Abstract
Objective
To examine the association between food and beverage consumption and time spent in different sedentary behaviours such as watching TV and DVDs, playing computer/video games and quiet play/activities in preschoolers.
Methods
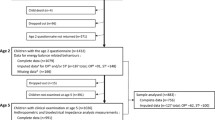
A sample of 6431 (51.8 % males) European preschoolers aged 3.5–5.5 years from six survey centres was included in the data analyses. Data on dietary habits and sedentary behaviours [watching TV, playing computer and quiet play (both during weekdays and weekend days)] were collected via standardized proxy-administered questionnaires. One-way analysis of covariance and general linear model (adjusted for sex, maternal education, body mass index and centre) were conducted.
Results
The results of the generalized linear model showed that the more strong associations in both males and females who were watching TV for > 1 h/day during weekdays were positively associated with increased consumption of fizzy drinks (β = 0.136 for males and β = 0.156 for females), fresh and packed juices (β = 0.069, β = 0.089), sweetened milk (β = 0.119, β = 0.078), cakes and biscuits (β = 0.116, β = 0.145), chocolate (β = 0.052, β = 0.090), sugar-based desserts and pastries (β = 0.234, β = 0.250), salty snacks (β = 0.067, β = 0.056), meat/poultry/processed meat (β = 0.067, β = 0.090) and potatoes (β = 0.071, β = 0.067), and negative associations were observed for the consumption of fruits (β = −0.057, β = −0.099), vegetables (β = −0.056, β = −0.082) and fish (β = −0.013, β = −0.013). During weekend days, results were comparable.
Conclusions
In European preschoolers, sedentary behaviours were associated with consumption of energy-dense foods and fizzy drinks. The present findings will contribute to improve the strategies to prevent overweight, obesity and nutrition-related chronic diseases from early childhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- FFQ:
-
Food frequency questionnaire
- ANCOVA:
-
Analysis of covariance
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
References
Lin L-J, Chang H-Y, Luh D-L, Hurng B-S, Yen L-L (2014) The Trajectory and the related physical and social determinants of body mass index in elementary school children: results from the child and adolescent behaviors in long-term evolution study. Hindawi Publ Corp J Obes. doi:10.1155/2014/728762
Duvinage K, Ibrugger S, Kreichauf S, Wildgruber A, De Craemer M, De Decker E, Androutsos O, Lateva M, Iotova V, Socha P, Zych K, Mouratidou T, Mesana Graffe MI, Manios Y, Koletzko B (2014) Developing the intervention material to increase physical activity levels of European preschool children: the ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):27–39. doi:10.1111/obr.12176
Hughes AR, Sherriff A, Ness AR, Reilly JJ (2014) Timing of adiposity rebound and adiposity in adolescence. Pediatrics 134(5):e1354–e1361. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-1908
Mouratidou T, Mesana MI, Manios Y, Koletzko B, Chinapaw MJ, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Socha P, Iotova V, Moreno LA (2012) Assessment tools of energy balance-related behaviours used in European obesity prevention strategies: review of studies during preschool. Obes Rev 13(Suppl 1):42–55. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00958.x
Miller A, Franzen-Castle L, Aguirre T, Krehbiel M, Colby S, Kattelmann K, Olfert MD, Mathews D, White A (2016) Food-related behavior and intake of adult main meal preparers of 9–10 year-old children participating in iCook 4-H: a five-state childhood obesity prevention pilot study. Appetite 101:163–170. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2016.03.006
Barnes J, Behrens TK, Benden ME, Biddle S, Bond D, Brassard P, Brown H, Carr L, Chaput JP, Christian H, Colley R, Duggan M, Dunstan D, Ekelund U, Esliger D, Ferraro Z, Freedhoff Y, Galaviz K, Gardiner P, Goldfield G, Haskell WL, Liguori G, Herman KM, Hinckson E, Larouche R, Leblanc A, Levine J, Maeda H, McCall M, McCubbin W, McGuire A, Onywera V, Owen N, Peterson M, Prince S, Ramirez E, Ridgers N, Saunders T, Schuna JM, Sherar L, Spruijt-Metz D, Taylor B, Tremblay M, Tucker J, Wijndaele K, Wilson J, Wilson J, Woodruff S, Network SBR (2012) Letter to the Editor: standardized use of the terms “sedentary” and “sedentary behaviours”. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab Physiologie Appliquee Nutrition Et Metabolisme 37(3):540–542. doi:10.1139/H2012-024
Biddle SJ (2007) Sedentary behavior. Am J Prev Med 33(6):502–504. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2007.08.002
de Jong E, Visscher TL, HiraSing RA, Heymans MW, Seidell JC, Renders CM (2013) Association between TV viewing, computer use and overweight, determinants and competing activities of screen time in 4- to 13-year-old children. Int J Obes (Lond) 37(1):47–53. doi:10.1038/ijo.2011.244
