Abstract
Purpose
To provide updated information on trends and determinants of underweight, overweight, and obesity in Italian adults.
Methods
We considered data from 5 surveys conducted annually between 2006 and 2010, on a total of 14,135 subjects aged 18 years or more (6,834 men and 7,301 women), representative of the Italian adult population, including self-reported information on height and weight.
Results
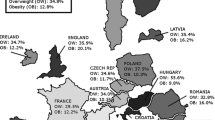
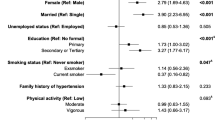
Overall, 3.1 % of the Italian adult population was underweight (body mass index, BMI, <18.5 kg/m2; 0.8 % men, 5.3 % women), 31.8 % overweight (25≤ BMI <30 kg/m2; 39.8 % men, 24.4 % women), and 8.9 % obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2; 8.5 % men, 9.4 % women). We observed no specific pattern of overweight/obesity across calendar years in men (multivariate prevalence ratios, PR, for 2010 vs 2006: 0.95; p for trend: 0.980) and a non-significant decreased trend in women (PR: 0.92; p for trend: 0.051). Prevalence of overweight/obesity significantly increased with age (PRs for ≥65 vs 18–24 years: 2.01 in men, 2.65 in women), decreased with education (PRs for high vs low education: 0.79 in men, 0.54 in women), and was less frequent in single than in married adults (PRs: 0.85 in men, 0.78 in women). Overweight/obesity was significantly more frequent in adults from southern versus northern Italy (PRs: 1.13 in men, 1.32 in women) and in former versus never smokers (PRs: 1.23 in men, 1.19 in women).
Conclusions
In Italy, we did not find unfavorable trends in overweight and obesity prevalence across calendar years. However, there are specific subgroups of the population with elevated prevalence of overweight and obesity, mainly adults from southern Italy and less educated ones.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 377(9765):557–567
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303(3):235–241
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J (2008) Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond) 32(9):1431–1437
Prentice AM (2006) The emerging epidemic of obesity in developing countries. Int J Epidemiol 35(1):93–99
WHO (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. WHO Obesity Technical Report Series 894. World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland
WHO (2011) Global database on body mass index. World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland. Available online at: http://apps.who.int/bmi/index.jsp
OECD (2010) Health at a glance: Europe 2010, OECD Publishing. Available online at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/health_glance-2010-en
Gallus S, Colombo P, Scarpino V, Zuccaro P, Negri E, Apolone G, La Vecchia C (2006) Overweight and obesity in Italian adults 2004, and an overview of trends since 1983. Eur J Clin Nutr 60(10):1174–1179
Micciolo R, Di Francesco V, Fantin F, Canal L, Harris TB, Bosello O, Zamboni M (2010) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Italy (2001–2008): is there a rising obesity epidemic? Ann Epidemiol 20(4):258–264
Skov T, Deddens J, Petersen MR, Endahl L (1998) Prevalence proportion ratios: estimation and hypothesis testing. Int J Epidemiol 27(1):91–95
Zocchetti C, Consonni D, Bertazzi PA (1997) Relationship between prevalence rate ratios and odds ratios in cross-sectional studies. Int J Epidemiol 26(1):220–223
Zaninotto P, Head J, Stamatakis E, Wardle H, Mindell J (2009) Trends in obesity among adults in England from 1993 to 2004 by age and social class and projections of prevalence to 2012. J Epidemiol Community Health 63(2):140–146
Lahti-Koski M, Seppanen-Nuijten E, Mannisto S, Harkanen T, Rissanen H, Knekt P, Rissanen A, Heliovaara M (2010) Twenty-year changes in the prevalence of obesity among Finnish adults. Obes Rev 11(3):171–176
ISTAT (2005) Stili di vita e condizioni di salute. Indagine multiscopo sulle famiglie “Aspetti della vita quotidiana”, Rome 2003: Available online at: http://www.istat.it/dati/catalogo/20051118_00
Eichholzer M, Bovey F, Jordan P, Schmid M, Stoffel-Kurt N (2010) [Body weight related data: results of the 2007 Swiss Health Survey]. Praxis (Bern 1994) 99(15):895–906
Roskam AJ, Kunst AE, Van Oyen H, Demarest S, Klumbiene J, Regidor E, Helmert U, Jusot F, Dzurova D, Mackenbach JP (2010) Comparative appraisal of educational inequalities in overweight and obesity among adults in 19 European countries. Int J Epidemiol 39(2):392–404
Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Galuska DA, Dietz WH (2002) Trends and correlates of class 3 obesity in the United States from 1990 through 2000. JAMA 288(14):1758–1761
