Abstract
Purpose
Several experimental studies showed that magnesium intake improved insulin resistance and glucose uptake in diabetes patients. However, epidemiological studies on the association between magnesium intake and diabetes risk have yielded inconsistent results. We investigated whether magnesium intake is related to the risk of developing diabetes in a population-based cohort study in Japan.
Methods
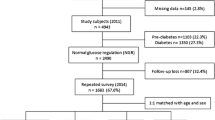
Study subjects were participants in the Takayama study. A total of 13,525 residents in Takayama City, Japan, responded to a self-administered questionnaire in 1992 and to a follow-up questionnaire seeking information about diabetes in 2002. Magnesium and other nutrient intakes were estimated from a validated food frequency questionnaire administered at the baseline.
Results
During a follow-up of 10 years, 438 subjects reported diabetes newly diagnosed by physician. Compared with women in the low quartile of magnesium intake, women in the high quartile were at a significantly reduced risk of diabetes (HR 0.50; 95 % CI 0.30–0.84; P-trend 0.005) after adjustments for covariates. In men, there was no association between magnesium intake and the risk of diabetes.
Conclusion
These results suggest that diets with a high intake of magnesium may decrease the risk of diabetes in women.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FFQ:
-
Food frequency questionnaire
References
Pham PC, Pham PM, Pham SV, Miller JM, Pham PT (2007) Hypomagnesemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:366–373. doi:10.2215/CJN.02960906
Barbagallo M, Dominguez LJ (2007) Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch Biochem Biophys 458:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2006.05.007
Balon TW, Gu JL, Tokuyama Y, Jasman AP, Nadler JL (1995) Magnesium supplementation reduces development of diabetes in a rat model of spontaneous NIDDM. Am J Physiol 269:E745–E752
Mather HM, Nisbet JA, Burton GH, Poston GJ, Bland JM, Bailey PA, Pilkington TR (1979) Hypomagnesaemia in diabetes. Clin Chim Acta 95:235–242. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(79)90364-4
Ma J, Folsom AR, Melnick SL, Eckfeldt JH, Sharrett AR, Nabulsi AA, Hutchinson RG, Metcalf PA (1995) Associations of serum and dietary magnesium with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, insulin, and carotid arterial wall thickness: the ARIC study. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J Clin Epidemiol 48:927–940. doi:10.1016/0895-4356(94)00200-A
Song Y, Manson JE, Buring JE, Liu S (2004) Dietary magnesium intake in relation to plasma insulin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care 27:59–65. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.1.59
Paolisso G, Barbagallo M (1997) Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and insulin resistance: the role of intracellular magnesium. Am J Hypertens 10:346–355. doi:10.1016/S0895-7061(96)00342-1
Lordes Lima M, Cruz T, Pousada JC, Rodrigues LE, Barbosa K, Canguçu V (1998) The effect of magnesium supplementation in increasing doses on the control of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 21:682–686. doi:10.2337/diacare.21.5.682
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309303291401
Nadler JL, Buchanan T, Natarajan R, Antonipillai I, Bergman R, Rude R (1993) Magnesium deficiency produces insulin resistance and increased thromboxane synthesis. Hypertension 21:1024–1029. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.21.6.1024
Altura BM, Altura BT, Gebrewold A, Ising H, Günther T (1984) Magnesium deficiency and hypertension: correlation between magnesium-deficient diets and microcirculatory changes in situ. Science 223:1315–1317
Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, Khawaja JA, Lewenstam A (2000) Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta 294:1–26. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(99)00258-2
Paolisso G, Sgambato S, Gambardella A, Pizza G, Tesauro P, Varricchio M, D’Onofrio F (1992) Daily magnesium supplements improve glucose handling in elderly subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 55:1161–1167
Kao WH, Folsom AR, Nieto FJ, Mo JP, Watson RL, Brancati FL (1999) Serum and dietary magnesium and the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Arch Intern Med 159:2151–2159. doi:10.1001/archinte.159.18.2151
Salmerón J, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Wing AL, Willett WC (1997) Dietary fiber, glycemic load, and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. JAMA 277:472–477. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540300040031
Lopez-Ridaura R, Willett WC, Rimm EB, Liu S, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Hu FB (2004) Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care 27:134–140. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.1.134
Salmerón J, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Spiegelman D, Jenkins DJ, Stampfer MJ, Wing AL, Willett WC (1997) Dietary fiber, glycemic load, and risk of NIDDM in men. Diabetes Care 20:545–550. doi:10.2337/diacare.20.4.545
Meyer KA, Kushi LH, Jacobs DR Jr, Slavin J, Sellers TA, Folsom AR (2000) Carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and incident type 2 diabetes in older women. Am J Clin Nutr 71:921–930
Møller JB, Dalla Man C, Overgaard RV, Ingwersen SH, Tornøe CW, Pedersen M, Tanaka H, Ohsugi M, Ueki K, Lynge J, Vasconcelos NM, Pedersen BK et al (2014) Ethnic differences in insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and hepatic extraction between Japanese and Caucasians: a minimal model analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:4273–4280. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-1724
Fukushima M, Suzuki H, Seino Y (2004) Insulin secretion capacity in the development from normal glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 66:S37–S43. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2003.11.024