Santaliestra-Pasias AM, Mouratidou T, Verbestel V, Huybrechts I, Gottrand F, Le Donne C, Cuenca-Garcia M, Diaz LE, Kafatos A, Manios Y, Molnar D, Sjostrom M, Widhalm K, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Moreno LA (2012) Food consumption and screen-based sedentary behaviors in European adolescents: the HELENA study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 166(11):1010–1020. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2012.646
Borghese MM, Tremblay MS, Leduc G, Boyer C, Belanger P, LeBlanc AG, Francis C, Chaput JP (2014) Independent and combined associations of total sedentary time and television viewing time with food intake patterns of 9- to 11-year-old Canadian children. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39(8):937–943. doi:10.1139/apnm-2013-0551
Rey-Lopez JP, Vicente-Rodriguez G, Repasy J, Mesana MI, Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Kafatos A, Huybrechts I, Cuenca-Garcia M, Leon JF, Gonzalez-Gross M, Sjostrom M, de Bourdeaudhuij I, Moreno LA (2011) Food and drink intake during television viewing in adolescents: the Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence (HELENA) study. Public Health Nutr 14(9):1563–1569. doi:10.1017/S1368980011000383
Johansson L, Thelle DS, Solvoll K, Bjorneboe GE, Drevon CA (1999) Healthy dietary habits in relation to social determinants and lifestyle factors. Br J Nutr 81(3):211–220
Wang MC, Kim S, Gonzalez AA, MacLeod KE, Winkleby MA (2007) Socioeconomic and food-related physical characteristics of the neighbourhood environment are associated with body mass index. J Epidemiol Community Health 61(6):491–498. doi:10.1136/jech.2006.051680
Vereecken CA, Inchley J, Subramanian SV, Hublet A, Maes L (2005) The relative influence of individual and contextual socio-economic status on consumption of fruit and soft drinks among adolescents in Europe. Eur J Public Health 15(3):224–232. doi:10.1093/eurpub/cki005
Manios Y (2012) The ‘ToyBox-study’ obesity prevention programme in early childhood: an introduction. Obes Rev 13(Suppl 1):1–2. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00977.x
Androutsos O, Apostolidou E, Iotova V, Socha P, Birnbaum J, Moreno L, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Koletzko B, Manios Y (2014) Process evaluation design and tools used in a kindergarten-based, family-involved intervention to prevent obesity in early childhood. The ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):74–80. doi:10.1111/obr.12185
Manios Y, Androutsos O, Katsarou C, Iotova V, Socha P, Geyer C, Moreno L, Koletzko B, De Bourdeaudhuij I (2014) Designing and implementing a kindergarten-based, family-involved intervention to prevent obesity in early childhood: the ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):5–13. doi:10.1111/obr.12175
Gonzalez-Gil EM, Mouratidou T, Cardon G, Androutsos O, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Gozdz M, Usheva N, Birnbaum J, Manios Y, Moreno LA (2014) Reliability of primary caregivers reports on lifestyle behaviours of European pre-school children: the ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):61–66. doi:10.1111/obr.12184
Mouratidou T, Miguel ML, Androutsos O, Manios Y, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Cardon G, Kulaga Z, Socha P, Galcheva S, Iotova V, Payr A, Koletzko B, Moreno LA (2014) Tools, harmonization and standardization procedures of the impact and outcome evaluation indices obtained during a kindergarten-based, family-involved intervention to prevent obesity in early childhood: the ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):53–60. doi:10.1111/obr.12183
De Miguel-Etayo P, Mesana MI, Cardon G, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Gozdz M, Socha P, Lateva M, Iotova V, Koletzko BV, Duvinage K, Androutsos O, Manios Y, Moreno LA (2014) Reliability of anthropometric measurements in European preschool children: the ToyBox-study. Obes Rev 15(Suppl 3):67–73. doi:10.1111/obr.12181
van Stralen MM, te Velde SJ, van Nassau F, Brug J, Grammatikaki E, Maes L, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Verbestel V, Galcheva S, Iotova V, Koletzko BV, von Kries R, Bayer O, Kulaga Z, Serra-Majem L, Sanchez-Villegas A, Ribas-Barba L, Manios Y, Chinapaw MJ (2012) Weight status of European preschool children and associations with family demographics and energy balance-related behaviours: a pooled analysis of six European studies. Obes Rev 13(Suppl 1):29–41. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00959.x
Australia C (2009) Healthy eating and physical activity guidelines for early childhood settings
Tremblay MS, Leblanc AG, Carson V, Choquette L, Connor Gorber S, Dillman C, Duggan M, Gordon MJ, Hicks A, Janssen I, Kho ME, Latimer-Cheung AE, Leblanc C, Murumets K, Okely AD, Reilly JJ, Stearns JA, Timmons BW, Spence JC (2012) Canadian sedentary behaviour guidelines for the early years (aged 0–4 years). Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37(2):370–391. doi:10.1139/h2012-019
