):1057
Mei H, Sun J, Zhuo QJ, Yue XY (2017) Effects of cow’s milk beta-casein variants on symptoms of milk intolerance in Chinese adults: a multicentre, randomised controlled study. Nutr J 16(1):72
Zhao L, Zhang F, Ding X, Wu G, Lam YY, Wang X, Fu H, Xue X, Lu C, Ma J (2018) Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science 359(6380):1151–1156
Roat KJ, Pedro CL, Kristoffer F, Jaime HC, Li SS, Marja D, Yvonne VA, Georg Z, Shinichi S, Peer B (2016) MOCAT2: a metagenomic assembly, annotation and profiling framework. Bioinformatics 32(16):2520–2523
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, Lam TW, Yiu SM, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2009) SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 25(15):1966–1967
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28(23):3150–3152
Truong DT, Franzosa EA, Tickle TL, Scholz M, Weingart G, Pasolli E, Tett A, Huttenhower C, Segata N (2015) MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nat Methods 12(10):902
Sung J, Kim S, Cabatbat JJT, Jang S, Jin YS, Jung GY, Chia N, Kim PJ (2017) Global metabolic interaction network of the human gut microbiota for context-specific community-scale analysis. Nat Commun 8:15393
François IE, Lescroart O, Veraverbeke WS, Marzorati M, Possemiers S, Evenepoel P, Hamer H, Houben E, Windey K, Welling GW (2012) Effects of a wheat bran extract containing arabinoxylan oligosaccharides on gastrointestinal health parameters in healthy adult human volunteers: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Br J Nutr 108(12):2229–2242
Benarye E, Goldin E, Wengrower D, Stamper A, Kohn R, Berry E (2002) Wheat grass juice in the treatment of active distal ulcerative colitis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Scand J Gastroenterol 37(4):444–449
Renaldi K, Simadibrata M, Syam AF, Rani AA, Krisnuhoni E (2011) Influence of fucoidan in mucus thickness of gastric mucosa in patients with chronic gastritis. Indones J Gastroenterol Hepatol Dig Endosc 12(2):79–84
Raghavendran HRB, Srinivasan P, Rekha S (2011) Immunomodulatory activity of fucoidan against aspirin-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 11(2):157–163
Wang Y, Su W, Zhang C, Xue C, Chang Y, Wu X, Tang Q, Wang J (2012) Protective effect of sea cucumber (Acaudina molpadioides) fucoidan against ethanol-induced gastric damage. Food Chem 133(4):1414–1419
Shi H, Chang Y, Gao Y, Wang X, Chen X, Wang Y, Xue C, Tang Q (2017) Dietary fucoidan of Acaudina molpadioides alters gut microbiota and mitigates intestinal mucosal injury induced by cyclophosphamide. Food Funct 8(9):3383–3393
Shibata H, Iimuro M, Uchiya N, Kawamori T, Nagaoka M, Ueyama S, Hashimoto S, Yokokura T, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K (2010) Preventive effects of cladosiphon fucoidan against Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils. Helicobacter 8(1):59–65
Besednova NN, Zaporozhets TS, Somova LM, Kuznetsova TA (2015) Prospects for the use of extracts and polysaccharides from marine algae to prevent and treat the diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 20(2):89–97
Simon P, Goode P, Mobasseri A, Zopf D (1997) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori binding to gastrointestinal epithelial cells by sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides. Infect Immun 65(2):750–757
Lehmann FS, Burri E, Beglinger C (2015) The role and utility of faecal markers in inflammatory bowel disease. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 8(1):23–36
Røseth AG, Schmidt PM, Fagerhol MK (1998) Correlation between faecal excretion of indium-111-labelled granulocytes and calprotectin, a granulocyte marker protein, in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 34(1):50–54
Costa F, Mumolo MG, Ceccarelli L, Bellini M, Romano MR, Sterpi C, Ricchiuti A, Marchi S, Bottai M (2005) Calprotectin is a stronger predictive marker of relapse in ulcerative colitis than in Crohn’s disease. Gut 54(3):364–368
Massimo Montalto, Antonella Gallo, Gianluca Ianiro, Luca Santoro, Ferruccio Onofrio (2010) Can chronic gastritis cause an increase in fecal calprotectin concentrations? World J Gastroenterol 16(27):3406
Summerton CB, Longlands MG, Wiener K, Shreeve DR (2002) Faecal calprotectin: a marker of inflammation throughout the intestinal tract. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):841–845
Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB (1995) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr 125(6):1401–1412
Gibson GR, Probert HM, Loo JV, Rastall RA, Roberfroid MB (2004) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr Res Rev 17(2):259–275
Roberfroid MB (2000) Prebiotics and probiotics: are they functional foods?–. Am J Clin Nutr 71(6):1682S–1687S
