Abstract
Purposes
Hepatic lipid overloading induces lipotoxicity which can cause hepatocyte damage, fibrosis, and eventually progress to cirrhosis, which is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Adiponectin receptors play important roles in regulating lipid metabolism. In this study, we used a lentivirus system to overexpress the adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) in HepG2 cells to define the role of adiponectin and its receptor 1 in the development of fatty liver syndrome.
Methods and results
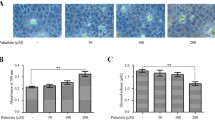
Exposure of human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, to palmitate (0.2 or 0.4 mM) for 16 h resulted in elevated apoptosis, whereas AdipoR1 decreased the palmitate-induced apoptosis. Transgene AdipoR1 increased the expression of FATP2, acyl-coA oxidase, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase I in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells. The transcript level of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase was upregulated by palmitate treatment, while AdipoR1 reversed the effect induced by palmitate. AdipoR1 increased the gene expression of cytochrome C oxidase, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, and decreased the gene expression of PGC1α and AMPKα in HepG2 cells under palmitate treatment. Palmitate suppressed ATP production, while transgene AdipoR1 reversed the decreased ATP production by palmitate. Transgene AdipoR1 enhanced AKT phosphorylation in HepG2 cells both with and without palmitate treatment. When PI3 kinase inhibitor was applied, the protective effect of AdipoR1 was absent, such that palmitate again decreased ATP production while also reducing cell viability.
Conclusion
AdipoR1 enhances fatty acid metabolism and cell viability in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells partially by activating AKT signaling. Therefore, AdipoR1 has therapeutic potential in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okamoto Y, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Libby P (2006) Adiponectin: a key adipocytokine in metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 110(3):267–278
Hug C, Wang J, Ahmad NS, Bogan JS, Tsao TS, Lodish HF (2004) T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(28):10308–10313
Staiger H, Kaltenbach S, Staiger K, Stefan N, Fritsche A, Guirguis A, Peterfi C, Weisser M, Machicao F, Stumvoll M, Haring HU (2004) Expression of adiponectin receptor mRNA in human skeletal muscle cells is related to in vivo parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 53(9):2195–2201
Wang H, Zhang H, Jia Y, Zhang Z, Craig R, Wang X, Elbein SC (2004) Adiponectin receptor 1 gene (ADIPOR1) as a candidate for type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetes 53(8):2132–2136
Bauer S, Weigert J, Neumeier M, Wanninger J, Schaffler A, Luchner A, Schnitzbauer AA, Aslanidis C, Buechler C (2010) Low-abundant adiponectin receptors in visceral adipose tissue of humans and rats are further reduced in diabetic animals. Arch Med Res 41(2):75–82
Bjursell M, Ahnmark A, Bohlooly YM, William-Olsson L, Rhedin M, Peng XR, Ploj K, Gerdin AK, Arnerup G, Elmgren A, Berg AL, Oscarsson J, Linden D (2007) Opposing effects of adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 on energy metabolism. Diabetes 56(3):583–593
Kola B, Boscaro M, Rutter GA, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2006) Expanding role of AMPK in endocrinology. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17(5):205–215
Kubota N, Yano W, Kubota T, Yamauchi T, Itoh S, Kumagai H, Kozono H, Takamoto I, Okamoto S, Shiuchi T, Suzuki R, Satoh H, Tsuchida A, Moroi M, Sugi K, Noda T, Ebinuma H, Ueta Y, Kondo T, Araki E, Ezaki O, Nagai R, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Ueki K, Minokoshi Y, Kadowaki T (2007) Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab 6(1):55–68
Chinetti G, Zawadski C, Fruchart JC, Staels B (2004) Expression of adiponectin receptors in human macrophages and regulation by agonists of the nuclear receptors PPARalpha, PPARgamma, and LXR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314(1):151–158
Karbowska J, Kochan Z (2005) Effect of DHEA on endocrine functions of adipose tissue, the involvement of PPAR gamma. Biochem Pharmacol 70(2):249–257
Sparagna GC, Hickson-Bick DL, Buja LM, McMillin JB (2000) A metabolic role for mitochondria in palmitate-induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279(5):H2124–H2132
Dyntar D, Eppenberger-Eberhardt M, Maedler K, Pruschy M, Eppenberger HM, Spinas GA, Donath MY (2001) Glucose and palmitic acid induce degeneration of myofibrils and modulate apoptosis in rat adult cardiomyocytes. Diabetes 50(9):2105–2113
Jung TW, Lee YJ, Lee MW, Kim SM, Jung TW (2009) Full-length adiponectin protects hepatocytes from palmitate-induced apoptosis via inhibition of c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase. FEBS J 276(8):2278–2284