Huybrechts I, De Backer G, De Bacquer D, Maes L, De Henauw S (2009) Relative validity and reproducibility of a food-frequency questionnaire for estimating food intakes among Flemish preschoolers. Int J Environ Res Public Health 6(1):382–399. doi:10.3390/ijerph6010382
Commission of the European Communities (2005) Green paper: promoting healthy diets and physical activity: a European dimension for the prevention of overweight, obesity, and chronic disease. Published 2005. Accessed 27 May 2012
Pearson N, Biddle SJH (2011) Sedentary behavior and dietary intake in children, adolescents, and adults. A systematic review. Am J Prev Med 41(2):178–188. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.002
Lipsky LM, Iannotti RJ (2012) Associations of television viewing with eating behaviors in the 2009 Health Behaviour in School-aged Children Study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 166(5):465–472
Boynton-Jarrett R, Thomas TN, Peterson KE, Wiecha J, Sobol AM, Gortmaker SL (2003) Impact of television viewing patterns on fruit and vegetable consumption among adolescents. Pediatrics 112(6 Pt 1):1321–1326
Pearson N, Biddle SJH, Williams L, Worsley A, Crawford D, Ball K (2014) Adolescent television viewing and unhealthy snack food consumption: the mediating role of home availability of unhealthy snack foods. Public Health Nutr 17(2):317–323. doi:10.1017/S1368980012005204
Sadjadi A, Hislop TG, Bajdik C, Bashash M, Ghorbani A, Nouraie M, Babaei M, Malekzadeh R, Yavari P (2009) Comparison of breast cancer survival in two populations: Ardabil, Iran and British Columbia, Canada. BMC Cancer 9:381. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-381
Santaliestra-Pasias AM, Mouratidou T, Huybrechts I, Beghin L, Cuenca-Garcia M, Castillo MJ, Galfo M, Hallstrom L, Kafatos A, Manios Y, Marcos A, Molnar D, Plada M, Pedrero-Chamizo R, Widhalm K, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Moreno LA (2014) Increased sedentary behaviour is associated with unhealthy dietary patterns in European adolescents participating in the HELENA study. Eur J Clin Nutr 68(3):300–308. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2013.170
Rae S, Ashford JR, Morgan DC, Pearson NG, Pasqual RSH (1963) A comparison of some alternative procedures in classification of chest radiographs for coal-workers pneumoconiosis. Br J Ind Med 20(4):293
Reilly JJ (2010) Low levels of objectively measured physical activity in preschoolers in child care. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(3):502–507. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cea100
Cameron AJ, Ball K, Pearson N, Lioret S, Crawford DA, Campbell K, Hesketh K, McNaughton SA (2012) Socioeconomic variation in diet and activity-related behaviours of Australian children and adolescents aged 2–16 years. Pediatr Obes 7(4):329–342. doi:10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00060.x
Chahal H, Fung C, Kuhle S, Veugelers PJ (2013) Availability and night-time use of electronic entertainment and communication devices are associated with short sleep duration and obesity among Canadian children. Pediatr Obes 8(1):42–51. doi:10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00085.x
Tremblay MS, LeBlanc AG, Kho ME, Saunders TJ, Larouche R, Colley RC, Goldfield G, Gorber SC (2011) Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 8:98. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-8-98
Pearson N, Ball K, Crawford D (2011) Mediators of longitudinal associations between television viewing and eating behaviours in adolescents. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-8-23
Connor SM (2006) Food-related advertising on preschool television: building brand recognition in young viewers. Pediatrics 118(4):1478–1485. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-2837
American Academy of Pediatrics (2001) American Academy of Pediatrics: Children, adolescents, and television. Pediatrics 107(2):423–426
Subar AF, Freedman LS, Tooze JA, Kirkpatrick SI, Boushey C, Neuhouser ML, Thompson FE, Potischman N, Guenther PM, Tarasuk V, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM (2015) Addressing current criticism regarding the value of self-report dietary data. J Nutr 145(12):2639–2645. doi:10.3945/jn.115.219634
Acknowledgments
The ToyBox-study was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (CORDIS FP7) of the European Commission under Grant Agreement No. 245200. The content of this article reflects only the authors’ views, and the European Community is not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein. Additionally, A.M. Santaliestra-Pasías was partially supported by grants from the Spanish Carlos III Health Institute: RD12/0026/0009 (Red SAMID: Maternal, Child Health and Development Research Network).