Zaporozhets TS, Besednova NN, Kuznetsova TA, Zvyagintseva TN, Makarenkova ID, Kryzhanovsky SP, Melnikov VG (2014) The prebiotic potential of polysaccharides and extracts of seaweeds. Russ J Mar Biol 40(1):1–9
Shang Q, Shan X, Cai C, Hao J, Li G, Yu G (2016) Dietary fucoidan modulates the gut microbiota in mice by increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Ruminococcaceae. Food Funct 7(7):3224
Lynch MB, Sweeney T, Callan JJ, O’Sullivan JT, O’Doherty JV (2010) The effect of dietary Laminaria-derived laminarin and fucoidan on nutrient digestibility, nitrogen utilisation, intestinal microflora and volatile fatty acid concentration in pigs. J Sci Food Agric 133(1):157–160
Wang Y, Han F, Hu B, Li J, Yu W (2006) In vivo prebiotic properties of alginate oligosaccharides prepared through enzymatic hydrolysis of alginate. Nutr Res 26(11):597–603
Shang Q, Song G, Zhang M, Shi J, Xu C, Hao J, Li G, Yu G (2017) Dietary fucoidan improves metabolic syndrome in association with increased Akkermansia population in the gut microbiota of high-fat diet-fed mice. J Funct Foods 28:138–146
Boffa LC, Lupton JR, Mariani MR, Ceppi M, Newmark HL, Scalmati A, Lipkin M (1992) Modulation of colonic epithelial cell proliferation, histone acetylation, and luminal short chain fatty acids by variation of dietary fiber (wheat bran) in rats. Cancer Res 52(21):5906–5912
Neyrinck AM, Possemiers S, Druart C, Van TDW, De FB, Cani PD, Larondelle Y, Delzenne NM (2011) Prebiotic effects of wheat arabinoxylan related to the increase in bifidobacteria, Roseburia and Bacteroides/Prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One 6(6):e20944
Davila AM, Blachier F, Gotteland M, Andriamihaja M, Benetti PH, Sanz Y, Tomé D (2013) Intestinal luminal nitrogen metabolism: role of the gut microbiota and consequences for the host. Pharmacol Res 69(1):114–126
Caminero A, Nistal E, Arias L, Vivas S, Comino I, Real A, Sousa C, de Morales JM, Ferrero MA, Rodríguez-Aparicio LB (2012) A gluten metabolism study in healthy individuals shows the presence of faecal glutenasic activity. Eur J Nutr 51(3):293–299
De Palma G, Nadal I, Collado MC, Sanz Y (2009) Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult human subjects. Br J Nutr 102(8):1154–1160
Caminero A, Nistal E, Herrán AR, Pérez-Andrés J, Vaquero L, Vivas S, de Morales JMR, Casqueiro J (2014) Gluten metabolism in humans: involvement of the gut microbiota. In: Wheat and rice in disease prevention and health. Elsevier, pp 157–170. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124017160000131
Caminero A, Nistal E, Herrán AR, Pérez-Andrés J, Ferrero MA, Ayala LV, Vivas S, de Morales JMR, Albillos SM, Casqueiro FJ (2015) Differences in gluten metabolism among healthy volunteers, coeliac disease patients and first-degree relatives. Br J Nutr 114(8):1157–1167
Laparra JM, Sanz Y (2010) Bifidobacteria inhibit the inflammatory response induced by gliadins in intestinal epithelial cells via modifications of toxic peptide generation during digestion. J Cell Biochem 109(4):801–807
Laparra JM, Olivares M, Gallina O, Sanz Y (2012) Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7347 modulates immune responses in a gliadin-induced enteropathy animal model. PLoS One 7(2):e30744
Sánchez E, Laparra JM, Sanz Y (2012) Discerning the role of Bacteroides fragilis in celiac disease pathogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(18):6507–6515
Kolho KL, Korpela K, Jaakkola T, Pichai MVA, Zoetendal EG, Salonen A, Vos WMD (2015) Fecal microbiota in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease and its relation to inflammation. Am J Gastroenterol 110(6):921
Lucke K, Miehlke S, Jacobs E, Schuppler M (2006) Prevalence of Bacteroides and Prevotella spp. in ulcerative colitis. J Med Microbiol 55(5):617
Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata N, Ubeda C, Bielski C, Rostron T, Cerundolo V, Pamer EG, Abramson SB (2013) Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. Elife Sci 2(1629):e01202
Acknowledgements
We thank Li Zhang from SPRIM China for their great work in coordinating the clinical trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Ethics statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All procedures involving human subjects were reviewed and approved by the IRB of Shanghai Nutrition Society. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kan, J., Cheng, J., Xu, L. et al. The combination of wheat peptides and fucoidan protects against chronic superficial gastritis and alters gut microbiota: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Nutr 59, 1655–1666 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02020-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02020-6