Kim JE, Song SE, Kim YW, Kim JY, Park SC, Park YK, Baek SH, Lee IK, Park SY (2010) Adiponectin inhibits palmitate-induced apoptosis through suppression of reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells: involvement of cAMP/protein kinase A and AMP-activated protein kinase. J Endocrinol 207(1):35–44
Ostrander DB, Sparagna GC, Amoscato AA, McMillin JB, Dowhan W (2001) Decreased cardiolipin synthesis corresponds with cytochrome c release in palmitate-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276(41):38061–38067
Yadav A, Kataria MA, Saini V (2013) Role of leptin and adiponectin in insulin resistance. Clin Chim Acta 417:80–84
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Chen CY, Hsu HC, Lee AS, Tang D, Chow LP, Yang CY, Chen H, Lee YT, Chen CH (2012) The most negatively charged low-density lipoprotein L5 induces stress pathways in vascular endothelial cells. J Vasc Res 49(4):329–341
Liu B-H (2009) Exploring the function and regulatory mechanisms of adiponectin and its receptors in pigs dissertation. National Taiwan University, Taipei
Dhanasekaran A, Gruenloh SK, Buonaccorsi JN, Zhang R, Gross GJ, Falck JR, Patel PK, Jacobs ER, Medhora M (2008) Multiple antiapoptotic targets of the PI3K/Akt survival pathway are activated by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/anoxia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294(2):H724–H735
Han JW, Zhan XR, Li XY, Xia B, Wang YY, Zhang J, Li BX (2010) Impaired PI3K/Akt signal pathway and hepatocellular injury in high-fat fed rats. World J Gastroenterol 16(48):6111–6118
Younossi ZM (1999) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 1(1):57–62
Abrass CK, Berfield AK, Ryan MC, Carter WG, Hansen KM (2006) Abnormal development of glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells in mice with targeted disruption of the lama3 gene. Kidney Int 70(6):1062–1071
Li ZZ, Berk M, McIntyre TM, Feldstein AE (2009) Hepatic lipid partitioning and liver damage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J Biol Chem 284(9):5637–5644
Listenberger LL, Ory DS, Schaffer JE (2001) Palmitate-induced apoptosis can occur through a ceramide-independent pathway. J Biol Chem 276(18):14890–14895
Sparagna GC, Hickson-Bick DL, Buja LM, McMillin JB (2001) Fatty acid-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes: redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 3(1):71–79
Hickson-Bick DL, Sparagna GC, Buja LM, McMillin JB (2002) Palmitate-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes is not dependent on the generation of ROS. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 282(2):H656–H664
Trauner M, Arrese M, Wagner M (2010) Fatty liver and lipotoxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta 3:299–310
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T (2005) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev 26(3):439–451
Miyazaki S, Izawa T, Ogasawara JE, Sakurai T, Nomura S, Kizaki T, Ohno H, Komabayashi T (2010) Effect of exercise training on adipocyte-size-dependent expression of leptin and adiponectin. Life Sci 86(17–18):691–698
Yamauchi T, Nio Y, Maki T, Kobayashi M, Takazawa T, Iwabu M, Okada-Iwabu M, Kawamoto S, Kubota N, Kubota T, Ito Y, Kamon J, Tsuchida A, Kumagai K, Kozono H, Hada Y, Ogata H, Tokuyama K, Tsunoda M, Ide T, Murakami K, Awazawa M, Takamoto I, Froguel P, Hara K, Tobe K, Nagai R, Ueki K, Kadowaki T (2007) Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat Med 13(3):332–339
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, Sugiyama T, Miyagishi M, Hara K, Tsunoda M, Murakami K, Ohteki T, Uchida S, Takekawa S, Waki H, Tsuno NH, Shibata Y, Terauchi Y, Froguel P, Tobe K, Koyasu S, Taira K, Kitamura T, Shimizu T, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2003) Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423(6941):762–769
Xiao-Yun X, Zhuo-Xiong C, Min-Xiang L, Xingxuan H, Schuchman EH, Feng L, Han-Song X, An-Hua L (2009) Ceramide mediates inhibition of the AKT/eNOS signaling pathway by palmitate in human vascular endothelial cells. Med Sci Monit 15(9):BR254–BR261
Ouchi N, Kobayashi H, Kihara S, Kumada M, Sato K, Inoue T, Funahashi T, Walsh K (2004) Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279(2):1304–1309
Wijesekara N, Krishnamurthy M, Bhattacharjee A, Suhail A, Sweeney G, Wheeler MB (2010) Adiponectin-induced ERK and Akt phosphorylation protects against pancreatic beta cell apoptosis and increases insulin gene expression and secretion. J Biol Chem 285(44):33623–33631
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express our gratitude to the laboratory members for their help and input during the study. This study was supported in part by a Grant (102R7615-3) from National Taiwan University and Grants (NSC 99-2313-B-002-031 and NSC 101-2313-B-002-030-MY3) from the National Science Council in Taiwan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, IP., Lin, Y.Y., Ding, ST. et al. Adiponectin receptor 1 enhances fatty acid metabolism and cell survival in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells through the PI3 K/AKT pathway. Eur J Nutr 53, 907–917 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0594-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0594-7