Coordinator
Yannis Manios.
Steering Committee
Yannis Manios, Berthold Koletzko, Ilse De Bourdeaudhuij, Mai Chin A Paw, Luis Moreno, Carolyn Summerbell, Tim Lobstein, Lieven Annemans, Goof Buijs.
External Advisors
John Reilly, Boyd Swinburn, Dianne Ward.
Harokopio University (Greece)
Yannis Manios, Odysseas Androutsos, Eva Grammatikaki, Christina Katsarou, Eftychia Apostolidou, Eirini Efstathopoulou, Christina-Paulina Lambrinou, Lydia Tsirigoti.
Ludwig Maximilians Universitaet Muenchen (Germany)
Berthold Koletzko, Kristin Duvinage, Sabine Ibrügger, Angelika Strauß, Birgit Herbert, Julia Birnbaum, Annette Payr, Christine Geyer.
Ghent University (Belgium)
Department of Movement and Sports Sciences: Ilse De Bourdeaudhuij, Greet Cardon, Marieke De Craemer, Ellen De Decker.
Department of Public Health: Lieven Annemans, Stefaan De Henauw, Lea Maes, Carine Vereecken, Jo Van Assche, Lore Pil.
VU University Medical Center EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research (the Netherlands)
EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research: Mai Chin A Paw, Saskia te Velde.
University of Zaragoza (Spain)
Luis Moreno, Theodora Mouratidou, Juan Fernandez, Maribel Mesana, Pilar De Miguel-Etayo, Esther M. González-Gil, Luis Gracia-Marco, Beatriz Oves.
Oslo and Akershus University College of Applied Sciences (Norway)
Agneta Yngve, Susanna Kugelberg, Christel Lynch, Annhild Mosdøl, Bente B Nilsen.
University of Durham (UK)
Carolyn Summerbell, Helen Moore, Wayne Douthwaite, Catherine Nixon.
State Institute of Early Childhood Research (Germany)
Susanne Kreichauf, Andreas Wildgruber.
Children’s Memorial Health Institute (Poland)
Piotr Socha, Zbigniew Kulaga, Kamila Zych, Magdalena Góźdź, Beata Gurzkowska, Katarzyna Szott.
Medical University of Varna (Bulgaria)
Violeta Iotova, Mina Lateva, Natalya Usheva, Sonya Galcheva, Vanya Marinova, Zhaneta Radkova, Nevyana Feschieva.
International Association for the Study of Obesity (UK)
Tim Lobstein, Andrea Aikenhead.
CBO B.V. (the Netherlands)
Goof Buijs, Annemiek Dorgelo, Aviva Nethe, Jan Jansen.
AOK-Verlag (Germany)
Otto Gmeiner, Jutta Retterath, Julia Wildeis, Axel Günthersberger.
Roehampton University (UK)
Leigh Gibson.
University of Luxembourg (Luxembourg)
Claus Voegele.
Authors’ contribution
Ms. Miguel-Berges conducted the data analysis and interpretation and the drafting of the manuscript. Dr. Santaliestra-Pasias, Dr. Mouratidou and Dr. Moreno Aznar contributed to data analysis and interpretation and the drafting of the manuscript. All authors have contributed in the study design and read and approved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miguel-Berges, M.L., Santaliestra-Pasias, A.M., Mouratidou, T. et al. Associations between food and beverage consumption and different types of sedentary behaviours in European preschoolers: the ToyBox-study. Eur J Nutr 56, 1939–1951 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1236-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1236-7