Monteiro CA, Conde WL, Lu B, Popkin BM (2004) Obesity and inequities in health in the developing world. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(9):1181–1186
Peytremann-Bridevaux I, Faeh D, Santos-Eggimann B (2007) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in rural and urban settings of 10 European countries. Prev Med 44(5):442–446
Tur JA, Serra-Majem L, Romaguera D, Pons A (2005) Profile of overweight and obese people in a Mediterranean region. Obes Res 13(3):527–536
Jeffery RW, Rick AM (2002) Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between body mass index and marriage-related factors. Obes Res 10(8):809–815
Sobal J, Rauschenbach B, Frongillo EA (2003) Marital status changes and body weight changes: a US longitudinal analysis. Soc Sci Med 56(7):1543–1555
Averett SL, Sikora A, Argys LM (2008) For better or worse: relationship status and body mass index. Econ Hum Biol 6(3):330–349
Healton CG, Vallone D, McCausland KL, Xiao H, Green MP (2006) Smoking, obesity, and their co-occurrence in the United States: cross sectional analysis. BMJ 333(7557):25–26
Munafo MR, Tilling K, Ben-Shlomo Y (2009) Smoking status and body mass index: a longitudinal study. Nicotine Tob Res 11(6):765–771
Shimokata H, Muller DC, Andres R (1989) Studies in the distribution of body fat. III. Effects of cigarette smoking. JAMA 261(8):1169–1173
Tavani A, Negri E, La Vecchia C (1994) Determinants of body mass index: a study from northern Italy. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 18(7):497–502
Xu F, Yin XM, Wang Y (2007) The association between amount of cigarettes smoked and overweight, central obesity among Chinese adults in Nanjing, China. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 16(2):240–247
Pagano R, Negri E, Decarli A, La Vecchia C (1987) Smoking and weight in the 1983 Italian National Health Survey. Int J Obes 11(4):333–338
Zimlichman E, Kochba I, Mimouni FB, Shochat T, Grotto I, Kreiss Y, Mandel D (2005) Smoking habits and obesity in young adults. Addiction 100(7):1021–1025
Bamia C, Trichopoulou A, Lenas D, Trichopoulos D (2004) Tobacco smoking in relation to body fat mass and distribution in a general population sample. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(8):1091–1096
Clair C, Chiolero A, Faeh D, Cornuz J, Marques-Vidal P, Paccaud F, Mooser V, Waeber G, Vollenweider P (2011) Dose-dependent positive association between cigarette smoking, abdominal obesity and body fat: cross-sectional data from a population-based survey. BMC Public Health 11(1):23
Flegal KM, Troiano RP, Pamuk ER, Kuczmarski RJ, Campbell SM (1995) The influence of smoking cessation on the prevalence of overweight in the United States. N Engl J Med 333(18):1165–1170
Yeomans MR (2010) Alcohol, appetite and energy balance: is alcohol intake a risk factor for obesity? Physiol Behav 100(1):82–89
Wang L, Lee IM, Manson JE, Buring JE, Sesso HD (2010) Alcohol consumption, weight gain, and risk of becoming overweight in middle-aged and older women. Arch Intern Med 170(5):453–461
Merrill RM, Richardson JS (2009) Validity of self-reported height, weight, and body mass index: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001–2006. Prev Chronic Dis 6(4):A121
Niedhammer I, Bugel I, Bonenfant S, Goldberg M, Leclerc A (2000) Validity of self-reported weight and height in the French GAZEL cohort. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(9):1111–1118
Spencer EA, Appleby PN, Davey GK, Key TJ (2002) Validity of self-reported height and weight in 4808 EPIC-Oxford participants. Public Health Nutr 5(4):561–565
Galesic M, Tourangeau R, Couper MP (2006) Complementing random-digit-dial telephone surveys with other approaches to collecting sensitive data. Am J Prev Med 31(5):437–443
Rossi M, Negri E, Bosetti C, Dal Maso L, Talamini R, Giacosa A, Montella M, Franceschi S, La Vecchia C (2008) Mediterranean diet in relation to body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio. Public Health Nutr 11(2):214–217
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted with contributions from the Italian Ministry of Health and the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC grant number 10068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallus, S., Odone, A., Lugo, A. et al. Overweight and obesity prevalence and determinants in Italy: an update to 2010. Eur J Nutr 52, 677–685 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0372-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0372-y