Nanri A, Mizoue T, Noda M, Takahashi Y, Kirii K, Inoue M, Tsugane S (2010) Magnesium intake and type II diabetes in Japanese men and women: the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 64:1244–1247. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2010.138
Hata A, Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Mukai N, Hirakawa Y, Hata J, Ozawa M, Uchida K, Shirota T, Kitazono T et al (2013) Magnesium intake decreases type 2 diabetes risk through the improvement of insulin resistance and inflammation: the Hisayama Study. Diabet Med 30:1487–1494. doi:10.1111/dme.12250
Kirii K, Iso H, Date C, Fukui M, Tamakoshi A (2010) Magnesium intake and risk of self-reported type 2 diabetes among Japanese. J Am Coll Nutr 29:99–106. doi:10.1080/07315724.2010.10719822
Shimizu H (1996) A basic report on Takayama Study. Department of Public Health, Gifu University School of Medicine, Gifu
Shimizu H, Ohwaki A, Kurisu Y, Takatsuka N, Ido M, Kawakami N, Nagata C, Inaba S (1999) Validity and reproducibility of a quantitative food frequency questionnaire for a cohort study in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 29:38–44. doi:10.1093/jjco/29.1.38
Shimizu H (2002) A supplementary comment on “reliability and validity of a questionnaire for assessment of physical activity in epidemiological studies” published in journal of epidemiology, 1998. J Epidemiol 12:54
Suzuki I, Kawakami N, Shimizu H (1998) Reliability and validity of a questionnaire for assessment of energy expenditure and physical activity in epidemiological studies. J Epidemiol 8:152–159
Nagata C, Nakamura K, Fujii K, Kawachi T, Takatsuka N, Oba S, Shimizu H (2008) Smoking and risk of cedar pollinosis in Japanese men and women. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 147:117–124. doi:10.1159/000135698
Oba S, Nagata C, Nakamura K, Fujii K, Kawachi T, Takatsuka N, Shimizu H (2010) Consumption of coffee, green tea, oolong tea, black tea, chocolate snacks and the caffeine content in relation to risk of diabetes in Japanese men and women. Br J Nutr 103:453–459. doi:10.1017/S0007114509991966
Seino Y, Nanjo K, Tajima N, Kadowaki T, Kashiwagi A, Araki E, Ito C, Inagaki N, Iwamoto Y, Kasuga M et al (2010) Report of the committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 1:212–228. doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00074.x
Nagata C, Nakamura K, Wada K, Tsuji M, Tamai Y, Kawachi T (2013) Branched-chain amino acid intake and the risk of diabetes in a Japanese community: the Takayama study. Am J Epidemiol 178:1226–1232. doi:10.1093/aje/kwt112
Willett WC (2013) Implication of total energy intake for epidemiological analyses. In: Willett WC (ed) Nutritional epidemiology, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 260–286
Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Augustin LS, Franceschi S, Hamidi M, Marchie A, Jenkins AL, Axelsen M (2002) Glycemic index: overview of implications in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr 76:266S–273S
Zhou BF, Stamler J, Dennis B, Moag-Stahlberg A, Okuda N, Robertson C, Zhao L, Chan Q, Elliott P (2003) Nutrient intakes of middle-aged men and women in China, Japan, United Kingdom, and United States in the late 1990s: the INTERMAP study. J Hum Hypertens 17:623–630. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001605
Suárez A, Pulido N, Casla A, Casanova B, Arrieta FJ, Rovira A (1995) Impaired tyrosine-kinase activity of muscle insulin receptors from hypomagnesaemic rats. Diabetologia 38:1262–1270
Sheehan JP (1991–1992) Magnesium deficiency and diabetes mellitus. Magnes Trace Elem 10:215–219
Ryschon TW, Rosenstein DL, Rubinow DR, Niemela JE, Elin RJ, Balaban RS (1996) Relationship between skeletal muscle intracellular ionized magnesium and measurements of blood magnesium. J Lab Clin Med 127:207–213. doi:10.1016/S0022-2143(96)90080-3
Takaya J, Higashino H, Kobayashi Y (2004) Intracellular magnesium and insulin resistance. Magnes Res 17:126–136
Wada K, Yatsuya H, Ouyang P, Otsuka R, Mitsuhashi H, Takefuji S, Matsushita K, Sugiura K, Hotta Y, Toyoshima H et al (2009) Self-reported medical history was generally accurate among Japanese workplace population. J Clin Epidemiol 62:306–313. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.04.006
Waki K, Noda M, Sasaki S, Matsumura Y, Takahashi Y, Isogawa A, Ohashi Y, Kadowaki T, Tsugane S (2005) Alcohol consumption and other risk factors for self-reported diabetes among middle-aged Japanese: a population-based prospective study in the JPHC study cohort I. Diabet Med 22:323–331. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01403.x
Schneider AL, Pankow JS, Heiss G, Selvin E (2012) Validity and reliability of self-reported diabetes in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Am J Epidemiol 176:738–743. doi:10.1093/aje/kws156
Unoki H, Takahashi A, Kawaguchi T, Hara K, Horikoshi M, Andersen G, Ng DP, Holmkvist J, Borch-Johnsen K, Jørgensen T et al (2008) SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat Genet 40:1098–1102. doi:10.1038/ng.208
Okamoto K, Iwasaki N, Nishimura C, Doi K, Noiri E, Nakamura S, Takizawa M, Ogata M, Fujimaki R, Grarup N et al (2010) Identification of KCNJ15 as a susceptibility gene in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Hum Genet 86:54–64. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.12.009
Imamura M, Maeda S, Yamauchi T, Hara K, Yasuda K, Morizono T, Takahashi A, Horikoshi M, Nakamura M, Fujita H et al (2012) A single-nucleotide polymorphism in ANK1 is associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Japanese populations. Hum Mol Genet 21:3042–3049. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds113
Acknowledgments
Our study has been financially supported by the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konishi, K., Wada, K., Tamura, T. et al. Dietary magnesium intake and the risk of diabetes in the Japanese community: results from the Takayama study. Eur J Nutr 56, 767–774 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1122-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1122-8